Chapter: Biotechnology Applying the Genetic Revolution: DNA, RNA, and Protein
Eukaryotic mRNA Is Processed before Making Protein
EUKARYOTIC
MRNA IS PROCESSED BEFORE
MAKING PROTEIN
Bacterial mRNA may be
translated without any processing. Indeed, bacteria often start translating
their mRNA while it is still being transcribed (known as coupled transcription/ translation).
However, eukaryotic RNA is processed in a variety of ways before it can leave
the nucleus and be translated into
protein. First, eukaryotic mRNA must have a cap added to the 5′ end of the message (Fig.
2.14). The cap is a GTP added in reverse orientation and which is methylated on
position 7 of the guanine base. Methyl groups may also be added to the first
one or two nucleotides of the mRNA.
The second modification of
eukaryotic mRNA is adding a long stretch of adenines to the 3′ end—the poly(A)
tail. Three sequences at the end of a new mRNA mediate the addition of the
tail: the recognition sequence for the polyadenylation
complex (AAUAAA); the cut site for cleavage binding factor; and the
recognition sequence for polyadenylation binding protein (a length of GU
repeats). First, the polyadenylation complex binds to the AAUAAA, and an
endonuclease in the complex cuts the mRNA after a CA dinucleotide downstream
from the AAUAAA recognition sequence. Next poly(A) polymerase adds 100 to 200
adenine nucleotides. Finally, the poly(A) binding protein binds to both the
poly(A) tail and the cap structure. This circularizes the mRNA.
A third modification made to
eukaryotic mRNA is the removal of introns. Eukaryotic DNA contains many
stretches of intervening sequence (introns) between regions that will
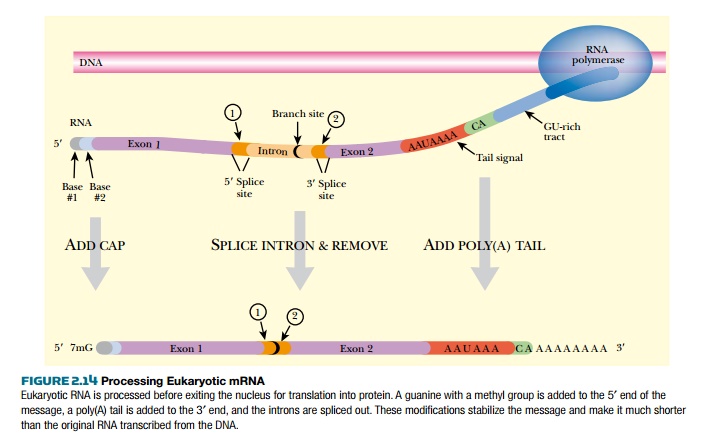
ultimately code for a protein
(exons). First the entire region is
transcribed into an RNA molecule called the primary transcript. After capping and tailing, this is processed to
remove the introns. The exons are spliced together to form the mRNA. Proteins
called splicing factors recognize the exon/intron borders, cut the DNA, and join
the neighboring exons.
Related Topics