Basis of Classification | Term 2 Unit 5 | 7th Science - Classification of Plants | 7th Science : Term 2 Unit 5 : Basis of Classification
Chapter: 7th Science : Term 2 Unit 5 : Basis of Classification
Classification of Plants
Classification
of Plants
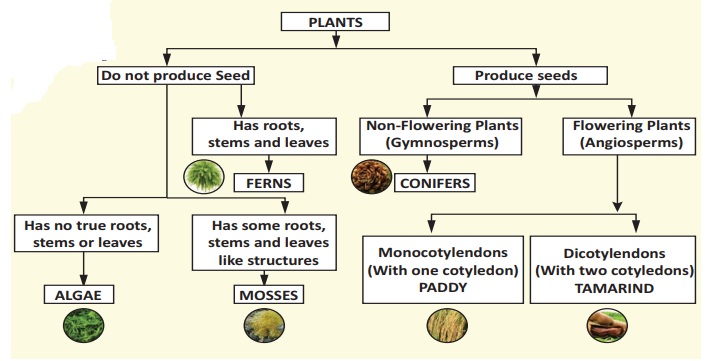
Based on dichotomy, plants also can be classified
into two main groups – Flowering and Non – flowering. Non – flowering plants do
not produce seeds and flowering plants produce seeds. Based on their nature of
plant body, Non flowering plants are classified into three types: algae, mosses
and ferns. Based on their fruit body, flowering plants are classified into two
types: gymnosperms and angiosperms.
Algae
* Plant is thallus, not well-differentiated into
root, stem, and leaves.
* They are predominantly aquatic.
* They are unicellular or multicellular -
filamentous. Example - Chara

Mosses
* Plant body is not differentiated into true root,
stem and leaves.
* They are water living plants, needs moisture to
complete its life cycle. Hence they are referred to as amphibious plants.
* They do not have any specialized vascular
tissues for conduction of water and food. Examples: Funaria
Ferns
* Plant body is well-differentiated into root,
stem, and leaves. Leaves may be large or small.
* Specialized vascular tissues are found for the
conduction of water and food.
* Basically they are the first land plants which
grows well in shady, moist, and cool places. (Examples: Adiantum)

Gymnosperms
* Plants are perennial, woody, evergreen with true
root, stem and leaves.
* They possess vascular tissues, xylem without vessels
and phloem without companion cells.
* Ovules are naked, without ovary. Hence they do
not produce fruits. Seed are naked. (Examples: Pinus, Cycas)

Angiosperms
* Plant body is well differentiated into true
root, stem, and leaves.
* They produce flower with four whorls (calyx,
corolla, androecium and gynoecium), hence known as flowering plants.
* Female reproductive organ, ovary is present
inside the flower which develops into fruit and ovule develops into seed.
* Plant possess well developed vascular system
with xylem vessels and phloem – companion cells.
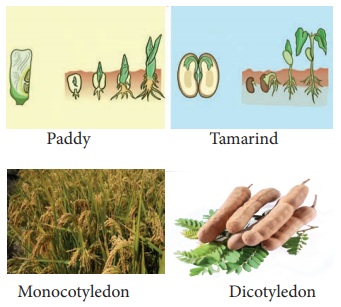
Angiosperms are the dominant plant forms of
present day. Based on the number of cotyledons, angiosperms are broadly divided
into two groups. a) monocotyledons b) dicotyledons. Plant seeds
which have only one cotyledon are said to be monocots. Plant seeds which have
two cotyledons are known as dicots. Example- Paddy (monocot), tamarind (dicot).
Related Topics