Chapter: Mechanical : Engineering Thermodynamics : Properties of a Pure Substance and Steam Power Cycle
The Measurements of Dryness Fraction
THE MEASUREMENTS OF DRYNESS FRACTION
Dryness fraction of wet
steam, representing the fraction of steam in the mixture of water and steam can
be measured by using (i) Throttling calorimeter and (ii) Separating and
Throttling calorimeter.
(i) Throttling calorimeter:
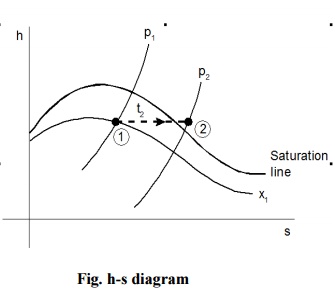
Let us consider a wet steam as represented by state
1 in the h-s diagram. When it undergoes a throttling process to state 2, it
enters into the superheated region. By measuring the temperature and pressure
after throttling the specific enthalpy can be obtained. As mentioned earlier
during throttling enthalpy remains constant. Therefore the initial state can be
completely fixed since the pressure before throttling and the corresponding
specific enthalpy are known.
Steam from the main is extracted through a
perforated tube projecting into it as shown in the Figure. Pressure of the
steam is measured. It is then throttled into a chamber where the necessary
pressure and temperature measurements are made. From the chamber the expanded
steam is then condensed by circulating cooling water and discharged.
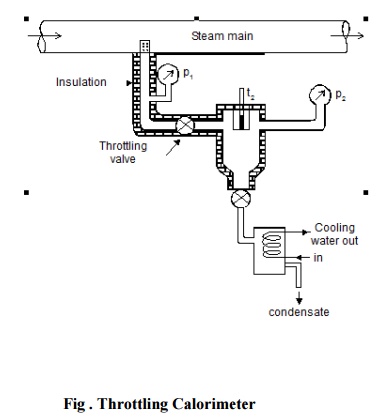
Fig . Throttling Calorimeter
(ii) Separating and Throttling
calorimeter:
When the dryness
fraction of the steam is very low, it becomes superheated vapour only at very
low end pressure on throttling. In general, the pressure after throttling for
dryness fraction measurement is preferred to be above atmospheric. In such
applications, separating and throttling calorimeters are used for dryness
fraction measurement.
Wet steam, when
subjected to sudden change in the direction of flow, a portion of the liquid
falls due to gravity and gets separated from the main stream. Thus the
remaining steam becomes rich in vapour, which upon throttling will become
superheated vapour even at a pressure higher than atmospheric pressure. This
principle is employed in the separating and throttling calorimeter.
The wet steam from the steam main is extracted
through a perforated tube and sent to the separator where a portion of the
liquid is separated due to sudden change in the direction. The remaining steam
is throttled into a chamber where the required pressure and temperature
measurements are made. Mass flow rate of liquid separated in the separator is
collected and measured. Mass of the remaining steam is also measured by
condensing the throttled steam and collecting it. Let be the mass of liquid
separated in the separator and be the mass of steam throttled
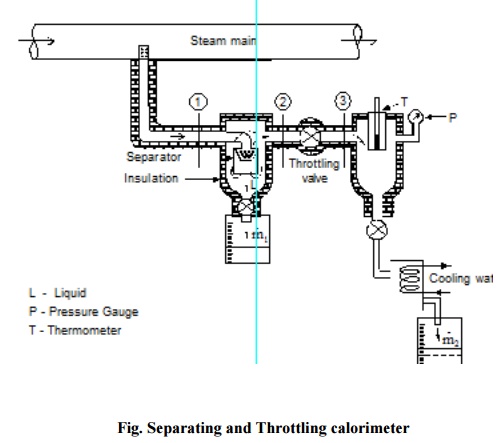
Fig. Separating and Throttling
calorimeter
Related Topics