Chapter: 11th Computer Science : Chapter 17 : Computer Ethics and Cyber Security
Types of Encryption
TYPES OF ENCRYPTION
There
are two types of encryption schemes as listed below:
•
Symmetric Key encryption
•
Public Key encryption
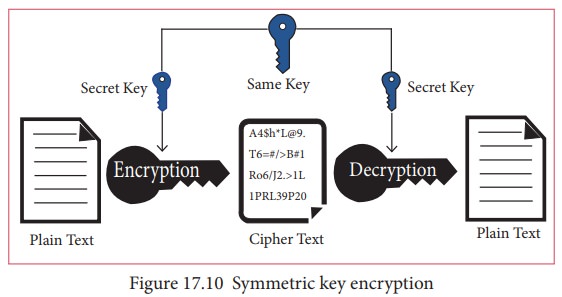
SYMMETRIC KEY ENCRYPTION
Symmetric
encryption is a technique to use the same key for both encryption and
decryption. The main disadvantage of the symmetric key encryption is that all
authorized persons involved, have to exchange the key used to encrypt the data
before they can decrypt it. If anybody intercepts the key information, they may
read all message. Figure 17.10
depicts the working of symmetric key encryption.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
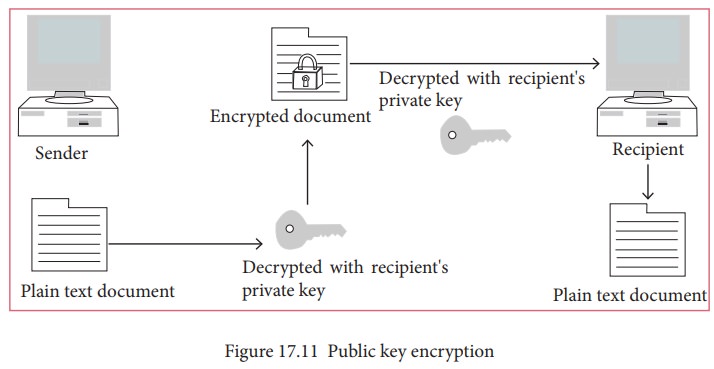
PUBLIC KEY ENCRYPTION
Public
key encryption isalso called Asymmetric encryption. It uses the concept of a
key value pair, a different key is used for the encryption and decryption
process. One of the keys is typically known as the private key and the other is
known as the public key.
The
private key is kept secret by the owner and the public key is either shared
amongst authorized recipients or made available to the public at large.
The
data encrypted with the recipient’s public key can only be decrypted with the
corresponding private key. Figure 17.11
shows the public key encryption.
Asymmetric Encryption in Digital Certificates:
A
digital certificate in a client-server model of communication is one of the
example of Asymmetric Encryption. A certificate is a package of information
that identifies a user and a server. It contains information such as an
organization’s name, the organization that issued the certificate, the users’
email address and country, and user’s public key.
When
a server and a client require a secure encrypted communication, they send a
query over the network to the other party, which sends back a copy of the
certificate. The other party’s public key can be extracted from the
certificate. A certificate can also be used to uniquely identify the holder.
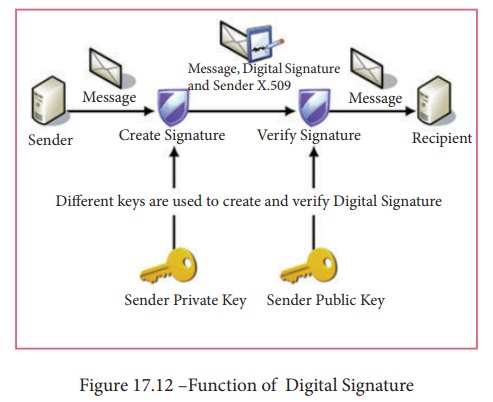
Digital Signature
Digital signatures are based on asymmetric cryptography and can provide assurances of evidence to origin, identity and status of an electronic document, transaction or message, as well as acknowledging informed by the signer.
To
create a digital signature, signing software (email) creates a one-way hash of
the electronic data to be signed. The user's private key to encrypt the hash,
returning a value that is unique to the hashed data. The encrypted hash, along
with other information such as the hashing algorithm, forms the digital
signature. Any change in the data, even to a single bit, results in a different
hash value. This attribute enables others to validate the integrity of the data
by using the signer's public key to decrypt the hash. If the decrypted hash
matches a second computed hash of the same data, it proves that the data hasn't
changed since it was signed. If the two hashes don't match, the data has either
been tampered with in some way (indicating a failure of integrity) or the
signature was created with a private key that doesn't correspond to the public
key presented by the signer (indicating a failure of authentication). Figure 17.12 shows the function of a
digital signature.
Related Topics