Partnership | Commerce - Types of Partners | 11th Commerce : Chapter 5 : Hindu Undivided Family and Partnership
Chapter: 11th Commerce : Chapter 5 : Hindu Undivided Family and Partnership
Types of Partners
Types of Partners
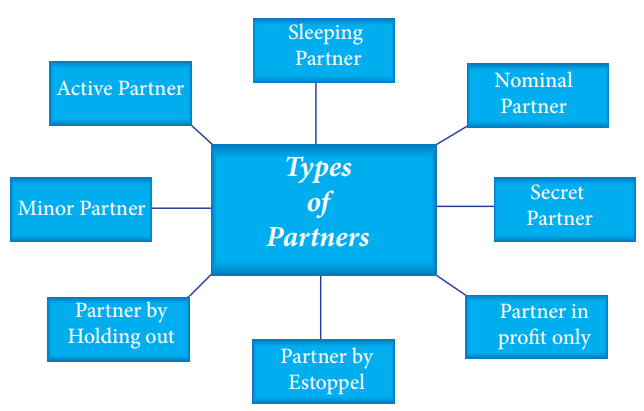
i. Active Partner
A partner who takes an active part in
the conduct of the partnership business is known as an active partner. Though
every partner is entitled to manage its affairs, all may not do so.
ii. Sleeping Partner or Dormant Partner
Such a partner contributes capital and
shares in the profits or losses of the firm but does not take part in the
management of the business. He may not be known as a partner to the outsiders;
yet he is liable to third parties to an unlimited extent as any other partner.
iii. Nominal Partner
Such a partner neither contributes any
capital nor is he entitled to manage the affairs of the business. He only lends
his name to the firm because on the strength of his name and reputation,
the firm may attract additional business
and raise funds easily. A nominal partner, however,
iv. Partner in Profits only
When a person joins a firm as a partner
on the condition that he is entitled to a specified share of the firm’s profit
only, he is called a partner in profits only. It means that he will not be
called upon to bear any portion of the losses sustained. He will, however, be
liable to third parties for all the debts of the firm like any other partner.
Such partners usually do not take part in the management of the business.
v. Partner by Estoppel
In case, a person represents himself/
herself by words or actions or has allowed him to be represented as a partner
of the firm, even though he is not a partner, he is called partner by
estoppels.
Such a partner cannot deny his
liability, if outside party lends money to the firm supposing him to be a
partner.
vi. Partner by Holding out
When a person is declared as a partner
and he does not deny this even after becoming aware of it, he becomes liable to
the third party, who lends money or credit to the firm on the basis of such a
declaration.
vii. Secret Partner
A secret partner is one whose
association is not known to the general public. Other than this distinct
feature, he is like rest of the partners in all respects.
viii. Minor Partner
Under the Indian Majority Act, person
who has not completed 18 years of age is a minor. However, he will continue to be a minor till he completes 21 years if a
guardian has been appointed to the minor. He can be admitted to the benefits of
partnership.
Partnership arises as a result of
contract. But a minor has no contractual capacity. Though a partnership cannot
be created with a minor as a partner, a minor can be admitted to the benefits
of a partnership which is already in existence. The consent of all partners is
a ‘must’ for such admission.
Registration of Partnership
The Indian Partnership Act does
not make the registration of a partnership
compulsory. Registration is optional. But the disabilities of non-registration
virtually make it compulsory.
Related Topics