Chapter: Biotechnology Applying the Genetic Revolution: Forensic Molecular Biology
Tracing Genealogies by Mitochondrial DNA and the Y Chromosome
TRACING
GENEALOGIES BY MITOCHONDRIAL DNA AND THE Y CHROMOSOME
Mitochondrial DNA sequences have been
very useful in tracing the recent evolution of the human species at the
molecular level. Analysis of mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) can also be used in
forensics. The main advantage is that mitochondrial DNA is present in multiple copies
per cell and so is relatively easier to obtain in sufficient amounts for
analysis. The sequence of mtDNA varies by 1% to 2% between unrelated
individuals.
The major disadvantage is that
mitochondrial DNA does not vary between closely related individuals.
Mitochondria are inherited maternally, and mitochondrial DNA sequences are therefore
shared among groups of people derived from the same maternal lineage. If two samples
of DNA show different mitochondrial sequences, this indicates that they come
from different people. However, the opposite is not true. Identical
mitochondrial sequences are found in people related on the mother’s side.
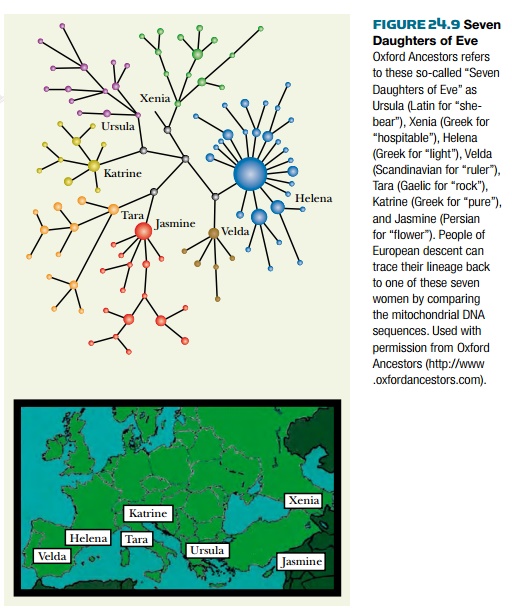
Mitochondrial DNA has been used to
derive family ancestries. Indeed, it is now possible to submit personal samples
of DNA for analysis to companies such as Oxford Ancestors. Their MatriLine
service allows persons of European descent to trace their maternal ancestry
back to one of seven ancestral females ( Fig. 24.9 ). Almost everyone in
Europe, or whose maternal roots are in Europe, is descended from one of only
seven women whose descendants make up well over 95% of modern Europeans. For
genealogical purposes, each of these seven women may be regarded as the founder
of a “maternal clan.” For those whose maternal roots lie outside Europe, a
similar analysis is available, but is not yet so detailed.
In contrast to mitochondrial DNA, the Y
chromosome follows a paternal pattern of inheritance. The Y chromosome contains
many STR sequences in noncoding regions. However, most have few different
alleles, and so only a few are suitable for forensic analysis. One advantage of
using Y-linked STR loci is that any sequence specific to the Y chromosome must
have come from a male. This is often useful in cases of sexual assault.
Related Topics