Chapter: Civil : Principles of Solid Mechanics : Strategies for Elastic Analysis and Design
Types of Partial Differential Field Equations
Types of Partial
Differential Field Equations
The world of Continuum Mechanics is very
much a study of partial differential field equations (p.d.e.s) describing how
vector and scalar components of tensors vary with position and how that field
may vary with time. To make it easy, con-sider the general second order, linear
p.d.e. in two variables:
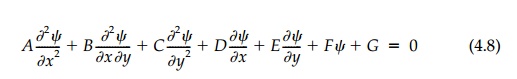
where _
is a general symbol for the field quantity and the two coordinates may be
either space coordinates or one space coordinate plus time.
There are an infinite
number of possible solutions to this general field equa-tion. The boundary
conditions determine which particular solution is appro-priate. The solution _
(x,y) is a surface above and/or below the xy plane and the
boundary is a specified curve in the xy plane. On this boundary, the
boundary conditions are then, either:
a. The
height _ 'above' the boundary curve (the value
of _)
called the Dirichlet conditions, or
b. The
slope of the _ surface normal to the
boundary curve (n ∑ Grad _) called the Neumann
condition, or
c. Both,
which is called the Cauchy boundary condition.
![]()
Three types of p.d.e.s are subsets of
Equation (4.8) which are classified as shown in Table 4.1 along with their simplest
examples. A unique and stable solution for each type of equation is possible
only if the boundary conditions
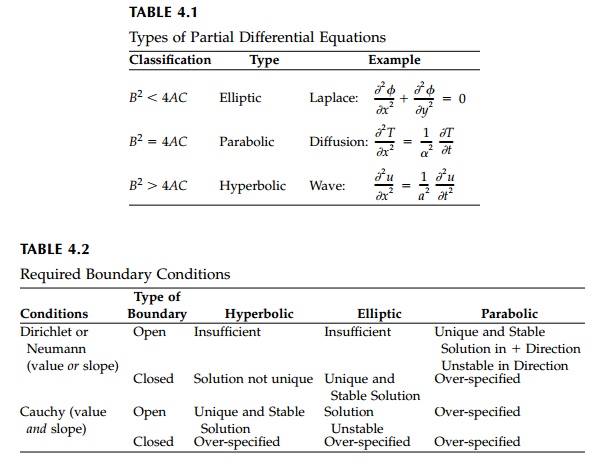
are specified properly* as shown in
Table 4.2. For example, it is not possible to look backward in time** with a
parabolic equation, which can describe such processes as the diffusion of a
pollutant into a stream, thermal diffusion of tem-perature, or consolidation of
saturated soil. The wave equation, on the other hand, which is hyperbolic,
works equally well with negative or positive time.
Related Topics