Chapter: Mechanical : Maintenance Engineering : Condition Monitoring
Thermistors
Thermistors
THERMal resISTORS
A
thermistor is a type of resistor used to measure temperature changes, relying
on the change in its resistance with changing temperature. Thermistor is a
combination of the words thermal and resistor. The Thermistor was invented by
Samuel Ruben in 1930, and has U.S. Patent #2,021,491.
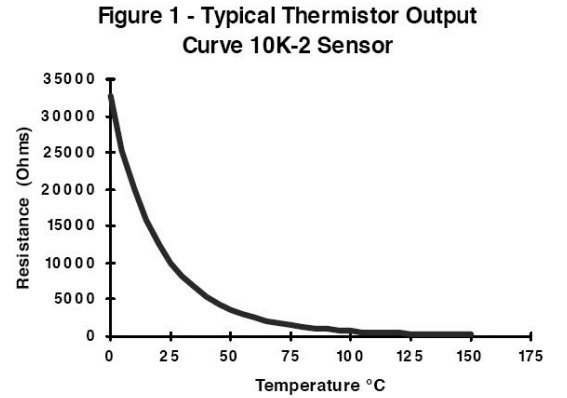
Assume a simple linear relationship between resistance and temperature for the following discussion:
ΔR
= k
ΔT
where
ΔR = change in resistance ΔT = change in
temperature
k = first-order temperature coefficient of resistance
Thermistors
can be classified into two types depending on the sign of k.
If k is
positive, the resistance increases with increasing temperature,
and the device is called a positive temperature coefficient (PTC)
thermistor, Posistor.
If k is
negative, the resistance decreases with increasing temperature,
and the device is called a negative temperature coefficient (NTC) thermistor.
Resistors
that are not thermistors are designed to have the smallest possible k, so that
their resistance remains almost constant over a wide temperature range.
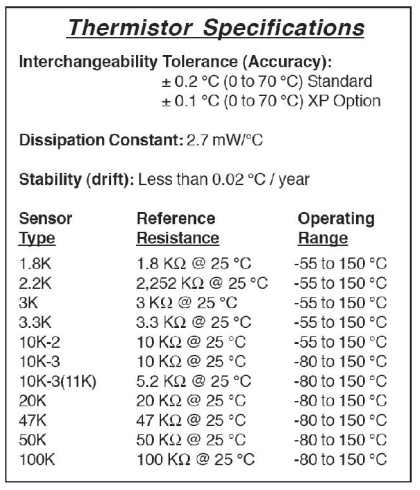
Thermistor-choice
is based on the nominal resistance you want at the operating temperature range,
on the size, and on the time constant.
Time
constants are about 5 - 10 seconds. (Check this out with your thermistor).
Example Applications:
1.
Temperature measurement.
2.
Time delay (self heating from large current
‘opens’ the thermistor so it can be used
as a slow switch). Heating = i2 R where R is the resistance
and i is the current.
Surge
suppression when a circuit is first energized. Current needs to flow through
the thermistor
for awhile to heat it so that it ‘opens’, and acts again as a switch.

Related Topics