Chapter: Civil : Railway Airport Harbour Engineering : Railway Engineering : Rehabilitation and Renewal of Track
Track Renewal Trains
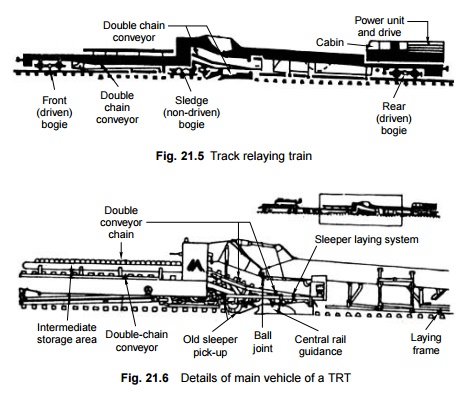
Track Renewal Trains
Indian Railways has recently purchased two track renewal
trains (TRTs) (Fig. 21.5) of modern design, which can carry out track re-laying
work automatically with minimum manual effort. These trains are of the P-811
model and are manufactured by the Tamper Corporation of the USA. The cost of a
TRT along with all ancillary units is about Rs 100 million.
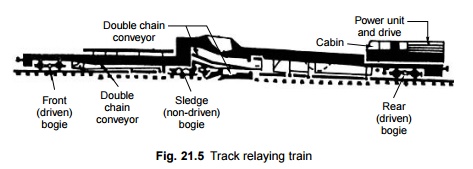
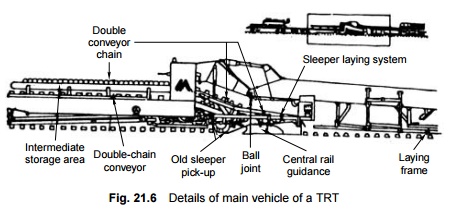
1 Structure of Track Relaying Train
A track relaying train is
designed to simultaneously and continuously perform all the operations involved
in the replacement of rails and sleepers. The train carries out multifarious
functions such as removal of old rails, removal and stacking of old sleepers,
levelling and compacting of the ballast bed, placing new sleepers in their
proper positions, laying of new rails, and removal of released rails.
The train consists of three main
units, which are described in the subsequent paragraph.
Main vehicle
The main vehicle weighs about 110
t and has an overall length of about 45 m. It further comprises of the
following parts.
(a) A sleeper
handling device which removes the old sleepers and replaces them with new ones
with the help of several conveyors.
(b) A power
vehicle fitted with a rail lifting and guidance system for dissecting
the old rails at the side of the track.
(c) A triangular
smoothing plough and a compaction plate to prepare the ballast for new
sleepers.
Handling gantry
The train has a handling gantry for transporting old and new
sleepers. The gantry weighs about 6.6 t and has a lifting force of about 50 kN.
It can lift about 20 concrete sleepers at a time and travel at a maximum speed
of 15 km/h.
A set of BFRs
These are used for the storage of
old and new sleepers. They are fitted with an interconnecting rail track on
which the handling gantry runs. The renewal can be coupled with a normal train
and can reach a speed of up to 100 km/h. The train can, however, move independently
with the help of a hydraulic drive and can achieve a maximum speed of 720 m/h
when in use.
2 Working of TRTs
The following steps are involved in the working of track
relaying trains.
Removal of fastenings The
fastenings joining the old rails to the sleepers are removed ahead of
the commencement track renewal work.
Placement of new rails The duly
welded rails are placed in advance either beside the track duly welded
or fish plated, at a distance of 1.5 m from the track.
Positioning on the track The main
vehicle is now positioned on the track to be renewed. The design of the
machine is such that with the help of a guidance sled it is possible to
acquire an accurate reproduction of the old track layout without the aid of an
external guidance system.
Lifting of old rails The old
rails, which are already free from their fastenings, are lifted with the
help of the rail lifting and guidance frame. The machine continuously lifts the
old rails and deposits them on either side of the track. The ballast can be
simultaneously screened if necessary, while the rails are resting on the ends
of the sleepers.
Picking up of old sleepers The old
sleepers are picked up with the help of a sleeper pick-up system and
placed upright on the conveyor system.
Levelling and compaction of ballast bed The TRT
also consists of a vibratory plough and compactor. The plough levels the
ballast readies it to accept the new sleepers. The plough can be adjusted
vertically to remove the ballast as necessary. It can remove up to 80 mm of
ballast from below the base of the sleepers and transfer it to the shoulders.
Thus, a smooth track bed is made and compacted with the help of the plough and
compactor.
Laying of new sleepers New
sleepers are already stacked in wagons. They are now automatically
placed at specified distances using a wheel of definite diameter. Due to the
unique geometry of this mechanism, the system ensures that the sleepers are
laid squarely at specified distances.
Laying of new rails The new rails,
which are already laid along the track, are then lifted and placed in
their appropriate positions on the sleepers. The equipment is so designed as to
cause minimum stress in the rails being lifted.
Fixing insulators and elastic
rail clips Elastic rail clips and insulators are then fixed
to the rail with the help of a small mechanical appliance. These items are
normally carried in a separate wagon.
Picking up of old rails The final
operation is the removal of old rails. It is imperative that prior to
rail pick up, the rails are cut into lengths of 39 m to ensure that they are
handled properly. The wagons, which are towed by a utility vehicle (UTV),
contain a mobile crane that picks up the old rails and places them into the
wagons for transportation to the depot.
The manufacturers claim that a
TRT can lay 16 sleepers/minute and give an average out put of about 300 to 400
m/h. In an average traffic block of 4 hours per day, it is expected that this
train will give an average output of 200 to 250 km per year.
Related Topics