Chapter: Computer Networks : Media Access & Internetworking
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP)
DYNAMIC HOST CONFIGURATION
PROTOCOL (DHCP)
Ethernet
addresses are configured into the network adaptor by the manufacturer, and this
process is managed in such a way that these addresses are globally unique. This
is clearly a sufficient condition to ensure that any collection of hosts
connected to a single Ethernet will have unique addresses. IP addresses by
contrast must be not only unique on a given internetwork, but also must reflect
the structure of the internetwork. They contain a network part and a host part;
the network part must be the same for all hosts on the same network.
Thus, it
is not possible for the IP addresses to be configured once into a host when it
is manufactured, since that would imply that the manufacturer knew which hosts
were going to end up on which networks, and it would mean that a host, once
connected to one network, could never move to another. For this reason, IP
addresses need to be reconfigurable.
There are
some obvious drawbacks in manual configuration by system administrator. So
automated configuration methods are required. The primary method uses a
protocol known as
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP).
DHCP
relies on the existence of a DHCP server that is responsible for providing
configuration information to hosts. At the simplest level, the DHCP server can
function just as a centralized repository for host configuration information.
The configuration information for each host could be stored in the DHCP server
and automatically retrieved by each host when it is booted or connected to the
network. The configuration information for each host stored in a table that is
indexed by some form of unique client identifier, typically hardware address.
To
contact a DHCP server the host sends a DHCPDISCOVER message to a special IP
address (255.255.255.255) that is an IP broadcast address. It will received by
all host and routers on the network. DHCP uses the concept of a relay agent.
There is at least one relay agent on each network, and it is configured with
just one piece of information, the IP address of DHCP server. When a relay
agent receives a DHCPDISCOVER message, it unicasts it to the DHCP server and
awaits the response, which it will send back to the requesting client
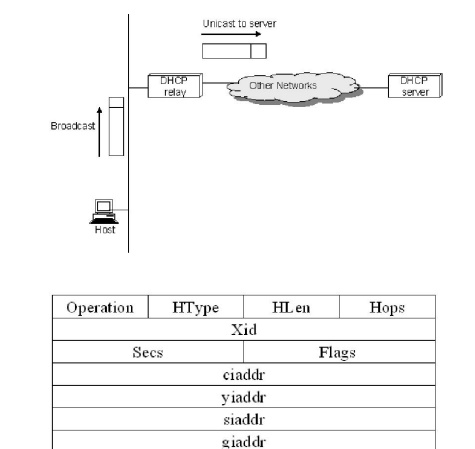
The
packet format is shown above. The message is sent using a protocol called the
User Datagram Protocol (UDP). When trying to obtain the configuration
information, the client puts its hardware address in the chaddr field. The DHCP
server replies by filling in the yiaddr (your IP address) field and sending to
the client.
Related Topics