Chapter: Computer Networks : Media Access & Internetworking
Bluetooth (802.15.1)
BLUETOOTH (802.15.1)
Bluetooth
fills the niche of very short-range communication between mobile phones,PDAs,
Notebook computers, and other personal or peripheral devices. For example,
Bluetooth can be used to connect a mobile phone to a headset, or a notebook
computer to a printer. Bluetooth is a more convenient alternative to connecting
two devices with a wire. In such applications, it is not necessary to provide much
range or bandwidth. This is fortunate for some of the target battery-powered
devices, since it is important that they not consume much power.
Bluetooth
operates in the license-exempt band at 2.45 GHz. It has a range of only about
10 m. For this reason, and because the communicating devices typically belong
to one individual or group, Bluetooth is sometimes categorized as a personal
area network (PAN). Version 2.0 provides speeds up to 2.1 Mbps. Power
consumption is low.
Bluetooth
is specified by an industry consortium called the Bluetooth Special Interest
Group. It specifies an entire suite of protocols, going beyond the link layer
to define application protocols, which it calls profiles, for a range of applications. For example, there is a
profile for synchronizing a PDA with a personal computer. Another profile gives
a mobile computer access to a wired LAN in the manner of 802.11, although this
was not Bluetooth’s original goal. The
IEEE
802.15.1 standard is based on Bluetooth but excludes the application protocols.
The basic Bluetooth network configuration, called a piconet, consists of a master device and up to seven slave devices.
Any communication is between the master and a slave; the slaves do not
communicate directly with each other. Because slaves have a simpler role, their
Bluetooth hardware and software can be simpler and cheaper.
Since
Bluetooth operates in an license-exempt band, it is required to use spread spectrum
Technique
to deal with possible interference in the band. It uses frequency hopping with
79 channels (frequencies), using each for 625 ÎĽm at a time. This provides a
natural time slot for Bluetooth to use for synchronous time division
multiplexing. A frame takes up 1, 3, or 5 consecutive time slots.
A slave
device can be parked: set to an inactive, low-power state. A parked device
cannot communicate on the piconet; it can only be reactivated by the master. A
piconet can have up to 255 parked devices in addition to its active slave
devices. ZigBee is a newer technology that competes with Bluetooth to some
extent. Devised by the ZigBee alliance and standardized as IEEE 802.15.4, it is
designed for situations where the bandwidth requirements are low and power
consumption must be very low to give very long battery life. It is also intended
to be simpler and cheaper than Bluetooth, making it financially feasible to
incorporate in cheaper devices such as a wall switch that wirelessly
communicates with a ceiling-mounted fan.
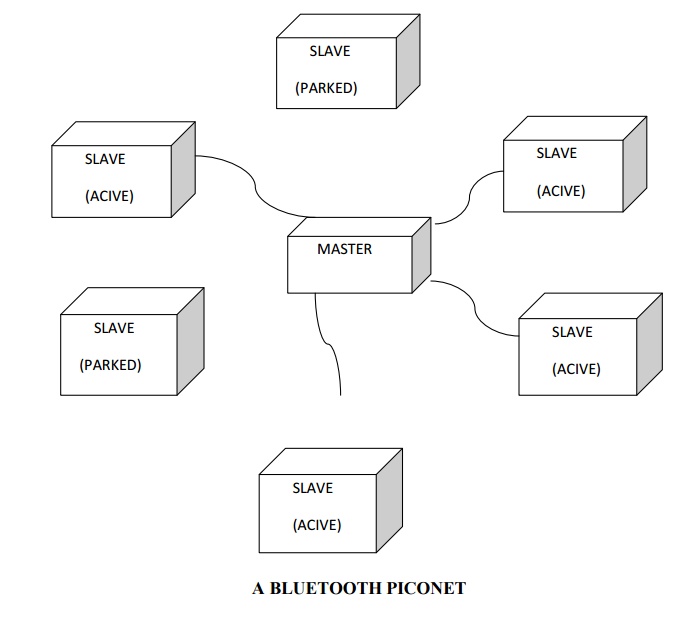
A BLUETOOTH PICONET
Related Topics