Basis of Classification | Term 2 Unit 5 | 7th Science - The Five Kingdom Classification | 7th Science : Term 2 Unit 5 : Basis of Classification
Chapter: 7th Science : Term 2 Unit 5 : Basis of Classification
The Five Kingdom Classification
The Five
Kingdom Classification
The five kingdom classification was proposed by
R.H. Whittaker in 1969. Five kingdoms were formed on the basis of
characteristics such as cell structure, mode of nutrition, source of nutrition
and body organization.
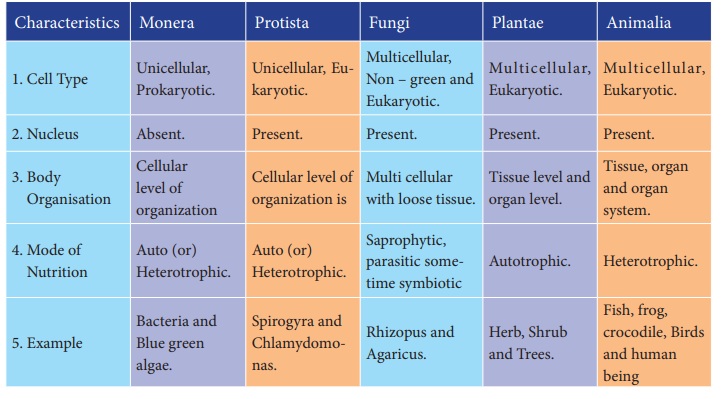
1. Kingdom
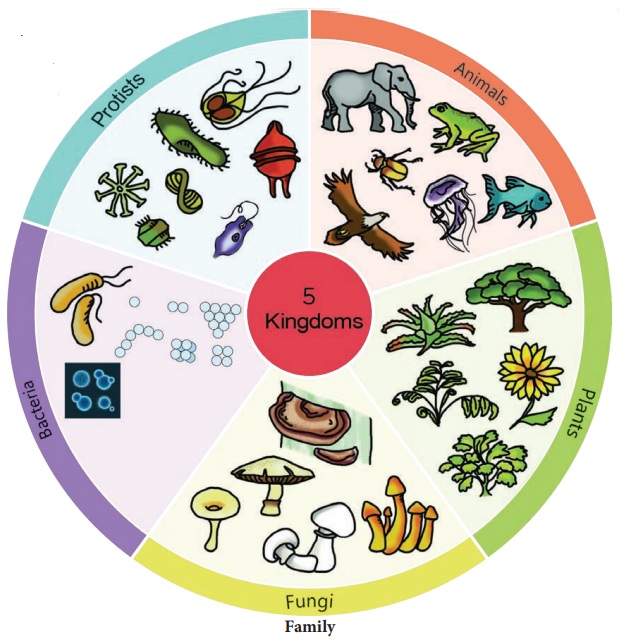
Monera - Bacteria
All prokaryotes belong to the Kingdom Monera,
which do not posses true nucleus. Cells of prokaryotes do not have a nuclear
membrane and any membrane bound organelles. Most of the bacteria are heterotrophic,
but some are autotrophs. Bacteria and Blue green algae are examples for monera.
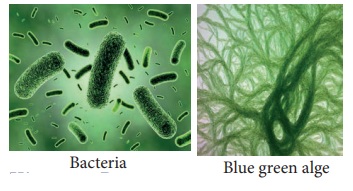
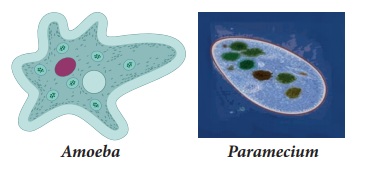
2. Kingdom Protista:
The Kingdom Protista includes unicellular and a
few simple multicellular eukaryotes.
There are two main groups of protists. The plant
like protists are photosynthetic and are commonly called algae. Algae include
unicellular and multicellular types. Animals like protists are often called protozoans.
They include amoeba and paramecium.
3. Kingdom
Fungi:
Fungi are eukaryotic, and mostly are
multicellular. They secrete enzymes to digest the food and absorb the food
after digested by the enzymes. Fungi saprophytes as decomposers (decay –causing
organisms) or as parasites. Kingdom Fungi includes molds, mildews, mushrooms
and yeast.

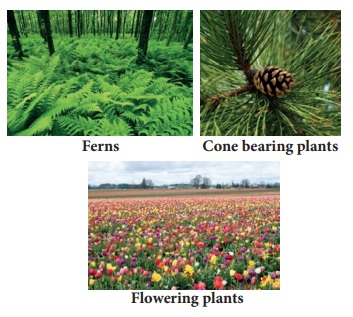
4. Kingdom
Plantae:
Planatae (plants) are multicellular eukaryotes
that carry out photosynthesis. Reserve food materials are starch and lipids in
the form of oil or fat. Plant cells have cell wall and specialized functions,
such as photosynthesis, transport of materials and support. Kingdom Plantae
includes ferns, cone bearing plants and flowering plants.
5. Kingdom
Animalia:
Animalia (animals) are multicellular, eukaryotic
and heterotrophic animals. Cells have no cell wall. Most members of the animal
kingdom can move from place to place. Eg. Invertebrates like sponges, hydra,
flatworms round worms, insects, snails, starfishes. Vertebrates like Fish,
amphibians, reptiles, birds, and mammals including human beings belong to the
kingdom Animalia.


IMPORTANT
CHARACTERISTICS OF FIVE KINGDOMS
Merits of
five Kingdom Classification
* This system of classification is more scientific
and natural.
* This system of classification clearly indicates
the cellular organization, mode of nutrition, and characters for early
evolution of life.
* It is the most accepted system of modern
classification as the different groups of organisms are placed
phylogenetically.
* It indicates gradual evolution of complex
organisms from simpler one.
Demerits of
five Kingdom Classifications
* In this system of classification of viruses have
not been given a proper place.
* Multicellular organisms have originated several
times from protists.
* This type of classification has drawn back with
reference to the lower forms of life.
* Some organisms included under protista are not
eukaryotic.
Related Topics