Chapter: Clinical Dermatology: Skin reactions to light
Sunburn
Sunburn
Cause
UVB penetrates the epidermis and superficial dermis, stimulating the production and release of prostag-landins, leukotrienes, histamine, interleukin 1 (IL-1) and tumour necrosis factor α (TNF-α), which cause pain and redness.
Presentation and course
Skin
exposed to too much UVB smarts and becomes red several hours later. Severe
sunburn is painful and may blister. The redness is maximal after 1 day and then
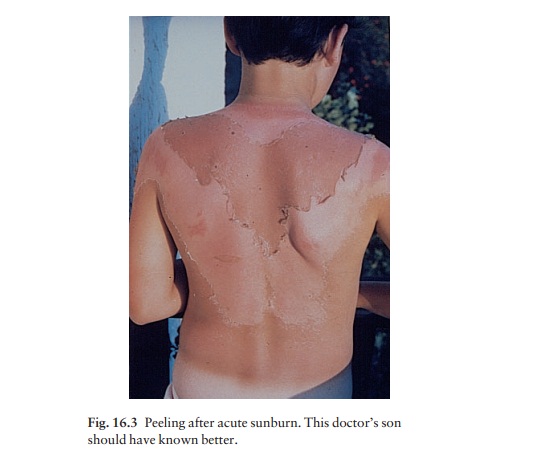
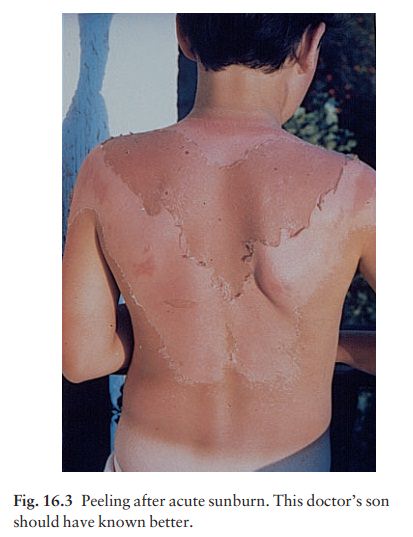
settles over the next 2 or 3 days, leaving sheet-like desquamation (Fig. 16.3),
diffuse pigmentation (a ‘tan’) and, sometimes, discrete lentigines.
Differential diagnosis
Phototoxic
reactions caused by drugs are like an exag-gerated sunburn.
Investigations
None
are required.
Treatment
The treatment is symptomatic. Baths may be cooling and oily shake lotions (e.g. oily calamine lotion), oil-in-water lotions or creams comforting. Potent topical corticosteroids (Formulary 1) help if used early and briefly. Oral aspirin (a prostaglandin synthesis inhibitor) relieves the pain. Sprays containing benzo-caine also relieve pain, but occasionally sensitize.
Related Topics