Chapter: Maternal and Child Health Nursing : The Female Reproductive System
The Uterus
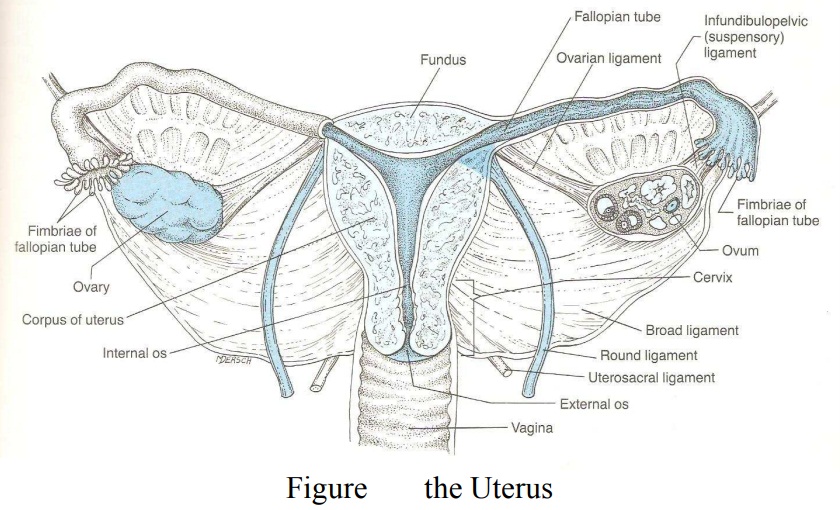
The Uterus
The
uterus is a thick walled pear shaped hollow, muscular organ lying in the pelvis
Functions
·
Prepares for pregnancy each month
·
Shelters the baby
·
Expels the uterine contents after pregnancy
Position - the uterus is situated in the
cavity of the true pelvis , behind the bladder and in front of the rectum. It leans
forward which is kown as anteversion;
It bends forwards on itself which is known as anteflexion. When the woman is standing this result in an almost
horizontal position with the fundus resting on the bladder .
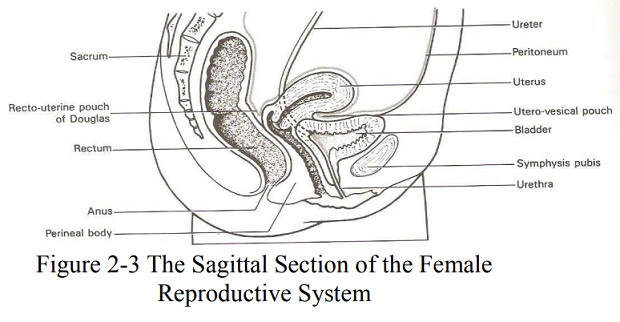
Relations
Anterior : in front of the uterus lie
the uterovesicalpouch and bladder
Posterior : behind the uterus are the
rectouterine pouch of Douglas and the rectum.
Lateral : on either side of the uterus
are the broad ligaments, the uterine tubes and the ovaries.
Superior : above the uterus lie the
intestines Inferior below the uterus
is the vagina
Supports
The
uterus is supported by the pelvic floor and maintained in position by several
ligaments, of which those at the level of the cervix are the most important The
Transverse Cervical Ligaments these fan out fromthe sides of the cervix
to the side walls of the pelvis. They are sometimes known as the ‘cardinal
ligaments’ or ‘Mackenrodt’s ligaments’
The
uterosacral ligaments these pass backwards fromthe cervix to the sacrum
The
pubocervical ligaments these pass forwards fromthe cervix, under the
bladder, to the pubic bones.
The broad
ligaments these are formed from the folds ofthe peritoneum
which are draped over the uterine tubes. They hang down like a curtain and
spread from the sides of the uterus to the sides walls of the pelvis
The round
ligaments. Thesehave
little value as asupport but tend to maintain the anteverted position of the
uterus. They arise from the cornua of the uterus in front of and below the insertion
of each uterine tube and pass between the folds of the broad ligament, through
the inguinal canal, to be inserted into each labium majus.
The
ovarian ligament.These also begin at the cornuaof the uterus but
behind the uterine tubes and pass down between the folds of the broad ligament
to the ovaries. It is helpful to note that the round ligament, the uterine tube
and the ovarian ligament are very similar in appearance and arise from the same
area of the uterus. This makes careful identification important when tubal
surgery is undertaken.
Structure
The non-
pregnant uterus is a hollow muscular pear-shaped organ situated in the true
pelvis. It is 7.5cm long, 5cm wide and 2.5 cm in depth. The cervix forms the
lower one third of the uterus and measures 2.5cm in each direction.
The
uterus consists of the following parts :
The Body or Corpus : This makes the upper two thirds ofthe uterus
and is the greater part.
The Fundus : This is the domed upper wall between
theinsertions of the uterine tubes.
The Cornua : These are the upper outer
angles of theuterus where the uterine tubes join.
The Cavity. : This is a potential space
between theanterior and posterior walls. It is triangular in shape, the base of
the triangle being uppermost
The Isthmus : this is a narrow area between the cavityand
the cervix which is 7cm long. It enlarges during pregnancy and labour to form
part of the lower uterine segment
The Cervix or Neck. : This
protrudes into the vagina, theupper half being above the vagina, is known as
the supravaginal portion while the lower half is the infravaginal portion.
The Internal Os (Mouth) this is
the narrow openingbetween the isthmus and the cervix.
The External Os. : This is a small round opening
at thelower end of the cervix. After childbirth it becomes a transverse slit
with an anterior and a posterior lip.
The Cervical Canal lies
between these two and is acontinuation of the uterine cavity. This canal is
shaped like a spindle, narrow at each end and wider in the middle.
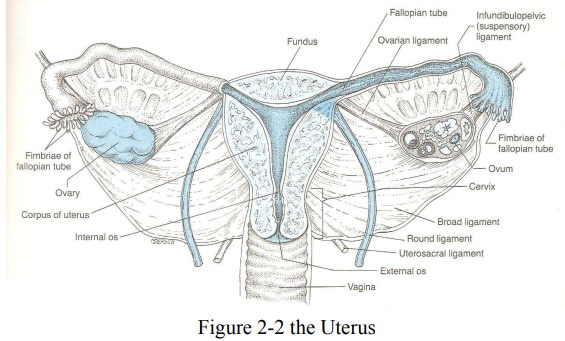
Layers
The
uterus has three layers, of which the middle muscle layer is by far the
thickest.
The Endometrium this layer forms a lining of
ciliatedepithelium(mucous membrane ) on a base of connective tissues or stroma
In the
uterine cavity this endometrium is constantly changing in thickness throughout
the menstrual cycle. The basal layer does not alter, but provides the
foundation from which the upper layers regenerate. The epithelial cells are
cubical in shape and dip down to form glands that secrete alkaline mucus.
The
cervical endometrium does not respond to the hormonal stimuli of the menstrual
cycle to the same extent. Here the epithelial cells are tall and columnar in
shape and the mucus-secreting glands are branching racemorse glands. The
cervical endometrium is thinner than that of the body and is folded into a
pattern known as the ‘arbor vitae’ (tree of life). This is though t to assist
the passage of the sperm. (the portion of the cervix that protrudes into the
vagina is covered with squamous epithelium similar to the squamo-columnar
junction and it is known as the intravaginal cervix ,about 1.5 cm.
The Myometrium or muscle coat. This layer is
thick inthe upper part of the uterus and is more sparse in the isthmus and
cervix. Its fibers run in all directions and interlace to surround the blood
vessels and lymphatics that pass to and from the endometrium. It is this
arrangement that facilitate the arrest of haemorrhage after delivery of the
baby-“living ligament” The ou ter layer is formed of longitudinal fibers that
are continuous in those of the uterine ligaments and the vagina
In the
cervix the muscles fibers embedded in collagen fibers, which enable it to
stretch in labor.
The Perimetrium.This is a double serous membrane
,and extension of the peritoneum, which is draped over the uterus, covering all
but a narrow strip on either side and the anterior wall of the supravaginal
cervix from where it is reflected up over the bladder
Blood supply
Uterine
artery which is a branch of internal iliac artery. Ovarian artery a branch of
abdominal aorta supply ovary and fallopian tube ad join with uterine artery
Lymphatic drainage
Lymph is
drained from uterine body to internal iliac glands mainly
Nerve supply
Mainly from autonomic, sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system via Lee
Frankenhauser’s plexus or pelvic plexus
Related Topics