Chapter: Computer Networks : Media Access & Internetworking
Address Resolution Protocol (ARP)
ADDRESS RESOLUTION PROTOCOL
(ARP):
IP data
grams contain IP addresses, but the physical interface hardware on the host or
router can only understands the addressing scheme of that particular network.
So the IP address should be translated to a link level address.
One
simplest way to map an IP address in to a physical network address is to encode
a host‟s physical address in the host
part of its IP address. For example, a host with physical address 00100001
01001001 (which has the decimal value 33 in the upper byte and 81 in the lower
byte) might be given the IP address 128.96.33.81. But in class C only 8 bits
for host part. It is not enough for 48 bit Ethernet address.
A more
general solution would be for each host to maintain a table of address pairs,
i.e, and the table would map IP addresses into physical address. While this
table could be centrally managed by a system administrator and then be copied
to each host ion the network, a better approach would be for each host to
dynamically learn the contents of the table using the network. This can be
accomplished by Address Resolution
Protocol (ARP). The goal of ARP is to enable each host on a network to
build up a table of mappings between IP address and link level addresses.
Since
these mappings may change over time, the entries are timed out periodically and
removed. This happens on the order of every 15 minutes. The set of mappings
currently stored in a host is known as ARP cache or ARP table.
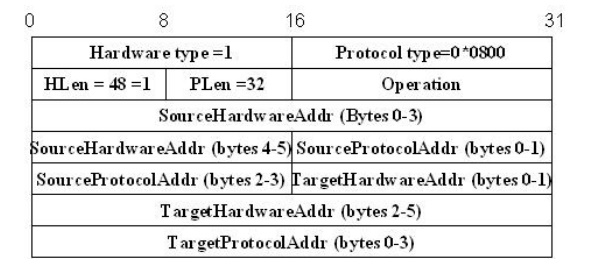
The above
figure shows the ARP packet format for IP to Ethernet address mappings. ARP can
be used for lots of other kinds of mappings the major difference is
their address
size. In addition to the IP and link level addresses of both sender and target,
the packet contains
o a
HardwareType fiels, which specifies the type of the physical network (ex.,
Ethernet)
o a
ProtocolType field, which specifies the higher layer protocol (ex., IP)
o
HLen (hardware address length) and PLen (protocol
address length) fields, which specifies the length of the link layer address
and higher layer protocol address, respectively
o An
Operation field, which specifies whether this is a request or a response o The source and target hardware
(Ethernet) and protocol (IP) address.
The
results of the ARP process can be added as an extra column in a forwarding
table.
Related Topics