Chapter: Biochemistry: Enzymes
Types of enzyme inhibition
Types of
enzyme inhibition
Enzyme inhibition may be of different types such as
(a) competitive
(b) uncompetitive
(c) non-competitive and
(d) allosteric inhibition.
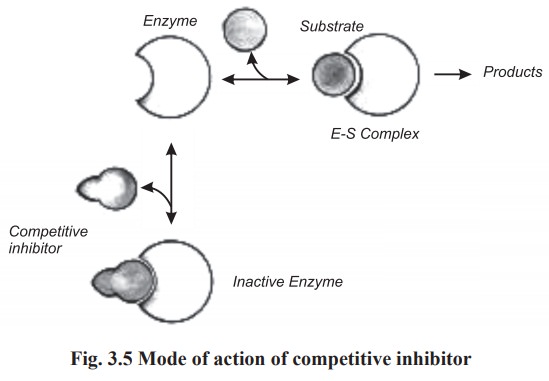
(a)Competitive inhibition
This type of inhibition occurs when the
structure of inhibitor resembles that of the substrate. The inhibitor competes
with the proper substrate for binding at the active site of the enzyme. In this
type of inhibition, both ES complex and EI complex (enzyme - inhibitor complex)
are formed during the reaction. The relative amounts of the two complexes
depend partly upon the affinity of the enzyme towards the substrate and
inhibitor and partly upon the relative concentration of substrate and the
inhibitor. Thus if the inhibitor is present in sufficiently high concentration,
it can displace the substrate entirely and thus blocks the reaction completely
(Fig.3.5).
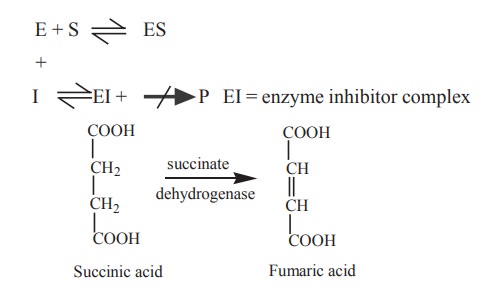
Succinate dehydrogenase catalyses the
conversion of succinic acid to fumaric acid
This reaction is completely inhibited by
malonic acid which has structural resemblence with succinic acid.
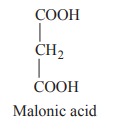 - a competitive inhibitor of succinate dehydrogenase
- a competitive inhibitor of succinate dehydrogenase
This type of inhibition can be reduced by
increasing the concentration of the substrate and for this reason competitive
inhibition is called as reversible inhibition. Many competitive inhibitors are
used as drugs to block particular metabolic reactions.
(b) Uncompetitive inhibition
In this type of inhibition, the inhibitor combines
with enzyme - substrate complex to give an inactive enzyme - substrate -
inhibitor complex which cannot undergo further reaction to yield the product
(Fig. 3.6).
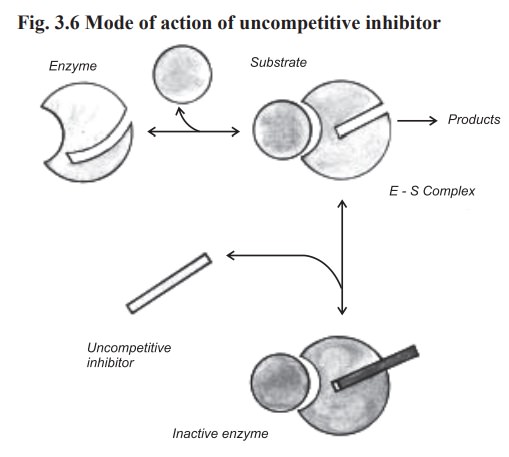
In this type, the degree of inhibition may increase when the substrate concentration is increased. This inhibition cannot be reversed by increasing the concentration of substrate.
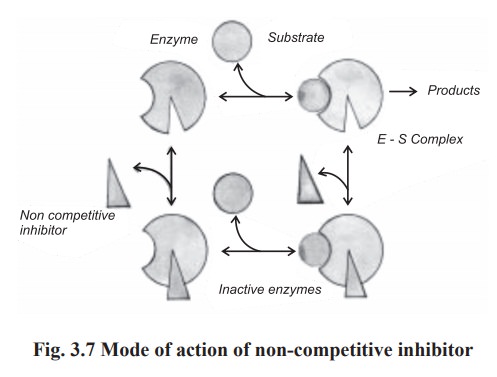
(c) Non competitive inhibition
In this type of inhibition, the inhibitor can
combine with either the free enzyme or the enzyme substrate complex,
interfering with the action of both. Non competitive inhibitor bind to the site
on the enzyme other than the active site, often to deform the enzyme, so that
it does not form the ES complex at its normal rate and once formed, the ES
complex does not decomposes at the normal rate to yield products. These effects
are not completely reversed by increasing the substrate concentration (Fig.
3.7).
Examples
a. Effect of iodoacetamide on - SH group
containing enzymes
b. Effect of diisopropyl phosphofluoridate on
acetyl choline esterase.
These two inhibitors completety inactivate the
respective enzymes.
This inhibition can be partially reversible.
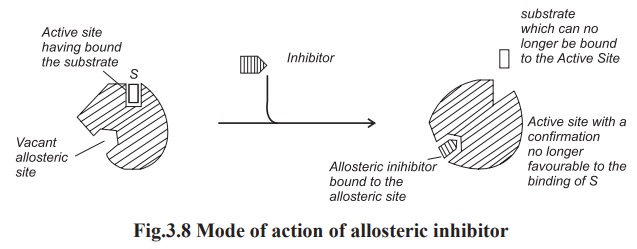
(d) Allosteric inhibition
This type of inhibition is otherwise known as
end product inhibition. The inhibitor binds with the modulator binding site
(or) allosteric site of the enzyme. The inhibitor present at the allosteric
site may affect the conformation at the active site with the result it becomes
difficult for the enzyme to take up the substrate molecule, and in the extreme
case, the enzyme completely fails to take up the substrate molecule (Fig. 3.8).
This type of inhibition is seen in multistep
reactions in which each step is catalysed by different enzymes as shown below.
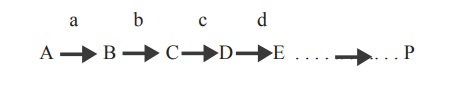
where A is the starting substrate B,C,D,F are
intermediates, a,b,c,d are enzymes and P the product. When the product
concentration (P) increases, it binds with the enzyme ‘a’ which is the first
enzyme in the reaction sequence. This enzyme which can be inhibited by the end
product is known as allosteric enzyme.
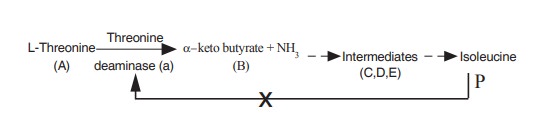
when isoleucine production increases, as a
regulatory mechanism, it binds with threonine deaminase in the allosteric site
and inhibit further binding of the substrate with the enzyme and ultimately
production of isoleucine is stopped. This inhibition is otherwise known as feed
back inhibition.
Many metabolic reactions in our body are
regulated by means of allosteric enzymes.
Related Topics