Chapter: Biotechnology Applying the Genetic Revolution: DNA, RNA, and Protein
Transcription Expresses Genes
TRANSCRIPTION
EXPRESSES GENES
Gene expression involves
making an RNA copy of information present on the DNA, that is, transcribing the
DNA. Making RNA involves uncoiling the DNA, melting the strands at the start of
the gene, making an RNA molecule that is complementary in sequence to the template strand of the DNA with an
enzyme called RNA polymerase, and
stopping at the end of the gene. The
newly made RNA is released from the DNA, which then returns to its supercoiled
form.
An important issue in
transcription is identifying the right gene. Which gene needs to be decoded to
make protein? There are different types of genes. Some are housekeeping genes that
encode proteins that are used all the time. Other genes are activated only
under certain circumstances. For
instance, in E. coli, genes that
encode proteins involved with the utilization of lactose are expressed only
when lactose is present (see later discussion). The same principle applies to
the genes for using other nutrients. Various inducers and accessory proteins
control whether or not these genes are expressed
or made into RNA and will be discussed in more detail in upcoming sections.
The final product encoded by
a gene is often a protein but may be RNA. Genes that encode proteins are
transcribed to give messenger RNA, which is then translated to give the
protein. Other RNA molecules, such as tRNA, rRNA, and snRNA, are used directly
(i.e., they are not translated to make proteins). Some RNA molecules, such as
large-subunit rRNA, are called ribozymes
and can catalyze enzymatic reactions. Most of the time though, genes ultimately
code for a protein via an mRNA intermediate. The coding region of a gene is
sometimes called a cistron or a structural gene and may encode a
protein or a nontranslated RNA. (The term cistron
was originally defined by genetic complementation using the cis/trans test.) In contrast, an open reading frame (ORF) is a stretch of DNA (or the corresponding RNA) that encodes a protein and therefore is not
interrupted by any stop codons for protein translation (see later discussion).
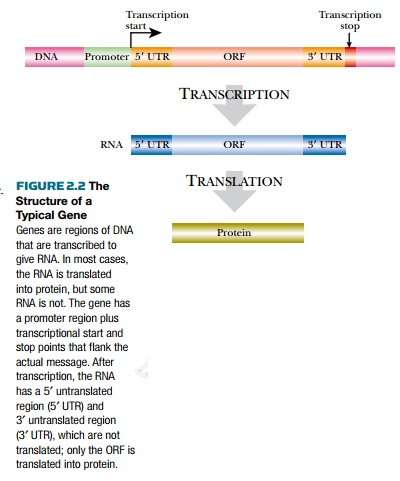
The next issue is finding the start site of the gene. Every gene has a region upstream of the coding sequence called a promoter (Fig. 2.2). RNA polymerase recognizes this region and starts transcription here. Bacterial promoters have two major recognition sites: the –10 and –35 regions. The numbers refer to their approximate location upstream of the transcriptional start site. (By convention, positive numbers refer to nucleotides downstream of the transcription start site and negative numbers refer to those upstream.) The exact sequences at –10 and –35 vary, but the consensus sequences are TATAA and T TGACA, respectively. When a gene is transcribed all the time or constitutively, then the promoter sequence closely matches the consensus sequence. If the gene is expressed only under special conditions, activator proteins or transcription factors are needed to bind to the promoter region before RNA polymerase will recognize it. Such promoters rarely look like the consensus.
Just after the promoter region is the transcription start site. This is where RNA polymerase starts adding nucleotides. Between the transcription start site and the ORF is a region that is not made into protein called the 5¢ untranslated region (5¢ UTR). This region contains translation regulatory elements like the ribosome binding site. Next is the ORF, where no translational stop codons are found. Then there is another untranslated region after the ORF, known as the 3¢ untranslated region (3¢ UTR). Finally comes the termination sequence where transcription stops.
Bacterial RNA polymerase is
made of different protein subunits. The sigma
subunit recognizes the –10 and –35 regions and the core enzyme catalyzes the RNA synthesis. RNA polymerase only
synthesizes nucleotide additions in a 5′ to 3′ direction. The core enzyme has four protein
subunits, a dimer of two α proteins, a β protein, and a related β’ subunit. The β and β’ subunits form the catalytic site, and the α subunit helps recognize the promoter. The 3D
structure of RNA polymerase shows a deep groove that can hold the template DNA,
and a minor groove to hold the growing RNA.
Related Topics