The Cell | Term 2 Unit 5 | 6th Science - The Structural Organization of the Cell | 6th Science : Term 2 Unit 5 : The Cell
Chapter: 6th Science : Term 2 Unit 5 : The Cell
The Structural Organization of the Cell
The
Structural Organization of the Cell
A typical cell consists of three major parts:
1. An outer cell
membrane.
2. A liquid cytoplasm.
3. A nucleus.
Analogous to the body's internal organ, like
eyes, heart, lungs organelles are specialized structures and perform valuable
functions necessary for normal cellular operation. Many of miniscule but
distinct structures called Organelles lie within the cell.
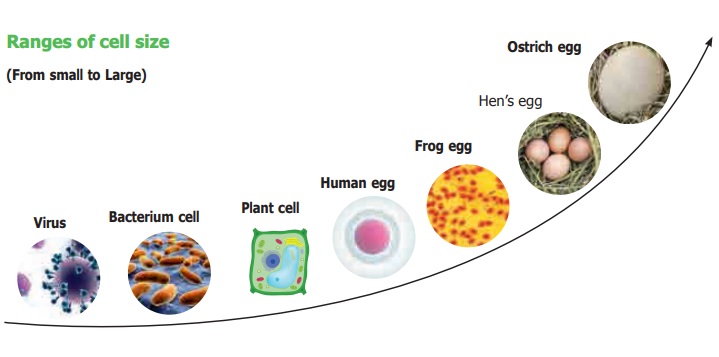
1. Size
of the cell
The size of cells may vary from a micrometer (a
million of a metre ) to a few centimeters. Most cells are microscopic and
cannot be seen with the nacked eye. They can be observed only through the
Microscope.
Smallest size of
the cell is present in Bacteria. The size of the bacterial cell ranges from
0.01 micrometer to 0.5 micro meter.
Activity
1:
Aim: To observe the structure of a single
cell (Hen’s egg).
Materials Needed: A hen’s egg and a plate.
Method: Crack the shell and break open
the egg in a plate.
Observation:
The egg has a yellow part
and a transparent part surrounding it. The white transparent part (albumin) is
jelly-like and represents the cell’s cytoplasm, while the yellow part (yolk) is
thicker and represents the cell’s nucleus. On the internal side of the shell
can be seen a thin membrane-like structure, which represents the cell membrane.

On the other hand
the largest cell is the egg of an ostrich with 170 millimeter width. We can see
this with the nacked eye.
In Human body the
nerve cells are believed to be the longest cells.
Cell size
has no relation to the size of an organism. It is not necessary that the cells of,
say an elephant be much larger than those of a mouse.
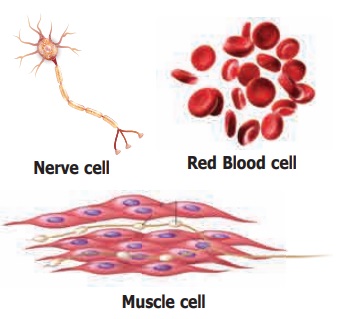
2. Shapes
Cells are of
different shapes. For example some shapes are given in the below pictures.
3. Number
The number of cells present in different
organisms may vary. Organisms may be either unicellular (single cell) or
multicellular. Organisms such as Bacteria, Amoeba, Chlamydomonas, and Yeast are
unicellular.
On the other hand, organisms such as Spirogyra, Mango, and Human beings are multicellular. (i.e) made up of a few hundreds to million cells.
Approximate
number of cells in the human body is 3.7 × 1013 or 37,000,000,000,000
Ranges of cell size
Related Topics