Definition, Characteristics, Classification - Teaching Aids | 11th Home Science : Chapter 8 : Communication
Chapter: 11th Home Science : Chapter 8 : Communication
Teaching Aids
TEACHING AIDS
A teaching aid is a tool used by teachers,
facilitators or tutors to help learners improve reading and other skills,
illustrate or reinforce a skill, fact, or idea and relieve anxiety, fears, or
boredom since many teaching aids are like games.
Definition of teaching aid are the
aids used by the facilitator to help him/her in facilitating his/her
lesson effectively.
Characterstics of Good Teaching aids
·
They should be meaningful and pur-poseful
·
They should be accurate in every aspect
·
They should be simple
·
·
They should be cheap
·
They should be improvised as for as possible
·
They should be large enough to be properly seen by the students
for whom they are meant
·
They should be up-to-date
·
They should be easily portable
·
They should be according to the men-tal level of the students.
·
They should motivate they learners
Classification of Teaching aids
On the basis of characteristic of the material used in the process of teaching aid classifications as mentioned below:
Audio-aids: Audio-aids help in
developing the listening skill of a learner. Audio-aids are those aids
which can be only listened. Examples, of such types of aids include, radio,
gramophone, tape recorder, audio-tapes, walkman and headphones etc.,
Visual-aids: Aids which require the involvement of learners visual senses are called visual aids.
Examples, of such types of aids include viz. graphic aids, 3d-aids, display
boards and print material etc.,
Audio-Visual aids: In these aids both the listening (ears) and viewing faculties (eyes) are involved.
Such aids include tel-evision programmes, video films, motion pictures,
synchronized audio slide pro-jectors, computers and computer-assisted
instructions etc.,
Projected: Projected refer to
those aids where a bright light is passed through a transparent picture by
means of a lens and an enlarged picture is thrown or projected on the screen or
the white wall. Eg: film-strip projector, slide projector, overhead projector,
TV/VCR etc.,
Non-Projected: Non-Projected aids
refer to those aids which do not require projector elec-tricity or
projection screen. Such materials can be simply shown, can be hanged or touched.
Eg: Chalkboard, Whiteboard, Flannel board, Magnet board, Charts and
Wall-Charts, Posters and Pictorial Materials, Models etc.,
Dr.Edgar Dale has classified and
arranged audio-visual aids in a procto-rial form called “Cone of Experience”
The primary source of contact between the
individual and external world and any intellectual activity depends on
expe-riences coming through senses. Even mental activities such as
concentration, reflection, conception, imagination, asso-ciation, recollection
etc., have their basis in sensory experiences. Mind like stom-ach, works on
what it is fed. This feeding comes through senses. The raw material for mental
activity is provide by
i. Direct Experiences: Such expe-riences are
gained by the pupils through excursions and trips etc.,
ii. Representative Experiences: This type of
experiences are less con-crete but are quite useful. This type of experiences
are provided by models, specimens, film strips, radio etc.,
iii. Verbal and Symbolic Experiences: Such
experiences are those which the pupils gain through word-oral or written. This
type of experiences are very abstract and occur at con-ceptual level. E.g.
verbal illustra-tions. This type of experience can not be properly followed at
the initial stages of child-learning so at initial stage more emphasis be laid
on direct and representative experiences.
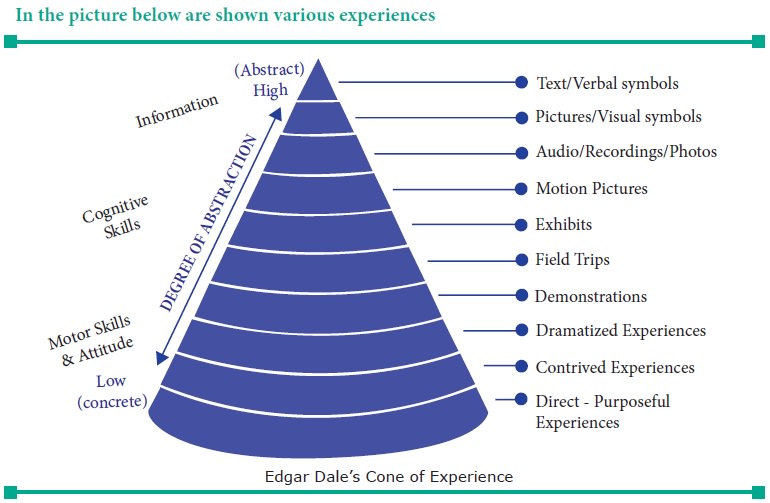
The above cone represents the material used
for audio-visual instructions.
The theory of audio-visual instruc-tion needs
that education must make learning permanent and experiences usa-ble. The
advocacy for the use of new mate-rial for improving instructions is based on
the fact that the verbalistic learning is out of date and the complexity of the
time has made our school curriculum very much heavy as the present day
knowledge has developed tremendously. We need new ways to adjust ourselves to
the changed circumstances and the trends towards realistic learning.
Related Topics