Economics - Types of Taxes | 10th Social Science : Economics : Chapter 4 : Government and Taxes
Chapter: 10th Social Science : Economics : Chapter 4 : Government and Taxes
Types of Taxes
Types of Taxes
Direct Taxes
A tax
imposed on an individual or organisation, which is paid directly, is a direct
tax. The burden of a direct tax cannot be shifted to others. J.S. Mill defines
a direct tax as “one which is demanded from the very persons who it is intended
or desired should pay it.” Some direct taxes are income tax, wealth tax and
corporation tax.
In India, Income Tax was introduced for the first timein 1860 by
Sir James Wilson in order to meet the losses sustained by the Governmenton
account of the Mutiny of 1857.
Income tax
Income
tax is the most common and most important tax levied on an individual in India.
It is charged directly based on the income of a person. The rate at which it is
charged varies, depending on the level of income.
Students are asked to search a Income Tax website and know the
Income Tax slab for current year.
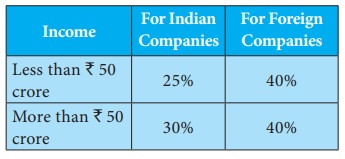
Corporate tax
This tax
is levied on companies that exist as separate entities from their shareholders.
It is charged on royalties, interest gains from sale of capital assets located
in India and fees for a technical services and dividends.
Foreign
companies are taxed on income that it arises in India.
Wealth tax
Wealth
tax is charged on the benefits derived from property ownership. The same
property will be taxed every year on its current market value. The tax is
levied on the individuals and companies alike.
In India taxes are collected by all the three tiers of
government. There are taxes that can be easily collected by the Union
government. In India almost all the direct taxes are collected by the Union
governments. Taxes on goods and services are collected by both Union and State
governments. The taxes on properties are collected by local governments.
In India we collect more tax revenue through indirect taxes than
through direct taxes. The major indirect taxes in India are customs duty and
GST.
Indirect Taxes
If the
burden of the tax can be shifted to others, it is an indirect tax. The impact
is on one person while the incidence is on the another person. Therefore, in
the case of indirect taxes, the tax payer is not the tax bearer.
Some
indirect taxes are stamp duty, entertainment tax, excise duty and goods and
service tax (GST).
Stamp duty
Stamp
duty is a tax that is paid on official documents like marriage registration or
documents related to a property and in some contractual agreements.
Entertainment tax
Entertainment
tax is a duty that is charged by the government on any source of entertainment
provided. This tax can be charged on movie tickets, tickets to amusement parks,
exhibitions and even sports events.
Excise duty
An excise
tax is any duty on manufactured goods levied at the movement of manufacture,
rather than at sale. Excise is typically imposed in addition to an indirect tax
such as a sales tax.
Goods and service tax (GST)
The goods
and service tax (GST) is one of the indirect taxes. The GST was passed in
Parliament on 29 March 2017. The act came into effect on 1 July 2017. The motto
is one nation, one market, one tax.
France was the first country to implement GST in 1954.
Structure of Goods and Service Tax (GST)
State Goods and
Service Tax (SGST): Intra state (within the state) VAT/sales
tax, purchase tax, entertainment tax, luxury tax, lottery tax and state
surcharge and cesses
Central Goods and
Service Tax (CGST): Intra state (within the state) Central
Excise Duty , service tax, countervailing duty, additional duty of customs,
surcharge, education and secondary/higher secondary cess
Integrated Goods
and Service Tax (IGST): Inter state (integrated GST)
There are four major GST rates: (5%, 12%, 18% and 28%) Almost all the necessities of life like vegetables and food grains are excempted from this tax.
Related Topics