Chapter: Civil : Railway Airport Harbour Engineering : Railway Engineering : Rehabilitation and Renewal of Track
Criteria for Rail Renewals
Criteria for Rail Renewals
The need for rail renewal can be felt because of any one of
the following reasons.
(a) Incidences
of rail fractures or failures
(b) Wear of
rails
(c) Maintaining
tracks at the prescribed standards
(d) Shortened
service life of rails
(e) Plan-based
renewal
These
criteria are discussed in detail in the subsequent sections.
1 Incidences of Rail Fractures or
Failures
Since this factor has a direct and vital bearing on the safety
of the track, it should take precedence over all other factors when deciding on
the rail renewals to be carried out. A spate of rail fractures or failures on a
particular length of a track may necessitate rail renewal. In such cases, an
ultrasonic test of the rails should be carried out, the results scrutinized,
and the section is considered for rail renewal only if the rail fractures are
high for a particular season (4% in a year or 10% overall).
2 Wear of Rails
Rail renewals may also become necessary because of excessive
wear. This wear can be of various types as a result of the following.
Limiting loss of section
Rail renewal is called for when the loss in the weight of the
section exceeds the prescribed limits given in Table 21.1. In such cases, the
rails should be tested frequently using ultrasonic rail flaw detectors because
such rails are more prone to rail failures.
The loss of weight can be assessed either directly by
measuring the actual weight or empirically by measuring the horizontal and
vertical wear of the rail.
Table 21.1 Limiting loss in weight
of rail sections

Wear due to corrosion
Rails get corroded due to the
vagaries of weather, atmospheric conditions, and chemical reactions that take
place when certain materials come in contact with rail metal, thereby resulting
in wear. Such wear is more prominent in coastal areas. Corrosion beyond 1.5 mm
in the web and the foot of the rail is specified as the criterion for rail
renewal due to corrosion.
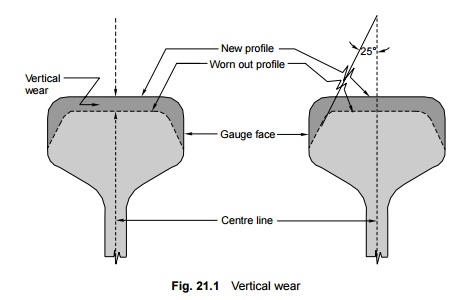
Vertical wear
When vertical wear (Fig. 21.1) causes a reduction in the depth
of the rail head until a point beyond which there is a risk of the wheel
flanges grazing the fish plates, the rails should be renewed. The limits of
vertical wear for the different rail sections are given in Table 21.2.
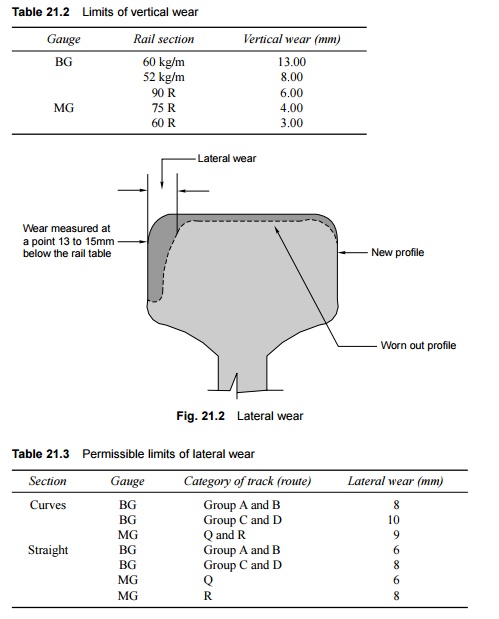
Lateral wear
Lateral wear (Fig. 21.2) is measured at a distance of 13 to 15
mm below the rail top table. The profile of the worn out rail is recorded and
superimposed over a new profile to determine lateral wear. Excessive lateral
wear causes lateral hunting of vehicles, resulting in an uncomfortable ride.
This condition will manifest itself in the form of high values of the ride
index during oscillograph car runs. When it becomes uneconomical to maintain
such a track, through rail renewal becomes crucial. The permissible limits of
lateral wear under various conditions on the Railways are presented in Table
21.3.
3 Maintaining Tracks at the Prescribed
Standards
There may be situations in which
renewals become necessary even though the service life of a rail has not yet
expired, due to local factors such as curves, steep gradients, high speeds,
heavy axle loads, burrs, scabbing, and wear of rails that have the following
adverse effects on the track.
(a) Poor
running quality of track in spite of the extra maintenance labour engaged on
the section.
(b) Disproportionate
cost of maintaining the track under safe conditions.
(c) Poor
condition of the rail due to hogging, battering, scabbing, wheel burn, etc. and
other causes such as the excessive corrugation of the rail and which make track
maintenance difficult and uneconomical and affect riding quality.
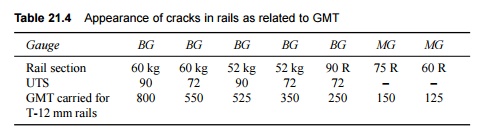
4 Shortened Service Life of Rails
Due to the passage of moving
loads, alternating stresses are created in the rail section. The number of
reversals in the stresses are directed to the weight in gross million tonnes
(GMT) borne by the rails. The majority of rail fractures originate from fatigue
cracks, which develop after a rail has borne the threshold GMT approved for it,
as given in Table 21.4.
Table 21.4 Appearance of cracks in
rails as related to GMT
5 Plan-based Renewals
Plan-based renewals are planned
with the objective of modernizing the track structure on selected routes in the
quickest possible time. It may sometimes involve a premature renewal of the
track also.
Related Topics