Chapter: The Massage Connection ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY : Digestive System
The Pancreas - Structure and Function of Digestive System
THE PANCREAS
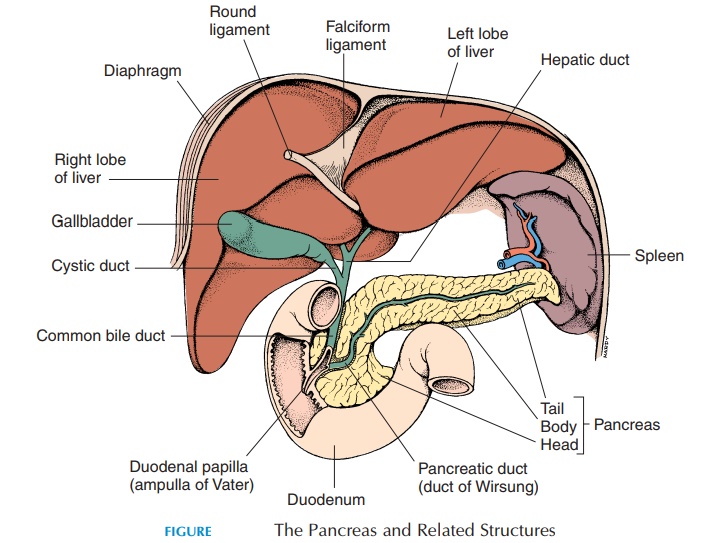
The pancreas (see Figure 11.9) is a gland that lies posterior to the stomach and to the left of the C-shaped curve of the duodenum. The end that lies in-side the curve of the C is larger and is known as the head. It tapers toward the other end, which extendsup to the spleen. This end is the tail of the pancreas, with the body in between.
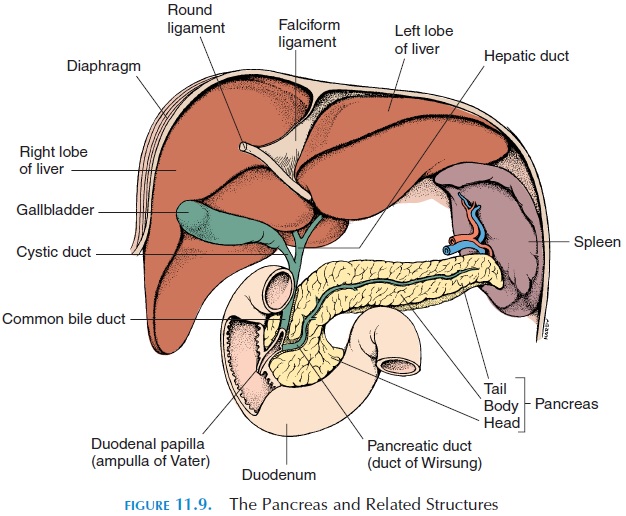
The pancreas has two functions—exocrine and en-docrine. The exocrine function manufactures en zymes that help with the digestion of proteins, fats, and carbohydrates. The secretions are drained from the gland to the duodenum by the pancreatic duct. Before the duct opens into the lumen, it meets with the common bile duct that drains bile from the liver and gallbladder. Pancreatic secretion is alkaline; about 1.5 liters (1.6 qt) of pancreatic juice is secreted every day.
The endocrine portion of the pancreas consists of cells known as the pancreatic islets, or islets of Langerhans. One important hormone secreted by these cells into the blood is insulin, which regulates blood glucose levels.
Related Topics