Economics - Taxes and Development | 10th Social Science : Economics : Chapter 4 : Government and Taxes
Chapter: 10th Social Science : Economics : Chapter 4 : Government and Taxes
Taxes and Development
Taxes and Development
The role
of taxation in developing economies is as follows.
1. Resource mobilisation: Taxation
enables the government to mobilise a substantial amount of revenue. The tax
revenue is generated by imposing direct taxes such as personal income tax and
corporate tax and indirect taxes such as customs duty, excise duty, etc.
2. Reduction inequalities of
income: Taxation follows the principle of equity. The direct taxes are
progressive in nature. Also certain indirect taxes, such as taxes on luxury
goods, is also progressive in nature.
3. Social welfare: Taxation
generates social welfare. Social welfare is generated due to higher taxes on
certain undesirable products like alcoholic products.
4. Foreign exchange: Taxation
encourages exports and restricts imports, Generally developing countries and
even the developed countries do not impose taxes on export items.
5. Regional development: Taxation
plays an important role in regional development, Tax incentives such as tax
holidays for setting up industries in backward regions, which induces business
firms to set up industries in such regions.
6. Control of inflation: Taxation can be used as an instrument for controlling inflation. Through taxation the government can control inflation by reducing the tax on the commodities.
Difference between Tax and other Payments
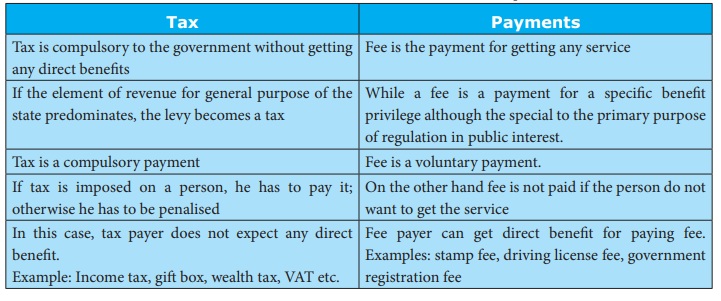
Tax
1. Tax is
compulsory to the government without getting any direct benefits
2. If the
element of revenue for general purpose of the state predominates, the levy
becomes a tax
3. Tax is
a compulsory payment
4. If tax
is imposed on a person, he has to pay it; otherwise he has to be penalised
5. In
this case, tax payer does not expect any direct benefit
6. Example:
Income tax, gift box, wealth tax, VAT etc.
Payments
1. Fee is
the payment for getting any service
2. While
a fee is a payment for a specific benefit privilege although the special to the
primary purpose of regulation in public interest.
3. Fee is
a voluntary payment.
4. On the
other hand fee is not paid if the person do not want to get the service
5. Fee
payer can get direct benefit for paying fee.
6. Examples:
stamp fee, driving license fee, government registration fee
Related Topics