Chapter: Computer Programming
Strings - C Programming
String
String is the collection of characters.
It can be represented by 1-d arrays. Header file used is string.h.
String
Declaration:
Datatypevariable_name[size];
Eg: char sar[30];
String
Initialization:
Datatype variable_name[size]=string;
Eg: char sar[30]={“Niro”};
1
Built in Sting functions/ String Operation/ Sting Manipulation Function:
There are several string functions to
work with string variables and its values. These functions are available C
header file called string.h. Consider the following exa,ple:
Char string1[15]=”Sriram”;
Char string2[15]=”College”;
Copying
String
Strcpy(string1,string2);
This function copy’s the value of
string2 to string1. Now the string1 be “College”. To add the string2 to string1
the size of the string1 must be sufficient enough to fit the value of string2.
This function will replace the existing value string1 with string2. Now string1
and string2 are “College”.
String
comparison[Case Sensitive]
Strcmp(string1,string2);
This function compares the value from
string2 with string1. If both the string1 and string2 are exactly the same then
the function will return zero or else it will return some positive or negative
value. For the above example the function will return negative of positive
value. Here string1 and string2 will not change.
Non-Case
Sensitive:
strcmpi(string1,string2);
Concatenation
Sting
strcat(string1,string2);
Copying
String
strcpy(string1,string2);
This function copy’s the contents of one
string into another string.
Find
a value in sting
strstr(string1,
string2);
This function will find the value of
string2 in string1. Assume string1 as “Apple” and string2 as “Ap” now the
function will return position of first occurrence of “Ap”, since “Ap” is found
in “Apple”.
Reversing
a string
strrev(string1);
This unction reverse the data o string1
and stores it in string1.
Length
of String
Strlen(string1);
This function will return length of the
string. For the above example it returns
8.
Convert
Uppercase to Lower case
strlwr(string1);
Convert
Lower case to Uppercase
strupr(string1);
Example:
Palindrome of string data
//To check whether the data is
palindrome
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
#include<string.h>
int r;
char s1[15],s2[15];
void main()
{
clrscr();
printf(“Enter anything:”);
scanf(“%s”,s1);
strcpy(s2,s1); //copy’s s1 to another
variable s2
strrev(s2); //reverse the value of s2
scanf(“%s\n”,s1);
scanf(“%s\n”,s2);
r=stremp(s1,s2);
if(r==0)
printf(“It is a Palindrome %s\n”,s1);
else
printf(“It is not a Palindrome
%s\n”,s1);
getch();
}
1-D
ARRAYS
P_1:
Accept 5 numbers & STORE IN Array also print the numbers in the Array.
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
void main()
{
int a[5];
printf(“\n Enter the element:”);
for(i=0;i<5;i++)
{
scanf(“%d”,&a[i]);
}
printf(“\n The elements in the array
are:”);
for(i=0;i<5;i++)
{
printf(“%d”,a[i]);
printf(“\n”);
}
getch();
}
P_2:
Reversing the elements in the Array
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
void main()
{
int a[10],i;
printf(“\n Enter the element:”);
for(i=0;i<10;i++)
{
scanf(“%d”,&a[i]);
}
printf(“\n The elements in the array
are:”);
for(i=9;i<=0;i--)
{
printf(“%d”,a[i]);
printf(“\n”);
}
getch();
}
P_3: To find the sum and average of
elements in the Array.
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
void main()
{
int a[20],I,sum=0;
floatavg=0;
printf(“\n Enter the element:”);
for(i=0;i<20;i++)
{
scanf(“%d”,&a[i]);
}
printf(“\n The elements in the array
are:”);
for(i=0;i<20;i++)
{
sum=sum+a[i];
}
printf(“\n The Sum of elements in the
array is %d”,sum);
avg=sum/20;
printf(“\n The Average of elements in
the array is %f”,avg);
getch();
}
P_4:
Find the maximum of elements present in the array
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
void main()
{
inti=0,x,a[5]={32,44,11,3,6};
clrscr();
x=a[0];
for(i=0;i<5;i++)
{
If(x<a[i])
x=a[i];
}
printf(“\n The value is %d.”,x);
getch();
}
P_5:
Program to arrange an array of elements in Ascending order.[BUBBLE SORT]
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
void main()
{
int a[10],i,n,j,t;
clrscr();
printf(“Enter size of array:”);
scanf(“%d”,&n);
printf(“Enter array elements:”);
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
printf(“array before sorting\n”);
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
Printf(“%d\n”,a[i]);
}
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
for(j=i;j<n;j++)
{
If(a[i]>a[j])
{
t=a[i];
a[i]=a[j];
a[j]=t;
}
}
}
printf(“\n after sorting\n”);
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
Printf(“%d\n”,a[i]);
}
getch();
}
P_6:
Program to arrange an array of elements in Ascending oreder.[Quicker sort]
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
void quicksort(int [10],int,int);
void main()
{
int x[20], size,i;
printf(“Enter size of the array: ”);
scanf(“%d”,&size);
printf(“Enter %d elements:”, size);
for(i=0;i<size;i++)
scanf(“%d”,&x[i]);
quicksort(x,0,size-1)
printf(“Sorted elements:”);
for(i=0;i<size;i++)
printf(“%d”,x[i]);
return 0;
}
void quicksort(int x[10],int first, int
last)
{
intpivot,j,temp,i;
if(first<last){
pivot=first;
i=first;
j=last;
while(i<j){
while(x[i]<=x[pivot]&&i<last)
i++;
while(x[j]>x[pivot])
j--;
if(i<j){
temp=x[i];
x[i]=x[j];
x[j]=temp;
}
}
temp=x[pivot];
x[pivot]=x[j];
x[j]=temp;
quicksort(x,first,j-1);
quicksort(x,j+1,last);
}
}
////[2-Dimensional
Arrays]///
P_1:
Initializing 2-D Array.
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
void main()
{
int a[5][5],i,j;
printf(“\n Enter the element:”);
for(i=0;i<5;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<5;j++)
{
printf(“Matrix[%d][%d]”,i,j);
scanf(“%d”,&a[i][j]);
}
}
printf(“\n Matrix is:”);
for(i=0;i<5;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<5;j++)
{
printf(“%d”,a[i][j]);
printf(“\n”);
}
getch();
}
P_2:
Program to demonstrate matrix multiplication.
Algorithm-Multiplication
of two matrixes:
Rule: Multiplication of two matrixes is
only possible if first matrix has size m X n and other matrix has size n x r.
Where m, n and r are any positive integer.
Multiplication
of two matrixes is define as
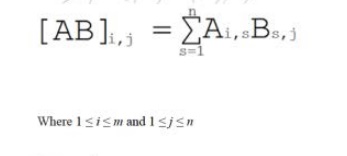
For example:
Suppose two matrixes A and B of size of
2x3 and 2x3 respectively:
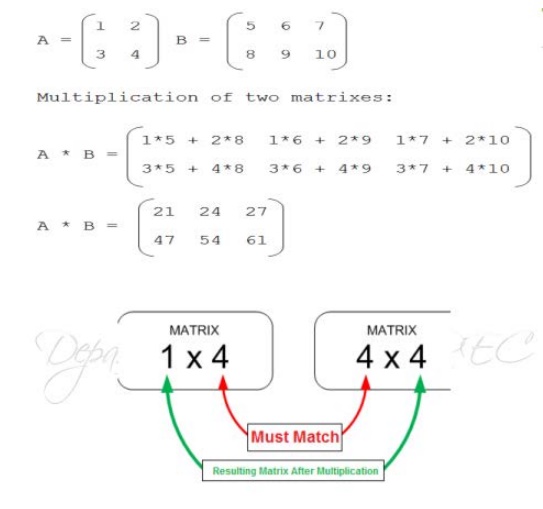
Program:
P_1:
Initializing 2-D Array.
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
void main()
{
int a[10][10],b[10][10],c[10][10],i,j,k,row1,col1,row2,col2;
clrscr();
printf(“\n Enter array1 size ”);
scanf(“%d%d”,&row1,&col1);
printf(“\n Enter array2 size ”);
scanf(“%d%d”,&row2,&col2);
if(row2!=col1)
{
printf(“Wrong choice entered”);
getch();
exit(0);
}
else
{
printf(“Enter elements”);
for(i=0;i<row1;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<col1;j++)
{
scanf(“%d”,&a[i][j]);
}
}
printf(“Enter elements 2”);
for(i=0;i<row2;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<col2;j++)
{
scanf(“%d”,&b[i][j]);
}
}
for(i=0;i<row1;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<col1;j++)
{
c[i][j]=0;
for(k=0;k<row2;k++)
{
c[i][j]=c[i][j]+(a[i][j]*b[i][j])
}
}
}
printf(“REQUIRED MATRIX”);
for(i=0;i<row1;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<col2;j++)
{
printf(“\n%d”,c[i][j]);
}
printf(“\n”);
}
getch();
}
}
P_3:
Program to demonstrate matrix addition.
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
void main()
{
int
a[3][3],b[3][3],c[3][3],i,j,row1,col1,row2,col2;
clrscr();
printf(“\n Enter array1 size ”);
scanf(“%d%d”,&row1,&col1);
printf(“\n Enter array2 size ”);
scanf(“%d%d”,&row2,&col2);
printf(“Enter the First matrix :”);
for(i=0;i<row1;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<col1;j++)
{
scanf(“%d”,&a[i][j]);
}
}
printf(“\n Enter the Second matrix: ”);
for(i=0;i<row2;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<col2;j++)
{
scanf(“%d”,&b[i][j]);
}
}
for(i=0;i<row1;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<col1;j++)
{
c[i][j]=a[i][j]+b[i][j];
}
}
printf(“\n The Addition of two matrix is
\n”);
for(i=0;i<row1;i++)
{
printf(“\n”);
for(j=0;j<col1;j++)
{
printf(“%d\t”,c[i][j]);
}
}
return 0;;
}
P_4:
Program to matrix transpose
/*2-D
Transpose*/
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
void main()
{
int a[10][10],b[10][10],row,col,i,j;
clrscr();
printf(“\n Enter row size ”);
scanf(“%d”,&row);
printf(“\n Enter column size ”);
scanf(“%d”,&col);
for(i=0;i<row;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<col;j++)
{
printf(“\n matrix [%d][%d]”,i,j);
scanf(“%d”,&a[i][j]);
}
}
for(i=0;i<row;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<col;j++)
{
b[i][j]=a[i][j];
}
}
printf(“\n Transpose of given Matrix: ”);
for(i=0;i<row;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<col;j++)
{
printf(“\n%d”,b[i][j]);
}
}
getch();
}
P_5:
To search the location of given data in the array / Linear Search [SEARCHING]
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
void main()
{
inti,n,data,a[20],f=0;
printf(“\n Enter the Array Capacity: ”);
scanf(“%d”,&n);
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
printf(“\n Enter the %d Data: ”,i+1);
scanf(“%d”,&a[i]);
}
}
printf(“\n Enter the data to be
searched:”);
scanf(“%d”,&data);
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
if(data==a[i])
{
printf(“\n Data is found in %d
location”, i+1);
f=1;
}
}
if(f!=1)
{
printf(“\n Data not Found:”);
}
getch();
}
P_6:
Binary Search in C:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
void main()
{
inti, first,last, middle, n, search,
array[100];
printf(“\n Enter number of elements\n
”);
scanf(“%d”,&n);
printf(“\n Enter %dintegers\n”,n);
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
scanf(“%d”,&array[i]);
printf(“\n Enter value to find\n”);
scanf(“%d”,&search);
first=0;
last=n-1;
middle = (first+last)/2;
while(first<=last)
{
if(array[middle]<search)
first=middle+1;
else if(array[middle]>search)
{
last=middle+1;
}
else
{
printf(“%d found at location
%d.\n”,search,middle+1);
if(first>last)
printf(“Not found! %d is not present in
the list. \n”,search);
return 0;
Related Topics