Term 3 Unit 1 | Geography | 7th Social Science - South America - Exploring Continents | 7th Social Science : Geography : Term 3 Unit 1 : Exploring Continents -North America and South America
Chapter: 7th Social Science : Geography : Term 3 Unit 1 : Exploring Continents -North America and South America
South America - Exploring Continents
South America - Exploring Continents
Next
to Asia, Africa and North America, South America is the fourth largest country
in the World. Most of the South American continent lies within the Southern
Hemisphere and hence called as the “Southern Continent”. The Isthmus of Panama
in the North West connects South America with North America.
Together with the Central America, South America is alsoknown as
Latin America, having been discovered and colonized mostly by the Latin’s,
i.e., The Spanish and the Portuguese.
Location
South
Americalies between 12ºn and 55ºS latitudes and 35ºW and 81ºW longitudes. The
Equator (0º latitude) passes through the mouth of the Amazon River. The Tropic
of Capricorn (231/2º S longitude) passes through the Rio de Janeiro in Brazil.
South America is inverted triangular shaped landmass. The area of the continent
is 17, 840, 000 Sq. Km., which occupies 12 percent of the world's land area.
Physiography
South America has marked
resemblances in structure and relief of North America. South America has some
of the oldest and the youngest rocks of the world. On the basis of
topographical features, the continent may be divided into the following
physiographic divisions:
* The Andes Mountains
* The River Basin or Central Plains
* The Eastern Highlands
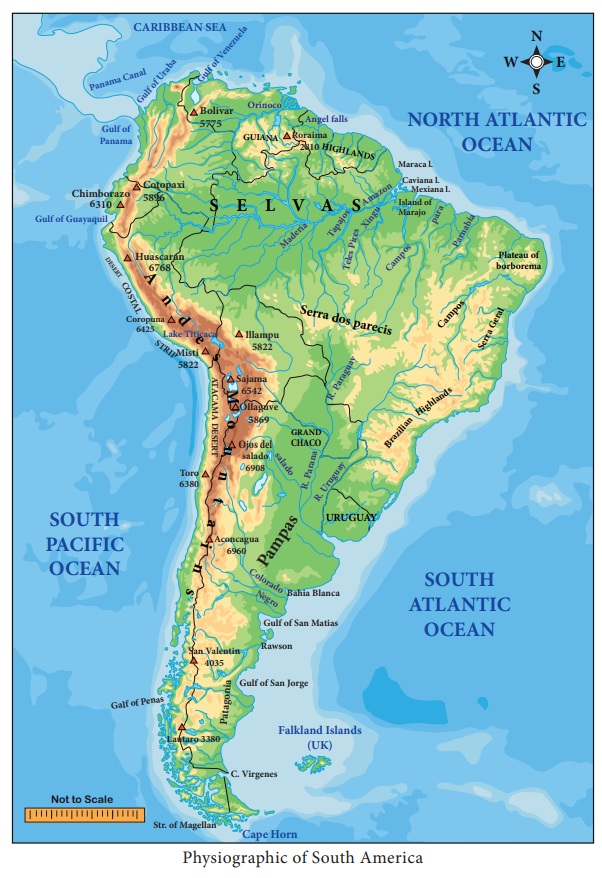
The Andes Mountains
The Andes are Fold Mountains like
the Himalayas. This is the longest mountain range in the world and extends for
more than 6,440 km along the Pacific Coast. The highest peak in the Andes is
Mount Aconcagua (an extinct volcano) in Argentina border which reaches at an
elevation of 6,961m. In Chile, the mountains run very close to the coast. The
slopes are steep on the western side and gentle on the eastern side like
Rockies in North America. The Andes
being a part of the Pacific Ring of
Fire these places are subject to great volcanic eruption and earthquake
activities. There are some active volcanoes like Cotopaxi (5,991m) on the Andes
range. The Andes are rich in minerals like Copper, Tin and Precious Gems
including Emeralds.

The River Basins (or)
the Central Plains
Nearly half of the Continent is
covered by the plains. Three great rivers drain into the Atlantic Ocean. The
biggest of them is the Amazon. The Amazon basin consisting mainly of the
alluvial deposits is the thickly forested part of the world. It is widest near
the Andes and narrowest near the mouth of the Amazon River. The Orinoco basin
is separated from the Amazon basin by low interfluves. It is also one of the
most productive parts of the continent. The Parana - Paraguay plain is an
ancient rocky surface covered with alluvial deposits and is rich in petroleum
deposits.
The Eastern Highlands
These are considerably older than
the Andes and are mainly Plateau which is cut by many rivers. They lie to the
north and south of the Amazon River. The Guiana Highland is located in the
northern part of the continent which has a number of waterfalls including the
Angel Falls. The Brazilian Highlands are found to the south of the Amazon
basin. They are gently rolling plateaus with steep cliffs along the east coast.
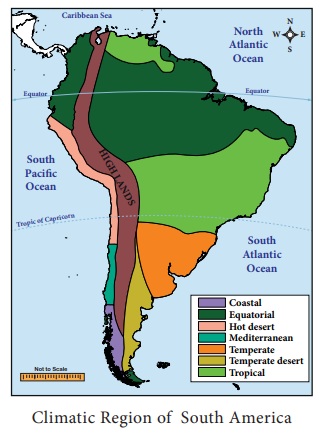
Climate
The climate of the continent of
South America has been closely influenced by the latitudes, attitudes and the
proximity of the Pacific and Atlantic Oceans. It is hot in the Amazon basin as
the equator passes through it whereas Quito, situated almost on the same
latitude on the Andes, has “Eternal Spring”. That is, it has a pleasant climate
throughout the year because of its high altitude at 9,350 feet or2849.88 meter
above the sea level. Most of South America regions have its summer from
November to January. When it is quite hot in Brazil Argentina has a relatively
cooler climate because of its location in more southerly latitudes.
The rainfall distribution is mainly
controlled by the physical features and the distance from the sea. The trade
winds bring a lot of rain to the east coast and the Westerlies to the west
coast. However, the Amazon basin gets rainfall everyday because of its
equatorial location. The regions around the Equator get what is called “4’o
Clock Rains” which are convectional rains. Rainfall decreases towards the
interior.
In equatorial regions convectional rain occurs almost daily in the
afternoons. It generally occurs at 4pm that’s why it is known as4’ o Clock
Rain.
Drainage
Owing to the position of the Andes
all the great rivers of the continent drain into the Atlantic. The Pacific
streams are short and swift but along the coastlands of Peru their waters are
used for irrigation and to some extent for hydro-electric power. Amazon is the
longest river of South America (6,450km) and is the largest river system in the
world. This river have over a thousand of tributaries. The rivers Rio Negro,
Madeira and Tapajos are important tributaries. At the point where it enters the
sea the river is so wide and powerful that it flows even at a distance of 80 km
into the high seas. The Orinoco River originates in the Guiana Highlands and
flows northwards into the Caribbean Sea. The river Paraguay has the Paraná and
Uruguay rivers as the main tributaries which together form and known as the
Platte River system. All the rivers are navigable for quite some distance in
the interior.
Amazon is the greatestriver of South America and the largest
drainage system in the world in terms of the volume of its flow and the area of
its basin.
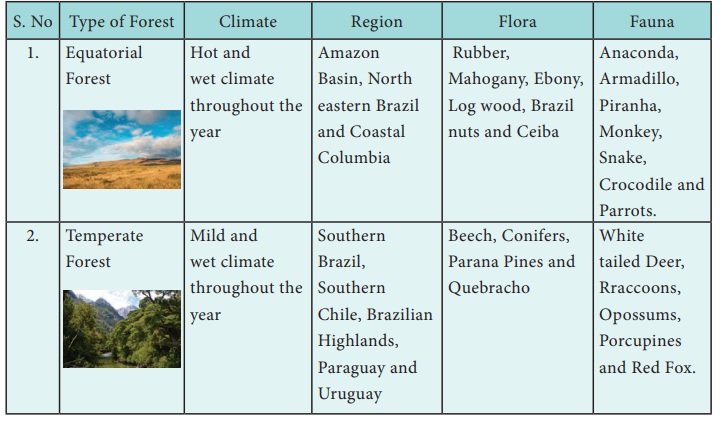
Natural Vegetation
There are four main natural
vegetation areas of South America and are the Amazon basin (the Selvas), the
Eastern Highlands, the Gran Chaco and the slopes of the Andes. The Selvas of
the equatorial regions are called the “lungs of the world”. The Amazon
rainforest are the largest of their kind in the world. They abound in hardwood
trees such as mahogany and Ebony which are very valuable. The other common
species are Rosewood Cinchona and a variety of Palm trees. The bark of the cinchona
tree is used for making quininethe drug to cure Malaria. The Amazon rainforest
are gradually getting depleted. Various developmental activities such as
construction of transportation lines, human settlements and agriculture have
led to widespread deforestation. Environmentalist fear that this might lead to
serious ecological disturbance in future.

The Eastern Highlands have many
varieties of trees which are of economic importance. The leaves of the Yerba
Mate tree are used to make you tea - like drink. The Gran Chaco region has
thick deciduous forests. An important hardwood tree found in these forests is
the Quebracho Tree (axe breaker). Quebracho tree yields tannin which is used
for tanning leather. The forests on the slopes of the Andes have coniferous
such as pine, fir and spruce. These forests are also called Montana. They yield
valuable softwood for the paper and pulp industry.
Wildlife
South America is blessed with a
variety of wildlife. The dense forests, swamps and rivers of the Amazon basin
are particularly rich in different species of animals, birds and reptiles. More
than 1,500 types of birds are found in the continent. The Condor is the largest
bird prey, Rhea is the flightless bird much like the ostrich of Africa.
Toucans, Macaw, Hummingbirds, Flamingoes and different type of Parrots are also
found here. The forest is home to a variety of monkeys. The spider monkeys,
howler monkeys, owl monkeys and squirrel monkeys are very gentle. The Anaconda
which is one of the largest snakes in the world is also found here. Ancient
madammals such as anteaters and armadillos are found in South America. Llamas
are animals typical found only in South America. The rivers of South America
have a rich variety of fish. The Piranha found in the Amazon is a fierce flesh
eating fish.

Agriculture
More than half of the people of
South America live by farming. Subsistence farming is practiced in this
continent. Most of areas are covered by forest like the Amazon basin. Only
three countries, the Argentina, Uruguay, and Brazil have well developed
agriculture. Argentina is one of the leading agricultural countries of South
America. The agricultural activities are mainly concentrated in the wet Pampas.
The Geo
climatic condition of Pampas are
ideal for agriculture. Wheat and Maize are grown on extensive forms in the
Argentine Pampas. In the piedmonts of Andes, where rivers descend and the
climate is favourable, the farmers concentrate on the agricultural vineyards
and other citrus fruits. Cash crops like coffee, cocoa, sugarcane, banana,
cotton etc., are also grown in this continent.
Wheat
The major wheat producers are
Argentina, Brazil, Paraguay, Uruguay and the Chile. The Wheat is grown
extensively on the Pampas of Argentina. Argentina is one of the largest
producer and exporter of wheat in the world.
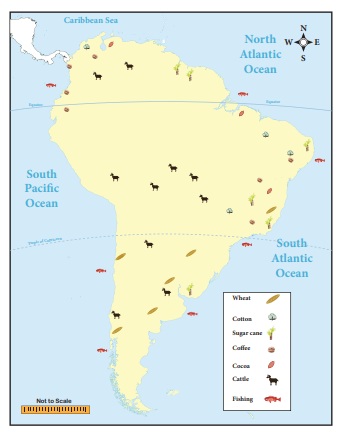
Sugarcane
Sugarcane has been cultivated in the
humid tropics of South America. Spanish and Portuguese introduced sugarcane to
the West Indies and Brazil. Brazil is the largest producer of sugar in South
America.
Maize
Maize is also known as corn. Maize
is grown in the warmer part of the Pampas and coastal regions of Brazil and in
some parts of the Amazon basin. It requires warm climate and frequent showers
in summer. Argentina is one of the largest producer and exporter of maize in
the world.
Coffee and Cocoa
Coffee and Cocoa are the most
important crops of South America. These crops need a warm temperature with
frequent heavy rainfall and well-drained soil. They grow well in the red soil
of the Brazilian Highland. Brazil is essentially an agrarian country. Brazil
stands first in the production of Coffee and third in Cocoa in the world. Minas
Gerais and Sao Paulo are the important Coffee growing areas in Brazil. It is
also known as the “coffee pot” of the world. Colombia and Venezuela also grow
large quantities of coffee. Coco is also grown in Ecuador and Colombia.

Cotton
Cotton is another important cash
crop of South America. Warm climate with frequent rainfall provides suitable
condition for growing cotton. Cotton is the second most important crop in
Brazil. Sao Paulo State produces half of the Country’s total cotton. Equator,
Venezuela and Peru are the other important cotton growing countries in South
America.
Barley, Rye and Oats
These are grown extensively in the
Pampas. Barley is a member of the grass family and is a major cereal grain
grown in temperate climates. Oats are grown in Argentina, Uruguay, Chile,
Andean region, highlands of Bolivia, Ecuador and Peru. In most countries Oats
are more important as fodder for livestock in the field.
Animal rearing
Animal rearing is an important
activity in South America. The Llanos and Campos in South America are the
extensive Tropical Grasslands. Beef cattle are raised in Pampas in Argentina.
Here cattles are mainly raised for draught purposes and meat. Llano grassland
are found in the basin of Orinoco of Venezuela, Brazil and Columbia. Here most
of the cattle are of Criollo breed well suited to the climatic conditions.
Cattles are fed on alfalfa and the breeds raised here on large pasturelands
known as “Estancias”.
Sheep are reared in the drier parts
of South America. The temperate grasslands of Tierra Del Fuego and Falkland
Islands are well suited for Sheep grazing. Argentina and Uruguay are the
important sheep rearing countries. Argentina is one of the largest exporters of
beef in the world.

Estancias
The Breeds raised on large pasture lands is known as Estancias.
These are divided into several paddocks. Besides this, there are small yards
known as corrals where animals are sorted and branded. The owner is the
Estanciera who has a number of gauchos
Fisheries
Peru is one of the world's largest
producers of tropical fish. Here the cool Humboldt Current helps to bring
plankton, which is the main food for fishes. Commercial deep sea fishing off of
Peru’s coastal belt of over 3000 km. Peruvian waters normally abound with sword
fish, mackerel, yellow fin, pompano and shark. More than 50 species are caught
commercially. There are over 40 fishing ports on the Peruvian coast. Paita and
Callao are being the most important centers in Peru. Besides coastal fishing
inland fishing are also carried out in South America. River Amazon is a great
aquarium. As many as 750 varieties of fish inhabit this river.
Minerals
South America is rich in minerals.
These mineral deposits are unevenly distributed. South America has many
valuable deposits of minerals particularly of iron ore, manganese, petroleum,
copper and bauxite. There are some active mines producing silver and gold. The
continent has little coal which is still one of the mainstays of industrial
economies. Northern Chile has the world's only natural deposits of sodium
nitrate an important ingredient of fertilizers.
Iron ore
South America contains about one
fifth of the world's iron ore reserves. Brazil and Chile both have massive
deposits of iron ore. Brazil has the second largest iron ore deposits in the
world after Russia, Brazil is estimated to have about 15% of the world export
of iron ore. High grade iron ore has long been mined at Itabira, Minas Gerais
and new site in the Carajas.
Manganese
Brazil also has large deposits of
Manganese. Manganese ore is mined at Lafaiete, Minas Gerais and in the Northern
State of Amapa.
Petroleum
Venezuela is rich in petroleum
deposits. Argentina, Colombia, Ecuador, Peru, Chile and Bolivia are the other
valuable oilfields. Petroleum is the only mineral produced in substantial
quantity. Argentina is almost self-sufficient in petroleum. Venezuela is one of
the world's leading producers of oil and largest oil exporter outside the
Middle East.
Copper
Chile is the third largest producer
of copper in the world. Copper provides over 40% of exports by value. Some of
the biggest copper mines of the world are located in Peru. It is found in the
Atacama Desert.
Bauxite
Brazil is the third largest bauxite
producing country. An important bauxite mining centre is located near the mouth
of the Amazon River. Bauxite is used for aluminum production.
Industries
Industries in South America have
developed slowly Argentina, Brazil and Chile are the most highly developed
industrial countries in this continent. Until World War I, the continent
exported most of its mining production and large amount of minerals
particularly Petroleum, Copper and iron are still exported. The continent lacks
infrastructure (especially transport) which is an essential need for
Industrialisation. Railways and the roads could not be developed sufficiently
owing to a rugged terrain. The Amazon and the La Plata rivers, provide cheap
water transport. In spite of having an abundance of natural resources,
industrialisation started quite late in South America. Recently, new industries
are being set up with locally available raw materials. Brazil is the most
industrialized country in the continent followed by Argentina.

Trade
South America has significant role
in the world trade. More than half of the South America’s trades are shared by
Brazil, Argentina, Venezuela, Peru and Chile. South America’s major exports are
mostly primary commodities such as sugar, coffee, cocoa, tobacco, beef, corn, wheat,
petroleum, natural gas, linseed, cotton, iron ore, tin and copper. South
America's products include mostly exported to North America and Europe. It’s
imports are machinery, vehicles, chemicals, pharmaceuticals, paper are
textiles. These are imported from North America and Europe.
Transport
Unlike North America, South America
still does not have an adequately integrated transportation network.
Significant efforts have been made to improve both the connection within the
countries and the linkages between them.
Roadways
South America has an extensive and
rapidly expanding network of roads. In many countries, however only a
relatively small percentage of roads are paved and the most remote areas, they
may be barely wide enough for two Vehicles to pass easily. A Road linking
Venezuela and Brazil allows north to south movement through the Amazon Basin.
Brazil continues to have the largest network of roads belonging to the Pan
American Highway System which extends throughout the America's.

Railways
In most South American countries,
railways have lost their dominant position of the major mode of transportation
and have been replaced by the road networks that have developed rapidly since
the 1960’s. Moreover, rail transport is plagued by operational problems as well
as by obsolete equipment. Almost all lines are single-tracked which makes
traffic slow and discourages passenger service. Many countries have two or more
track gauges which impedes the efficient integration of the rails system.

Waterways
Seaways have long been a vital
component of the transport systems of South American countries. Majority of
imports and exports to and from the continent are moved by ship. South America
has a number of outstanding natural harbours. They are Rio de Janeiro,
Salvador, Montevideo and Valparaiso. Several countries such as Chile and Brazil
are making a determined effort to develop and enlarge their sea routes.

There are two inland waterways
system of international importance. They are (i) The Paraguay - Uruguay basin
which includes territory in four countries and (ii) The Amazon basin which
includes six countries. Each has several thousand miles of navigable waterways.
Airways
Airways have developed rapidly since
World War II. The increase is particularly significant with respect to
passenger traffic and also handling of bulky freights. All the South America
capitals and most of the large cities are linked by direct air services to the
major traffic centres of the United States and Europe.
Population
South America contains the world's
most mixed population. Many people in South America are descended from
European, especially the Spanish and Portuguese, who begin to arrive during the
15th century. The descendants of African slaves brought over by the Europeans.
Native people still live in the mountain and the rainforests and keeping their
own languages and traditions. There are three major races found in South
America and are (i) American Indian,
European and (iii) Blacks. The mixed
population of Native Indians and Europeans is known as ‘Mestizo’. The mixed
population of European and the Blacks is called ‘Mulato’ and the mixture of
Native Indians and Blacks is called ‘Zambo’. The current population of South
America is 429, 115, 060 (42.25 cores). Population density of South America is
21 persons per square kilometer. South America is positioned 5th rank in total
population among the continents.
Population
distribution
* High densely populated areas are Guiana, Venezuela,
Suriname, Columbia, Brazil and Peru.
* Moderate populated areas are Paraguay, Chile and
Uruguay and
* Sparsely populated areas are Argentina, Bolivia
and Amazon Basin.
Languages and
Religions
Portuguese and Spanish are the
primary languages of the South America. Among otherlanguages used by many South
Americans are Dutch, French, English, German and Hindi. Christianity is the
dominant religion in South America. Other than Christianity, Hinduism and Islam
are also followed by South Americans.
South American nations have variety of music. Some of the most famous genres include Samba from Brazil, Tango from Argentina and Uruguay andCumbia from Colombia.
Related Topics