Chapter: Obstetrics and Gynecology: Third-Trimester Bleeding
Third-Trimester Bleeding: Vasa Previa
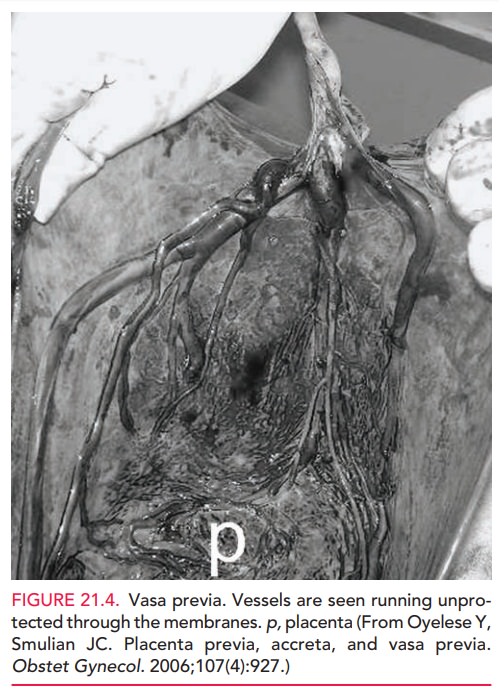
VASA PREVIA
Vasa previa describes the passage of fetal
blood vessels overthe internal os below the presenting part of the fetus. It
canoccur with a velamentous insertion,
in which the fetal blood vessels insert into the membranes between the amnion
and chorion instead of into the placenta and are not protected by Wharton jelly
(Fig. 21.4), or when there is a succenturiate lobe across the os from the main
pla-centa. Vasa previa occurs in 1 in 2500 pregnancies. Rupture of a fetal
vessel occurs rarely in pregnancy, but the risk is greatest with vasa previa.
Rupture of a vessel can quickly lead to fetal death, as fetal blood volume is
so small. Fetal mortality approaches 60% if rupture is not detected before
delivery. When performing artificial rupture of membranes, it is important to
ensure that no pulsating vessels are present which may represent a vasa previa.
An Apt test can help distinguish fetal
blood from maternal blood.
This test mixes the blood
specimen with water to achieve hemolysis. The centrifuged supernatant is mixed
with sodium hydroxide (NaOH). Fetal blood remains pink and maternal blood turns
yellow-brown.
Related Topics