Chapter: Maternal and Child Health Nursing : Urinary System
The urethra
The urethra
The
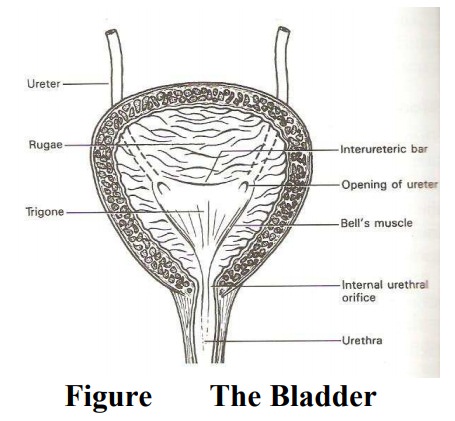
urethra is the final passage in the urinary tract. It extends from the apex of
the trigone (internal meatus) of the bladder and opens into the vestibule of
the valve as the external urethral meatus, in female it passes between the
levator and muscle and enclosed in the membranous sphincter of the urethra in
the outer layer of the anterior vaginal wall. The urethra is tubular in shape
and about 4cm long in female but becomes elongated during labor.
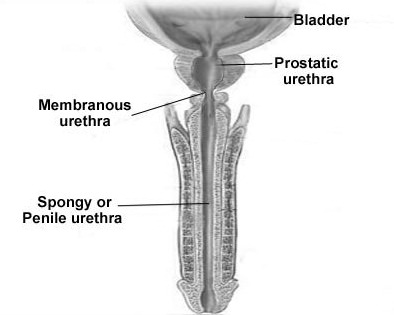
Structure
The wall
contains small blind ducts which open to the urethra just beside the meatus in
the vestibule urethral crypts, 2 longest tubes known as the Skene’s ducts. The
urethra forms the junctions between the urinary tract and the external
genitalia.
The upper
half in human is lined with transitional epithelium while the lower half is
lined with squamous epithelium. The human is normally close except when passing
urine.
·
Sub-mucous Coat: Beneath the epithelium is a bed of
vascular connective tissue.
·
Muscle layer: The muscle layer is arranged in 2
layers: inner longitudinal fiber which continues with the inner muscle fiber of
the bladder. Outer layer of circular muscle fiber. The circular fiber is
thickened around internal urethral meatus forming a sphincter to open the
sphincter during micturation.
·
The outer layer: is continuous with the outer
vaginal wall of the connectives tissue.
At the
lower end of the urethra, voluntary, striated muscle fiber form the membranous
sphincter of the urethra. It is not a sphincter but give some voluntary control
over the urge to urinate. The lower levator ani muscle also assist in
controlling continence of urine.
Blood Supply: Inferior vesical artery and
pudendal artery.
Venous
Drainage: Corresponding veins.
Lymphatic
Drainage- Internal iliac glands
Nerve
Supply: Sympathetic and parasympathetic nerves to the internal urethral
Sphincter.
External sphincter is under the control of will via the pudendal nerves.
Support
Anterior
vaginal wall and the Pelvic floor muscles Function: Convey urine from the
bladder to the external.
Related Topics