Chapter: Computer Networks : Media Access & Internetworking
Switching and Bridging
SWITCHING AND BRIDGING
Networking
and internet working devices are classified into four cate gories: repeaters,
bridges, routers, and gateways.
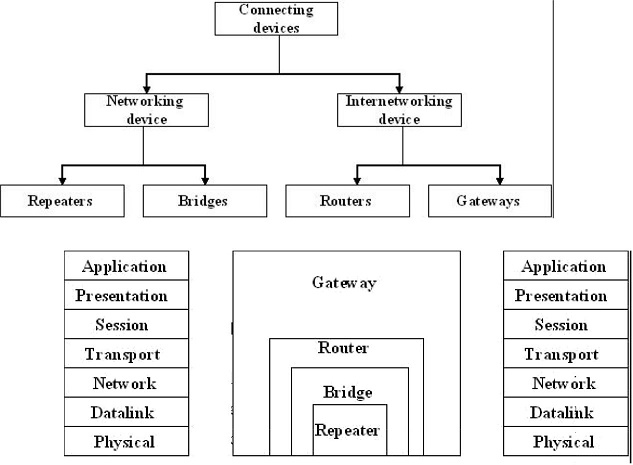
BRIDGES AND LAN SWITC HES:
It is a
node that forward frames from one Ethernet to the other. This n ode would be in
promiscuous mode, accepting all frames transmitted on either of the Ether nets,
so it could forward them to the other. A bridge is connected between two LANs
with port. By using the port number the LANs are addressed. Connected LANs are
known as extended LAN
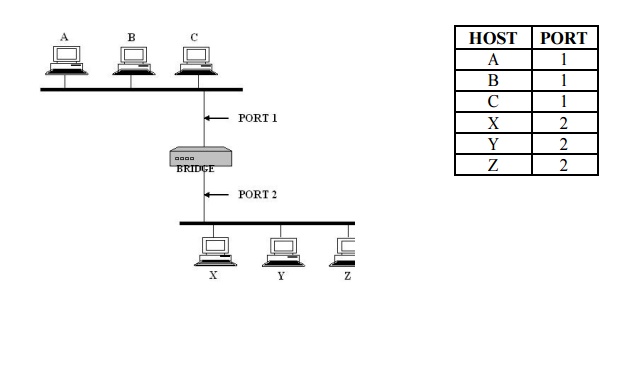
LEARNING BRIDGES:
Bridges
maintains a forwwarding table which contains each host with th eir port number.
Having a
human maintain this table is quite a burden, so a bridge can learn this
information for itself. The idea is for each bridge to inspect the source
address in all the frames it receives. When a bridge first boots, this table is
empty; entries are added over time. Also a timeout is associated with each
entry and the bridge is cards the entry after a specified period of time.
SPANNING TREE ALGORITHM
If the
extended LAN is having loops then the frames potentially loop through the
extended LAN forever. There are two reasons to an extended LAN to have a loop
in it. One possibility is that the network is managed by more than one
administrator; no single person knows the entire configuration of the network.
Second, loops are built in to network on purpose to provide redundancy in case
of failure. Bridges must be able to correctly handle loops. This problem is
addressed by having the bridges run a distributed spanning tree algorithm.
The
spanning tree algorithm wad developed by Digital Equipment Corporation. The
main idea is for the bridges to select the ports over which they will forward
frames. The algorithm selects as
follows.
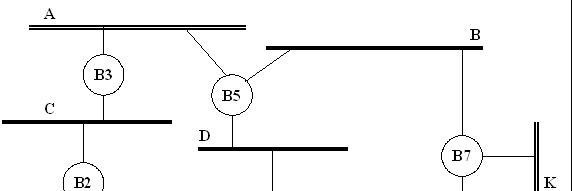
Each bridge has a unique identifier. In the above example they are labeled as
B1, B2, B3
… the
algorithm first elects the bridge with smallest ID as the root of the spanning
tree. The root bridge always forwards frames out over all of its ports. Then
each bridge computes the shortest path to root and notes which of its ports is
on this path. This port is also elected as the bridge‟s preferred path to the root.
Finally, all the bridges connected to a given LAN elect a single designated
bridge that will be responsible for forwarding frames toward the root bridge.
Each LANs designated bridge is the one that is closest to the root, and if two
or more bridges are equally close to the root, then the bridge which having
smallest ID wins.
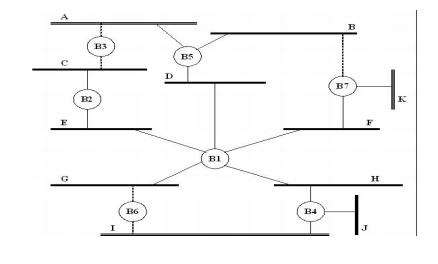
In the
above example, B1 is the root bridge since it having the smallest ID. Both B3
and
B5 are
connected to LAN A, but B5 is the designated bridge since it is closer to the
root.
Similarly
B5 and B7 are connected to LAN B, but B5 is the designated bridge even they are
equally
closer to the root since B5 having smallest ID.
The
bridges have to exchange configuration messages with each other and then decide
whether or not they are the root or a designated bridge based on this message.
The configuration contains three pieces of information.
1. The ID
for the bridge that is sending the message
2. The ID
for what the sending bridge believes to be the root bridge
3. The distance, measured in hops, from the sending bridge to the root bridge. Initially each bridge thinks it is the root bridge, so the configuration message will contain the sending and root same ID. By receiving the configuration message from other bridges they select the root bridge. The selection will be by,
• It identifies a root with a smaller ID or ď€
• It identifies a root with an equal ID but
with a shorter distance or ď€
• The root ID and distance are equal, but the
sending bridge has a smaller ID ď€
BROADCAST AND MULTICAST
Most LANs support both broadcast and multicast; then bridges must also support these two features.
Broadcast is simple, each bridge forward a frame with a destination broadcast address out on each active port other that the one on which the frame was received. In multicasting, each host deciding for itself whether or not to accept the message.
Related Topics