Chapter: Medicine and surgery: Nervous system
Upper motor neurone signs - Patterns of neurological disorders
Patterns of neurological disorders
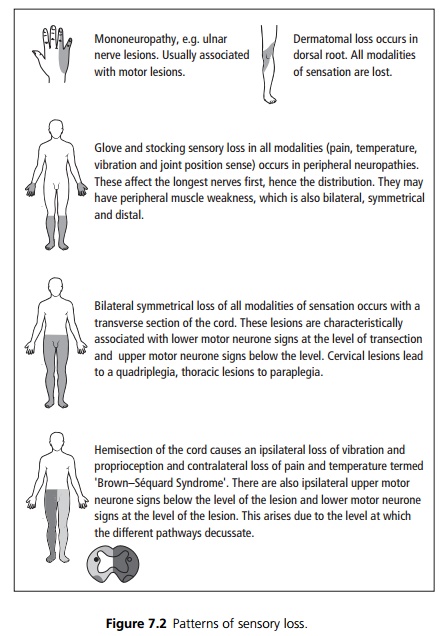
See Fig 7.2.
Upper motor neurone signs
The motor pathway originates in the precentral gyrus, with corticospinal tracts which pass down through the internal capsule, then into the brainstem, where they cross over (the pyramidal decussation) and then pass down to the contralateral spinal cord. Any lesion along this pathway can lead to upper motor neurone signs (UMN). Depending on the level of the lesion the weak-ness may be ipsilateral or contralateral to the lesion. Signs include:
· Pronator drift (downward drift and inward rotation of the upper limb with pronation).
· Increased tone (spasticity).
· Decreased power in a pyramidal distribution (i.e. affecting extensors more than flexors in the upper limbs, but affecting flexors more than extensors in the lower limbs).
· Increased tendon reflexes, absent abdominal reflexes and upgoing (extensor) plantar reflexes.
· No muscle wasting or fasciculations (wasting may occur in long standing lesions due to disuse atrophy).
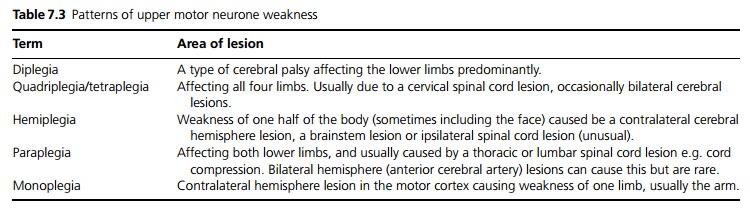
Patterns of UMN weakness
Depending on the severity, the weakness may be described as a ‘plegia’ = total paralysis, or a ‘paresis’ = partial paralysis, but these terms are often used inter-changeably (see Table 7.3).
Cerebral hemisphere disease may occur either in the cortex or the internal capsule. Common causes are strokes (vascular occlusion or haemorrhage) and tumours.
· Internal carotid artery occlusion may cause a hemiparesis.
· Occlusion of the middle cerebral artery territory may cause UMN signs more in the arms than the legs.
· Occlusion of the anterior cerebral artery (ACA) territory may cause UMN signs more in the legs than the arms.
Related Topics