Chapter: Maternal and Child Health Nursing : Urinary System
The bladder
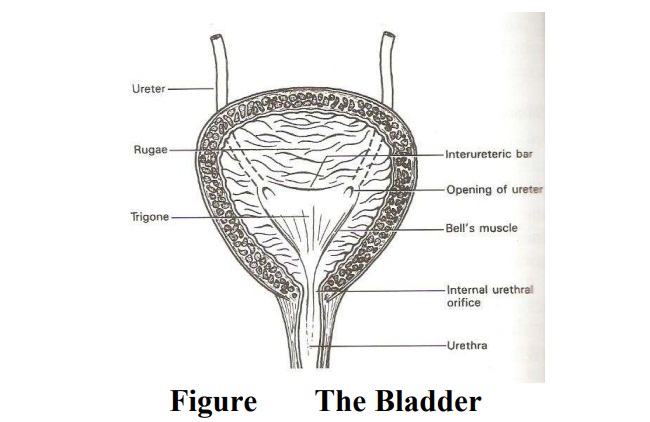
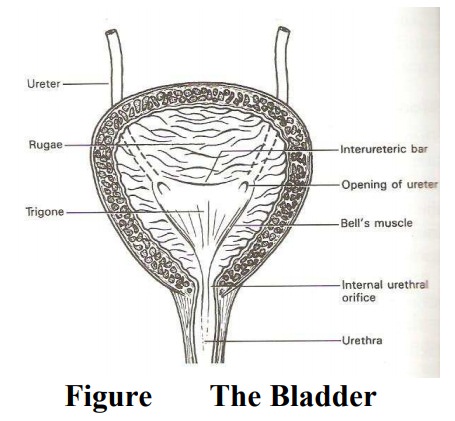
The bladder
Situation
The
bladder lies in the true pelvis, just behind the symphysis pubis and in front
of the vagina and the uterus. The base rest on the upper half of the vagina
while the apex point to the symphysis pubis.
The
uterus rests partially over it due to its anterverted and ante flexed position.
The intestines and the position cavity also lie above it. The ureters enter
from behind and the urethra leaves below. It is supported by the pelvic floor
muscles it may become abdominal organ when full and during pregnancy and labor.
Shape
It is
pyramidal in shape when empty but when full it becomes more globular in shape
as the walls become distended.
Size:
When
empty, its size is similar to that of the uterus but becomes larger when full.
The bladder can hold up to 600mls of urine. During pregnancy it can hold more
(under the influence of pregnancy hormone). The bladder is an important organ
in midwifery because of its close relationship to the uterus.
Structure
The
bladder is a hollow muscular organ capable of distension. The anterior part
lies close to the symphysis pubis and it is known as the apex. It has a trigone
where urine collects. From the apex, the urachus ligament runs up to the
anterior abdominal wall to the umbilicus.
Microscopic Structure
The wall
of the bladder excluding the trigone is made up of the following structures.
1.
Transitional Epithelium- This lies the cavity of the bladder. It is arranged in folds
known as rugae except over the trigone, to allow for distension as it expands
and fill up with urine.
2.
Connective Tissue- This lies beneath the
epithelium. It carries blood, lymphatic vessels and nerves.
3.
Muscle Layer: It is known as the destrusor muscle,
whose function is to expel urine. It is made up of three coats.
·
Inner longitudinal fibers,
·
Middle circular fibers, and
·
Outer longitudinal fibers
The circular fiber is thickly arranged around the internal meatus to
form the internal urethral sphincter of the bladder. It is always in a state of
contraction except during micturation.
4.
Peritoneum: Covers the upper surface while the
remaining surface is invested with visceral pelvic fascia.
5.
The Tri-Gone: The tri-gone is situated at the back
of the bladder. It is triangular in shape with its base behind and the apex in
front. Each side measures 2.5cm in length. It has three openings which
correspond with the angles. Two ureteric orifices where the ureters enter and
the third is the exit of the urethra. The apex of the trigone is the bladder
neck. The trigone is made up of special muscles.
·
Transitional epithelium: This lies the trigone but
not thrown into rugae.
·
Connective tissue- lies beneath the epithelium.
·
Muscle layer
Intermesentric
Bar (Mercier’s bar)- This lies between the ureteric orifices
Muscles
of bell- These extend from the ureteric orifice to the internal urethral
orifice.
Blood Supply: Superior and inferior vescical
arteries.
Various
Drainage- Corresponding veins. Lymphatic Drainage-External iliac and obturate
glands.
Nerve
Supply: sympathetic and parasympathetic nerves from Le Frankehauser’s plexus.
Supports
·
2 lateral ligaments-from the bladder to the side
walls of the pelvis.
·
2 pubo-vesical ligament-Forms the neck of the
bladder to the symphysis pubis.
·
Urachus Ligament: A fibrous band that extends from
the apex of the bladder to the umbilicus.
Relations
Anteriorly-Symphysis
pubis
Posteriorly-
Upper half of the vagina and the cervix.
Superiorly-
Utero vesical pouch, body of the uterus.
Inferiorly-
Urethra, lower half of the anterior vaginal wall.
Laterally-
pelvic floor muscles.
Functions
Reservoir
for urine
Expels
urine
Related Topics