Its Advantages and Disadvantages - Types of Departmentation | 12th Office Management and Secretaryship : Chapter 6 : Delegation of Authority
Chapter: 12th Office Management and Secretaryship : Chapter 6 : Delegation of Authority
Types of Departmentation
Types of Departmentation
There are several bases of Departmentation.
The more commonly used bases are— function, product, territory, process,
customer, time etc.
These are
explained below:
(A) Departmentation by Functions
The enterprise
may be divided into departments on the basis of functions like production,
purchasing, sales, financing, personnel etc. This is the most popular
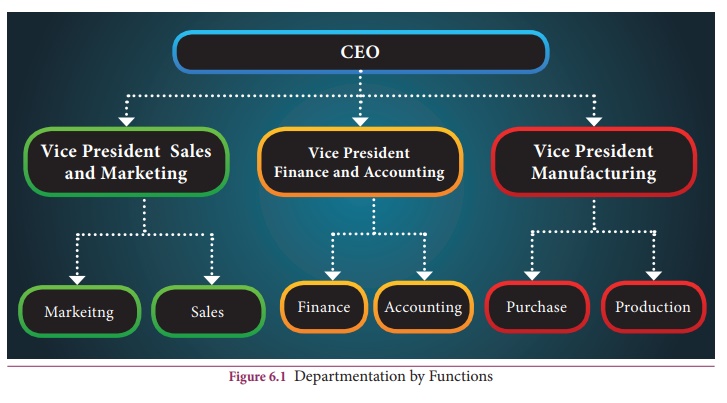
basis of
departmentation. If necessary, a major function may be divided into
sub-functions. For example, the activities in the production department may be
classified into quality control, processing of materials, and repairs and
maintenance.
Advantages
The advantages
of functional departmentation include the following:
·
It is the most logical and natural
form of departmentation.
·
It ensures the performance of all
activities necessary for achieving the organisational objectives.
·
It provides occupational
specialisation which makes optimum utilisation of manpower.
·
It facilitates delegation of
authority.
·
It enables the top managers to
exercise effective control over a limited number of functions.
·
It eliminates duplication of
activities.
·
It simplifies training because the
managers are experts only in a narrow range of skills.
Disadvantages:
There are some
problems associated with functional departmentation. These are mentioned below:
·
There may be conflicts between
departments.
·
The scope for management
development is limited. Functional managers do not get training for top
management positions. The responsibility for results cannot be fixed on any one
functional head.
·
There is too much emphasis on
specialization.
·
There may be difficulties in
coordinating the activities of different departments.
·
There may be inflexibility and
complexity of operations.
(B) Departmentation by Products
In product
departmentation, every major product is organized as a separate department.
Each department looks after the production, sales and financing of one product.
Product departmentation is useful when the expansion, diversification,
manufacturing and marketing characteristics of each product are primarily
significant.
It is
generally used when the production line is complex and diverse requiring
specialized knowledge and huge capital is required for plant, equipment and
other facilities such as in automobile and electronic industries.
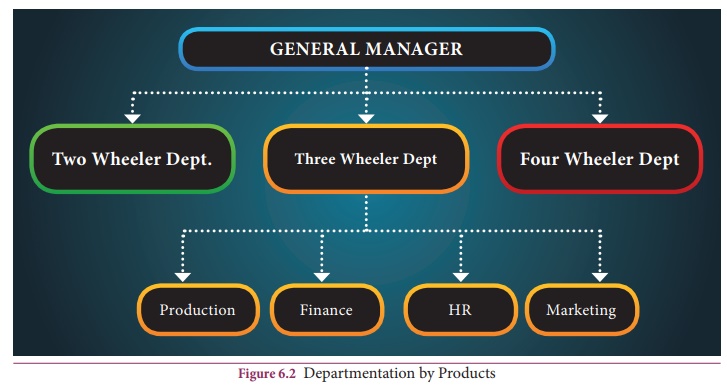
In fact, many
large companies are diversifying in different fields and they prefer product
departmentation. For example, a big company with a diversified product line may
have three product divisions, one each for plastics, chemicals, and metals.
Each division may be sub-divided into production, sales, financing, and
personnel activities.
Advantages:
Product
departmentation provides several advantages which may be stated as follows:
1. Product departmentation
focuses individual attention to each product line which facilitates the
expansion and diversification of the products.
2. It ensures
full use of specialized production facilities. Personal skill and specialized
knowledge of the production managers can be fully utilized.
3. The production
managers can be held accountable for the profitability of each product. Each
product division is semi-autonomous and contains different functions. So,
product departmentation provides an excellent training facility for the top
managers.
4. The
performance of each product division and its contribution to total results can
be easily evaluated.
5. It is more
flexible and adaptable to change.
Disadvantages
Product
departmentation presents some problems as follows:
1. It creates
the problem of effective control over the product divisions by the top
managers.
2. Each
production manager asserts his autonomy disregarding the interests of the
organisation.
3. The advantages
of centralization of certain activities like financing, and accounting are not
available.
4. There is
duplication of physical facilities and functions. Each product division
maintains its own specialized personnel due to which operating costs may be
high.
5. There may be
under-utilization of plant capacity when the demand for a particular product is
not adequate.
(C) Departmentation by Territory
Territorial or
geographical departmentation is specially useful to large -scale enterprises
whose activities are widely dispersed. Banks, insurance companies, transport
companies, distribution agencies etc, are some examples of such enterprises,
where all the activities of a given area of operations are grouped into zones,
branches, divisions etc.
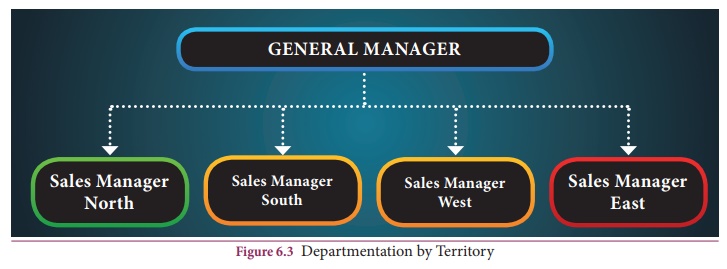
It is
obviously not possible for one functional manager to manage efficiently such
widely spread activities. This makes it necessary to appoint regional managers
for different regions.
Advantages
Territorial
departmentation offers certain facilities in operation. These are pointed out
below:
·
Every regional manager can
specialize himself in the peculiar problems of his region.
·
It facilitates the expansion of
business to various regions.
·
It helps in achieving the benefits
of local operations. The local managers are more familiar with the local
customs, preferences, styles, fashion, etc. The enterprise can gain intimate
knowledge of the conditions in the local markets.
·
It results in savings in freight,
rents, and labor costs. It also saves time.
·
There is better co-ordination of
activities in a locality through setting up regional divisions.
·
It provides adequate autonomy to
each regional manager and opportunity to train him as he looks after the entire
operation of a unit.
Disadvantages
Territorial
departmentation have the following problems:
· There is the problem of communication.
·
It requires more managers with
general managerial abilities. Such managers may not be always available.
·
There may be conflict between the
regional managers.
·
Co-ordination and control of
different branches from the head office become less effective.
·
Owing to duplication of physical
facilities, costs of operation are usually high.
·
There is multiplication of
personnel, accounting and other services at the regional level.
(D) Departmentation by Customers
In such method
of departmentation, the activities are grouped according to the type of
customers. For example, a large cloth store may be divided into wholesale,
retail, and export divisions. This type of departmentation is useful for the
enterprises which sell a product or service to a number of clearly defined
customer groups. For instance, a large readymade garment store may have a
separate department each for men, women, and children. A bank may have separate
loan departments for large-scale and small- scale businessmen.
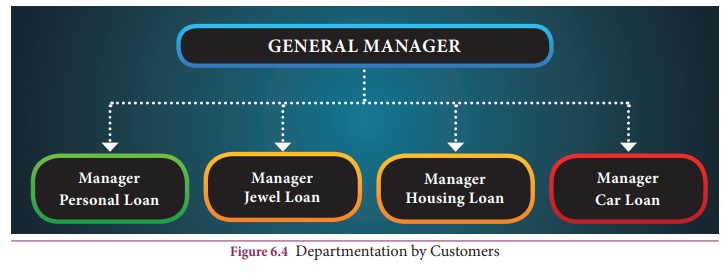
The
organisation chart of customer-oriented departmentation may appear as follows:
Advantages
The important
advantages of customer departmentation are the following:
·
Special attention can be given to
the particular tastes and preferences of each type of customer.
·
Different types of customers can
be satisfied, easily through specialized staff. Customers’ satisfaction
enhances the goodwill and sale of the enterprise.
·
The benefits of specialization can
be gained.
·
The enterprise may acquire
intimate knowledge of the needs of each category of customers.
Disadvantages:
This method of
departmentation may have certain disadvantages, specially when it is followed
very rigidly. These are as follows:
·
Co-ordination between sales and
other functions becomes difficult because this method can be followed only in
marketing division.
·
There may be under-utilization of
facilities and manpower in some departments, particularly during the period of
low demand.
·
It may lead to duplication of
activities and heavy overheads,
· The managers of customer departments may put pressures for special benefits and facilities.
(E) Departmentation by Process or Equipment
In such type
or departmentation the activities are grouped on the basis of production processes
involved or equipment used. This is generally used in manufacturing and
distribution enterprises and at lower levels of organisation. For instance, a
textile mill may be organised into ginning, spinning, weaving, dyeing and
finishing departments. Similarly, a printing press may have composing, proof
reading, printing and binding departments. Such departmentation may also be
employed in engineering and oil industries.
Advantages:
The basic
object of such departmentation is to achieve efficiency and economy of
operations. The processes are set in such a way that a series of operations is
feasible making operations economic. Efficiency can be achieved if departments
are created for each process as each one has its peculiarities.
It provides
the advantages of specialization required at each level of the total processes.
The maintenance of plant can be done in better way and manpower can be utilized
effectively.
Disadvantages
In such
departmentation, there may be difficulty in coordinating the different process-departments,
because the work of each process depends fully on the prece ding process. So,
there are chances of conflicts among the managers looking after the different
processes. It cannot be used where manufacturing activity does not involve distinct
processes.
(F) Departmentation by Time and Numbers
Under this
method of departmentation the activities are grouped on the basis of the time
of their performance. For instance, a factory operating 24 hours may have three
departments for three shifts—one for the morning, the second for the day, and
the third for the night.
In the case of departmentation by numbers, the activities are grouped on the basis of their performance by a certain number of persons. For instance, in the army, the soldiers are grouped into squads, companies, battalions, regiments and brigades on the basis of the number prescribed for each unit.
Such type of
departmentation is useful where the work is repetitive, manpower is an
important factor, group efforts are more significant than individual efforts,
and group performance can be measured. It is used at the lowest level of
organisation.
Related Topics