Chapter: Maternal and Child Health Nursing : The Female Reproductive System
The Vagina
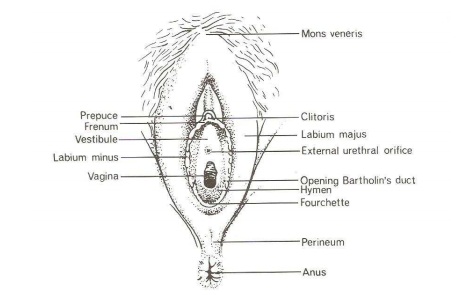
The Vagina
A
muscular tube that extends from the cervix above to the vulva below
Functions
·
It allows
passage of menstrual flow
·
It receives penis and sperm during sexual
intercourse
· It provides an exit for fetus during delivery.
Position
running from the vestibule to the cervix
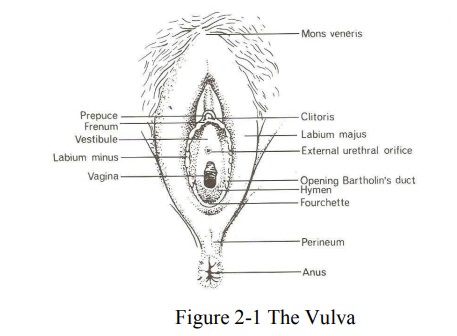
Relations
Anteriorly bladder and urethra
Posteriorly behind the pouch of Douglas , the
rectum and the perineal body. Each occupies approximately 1/3rd of the posterior vaginal wall.
Lateral Upper 2/3rd are pelvic fascia and
the uterus. Lower third are pelvic floor.
Superior above the vagina lies the uterus
Inferior below the vagina lies the
external genitalia
Structure posterior wall 10cm, anterior
wall 7.5 cm.Cervix projects at right angle into upper part. Upper end is the vault to which the cervix projects.
Vaginal walls are pink and thrown into small folds known as rugae.
Layers Lining is squamous epithelium.
Beneath it,vascular connective tissue. Muscular layer is weak innermost and the
outer layer are strong longitudinal fibers. Pelvic fascia surrounds the vagina.
Contents No glands in the vagina but
moistened by themucus from cervix. In spite of alkaline mucus vaginal fluid is
strongly acidic (pH 4.5) due to the presence of the lactic acid formed by the
Dederlein’s bacilli. This acid deters the growth of pathogenic organisms.
Blood supply is from branches of internal
iliac arteriesand branches of uterine arteries
Lymphatic drainage is via
inguinal, internal iliac andsacral glands.
Nerve supply is from Lee Frankanhauser plexus.
Related Topics