Chemistry in Everyday Life - Short Answer Questions | 12th Chemistry : UNIT 15 : Chemistry in Everyday Life
Chapter: 12th Chemistry : UNIT 15 : Chemistry in Everyday Life
Short Answer Questions
Chemistry in Everyday Life
Short Answer Questions
1. Which chemical
is responsible for the antiseptic properties of dettol.
Chloroxylenol
and α-terpineol is responsible for the antiseptic properties of Dettol.
2. What are antibiotics?
The
medicines have the ability to kill the pathogenic bacteria are antibiotics.
Examples:
Amoxicillin, ampicillin
3. Name one substance which can act as both analgesic and antiphyretic
Acetyl salicylicacid (Aspirin) can act as both analgesic and antipyretic
4. Write a note on synthetic detergents
• Synthetic detergents containing
either sodium salts of alkyl hydrogen sulphates or sodium salts of long chain
alkyl benzene sulphonic acids
• There are three types of
detergents
1.
Anionic detergents, Eg: Sodium Lauryl sulphate
2.
Cationic detergents
Eg:
n-hexadecyltrimethyl ammonium chloride
3.
Non-ionic detetrgents, Eg: Pentaerythrityl stearate.
• They can be used in hard water
and in acidic conditions
• The cleansing action is similar
to soaps
5. How do antiseptics differ from disinfectants?
• Both are stop or slow down the
growth of microorganisms.
• Antiseptics are applied to living
tissue whereas disinfectants are used to inanimated objects.
Examples for antiseptics: H2O2,
providone - Iodine.
Examples for disinfectants: Chlorine
compounds alcohol.
6. What are food preservatives?
Preservatives
are capable of inhibiting, retarding or arresting the process of fermentation,
acidification or other decomposition of food by growth of microorganisms.
Example:
Benzoic acid, Acetic acid, Sodium metasulphite
7. Why do soaps not
work in hard water?
Calcium
and magnesium ions present in hard water forms insoluble calcium and magnesium
soaps when sodium or potassium soaps are dissolved in hard water.
These insoluble soaps separate as scum and are useless as cleansing agent.
8. What are drugs? How are they classified
• A drug is a substance that is
used to modify or explore physiological systems or pathological states for the
benefit of the recipient.
• It is used for the purpose of
diagnosis, prevention, cure/relief of a disease.
I. Classification based on the
chemical structure:
Drugs
with a common chemical skeleton. Example: ampicillin, amoxicillin, methicillin
are in pencillin group
II. Classification based on
Pharmacological effect:
Based
on their biological effect that they produce on the recipient. Example:
Antibiotics, antihypertensive drugs
III. Classification based on the
target system (drug action):
Based
on the biological system / process, that they target in the recipient.
Example:
streptomycin and erythromycin. Streptomycin inhibits the initiation of protein
synthesis, while erythromycin prevents the incorporation of new amino acids to
the protein.
IV. Classification based on the
site of action (molecular target):
It
is classified based on the drug target with which it binds. This classification
is highly specific compared to the others.
9. How the tranquilizers work in body.
Tranquilizers
acts on the central nervous system by blocking the neurotransmitter dopamine in
the brain.
Example:
Haloperidol, clozapine, Diazepam (Valium), alprazolam
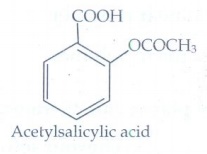
10. Write the structural formula of aspirin.
11. Explain the mechanism of cleansing action of soaps and detergents
• The cleansing action of soaps and
detergents is directly related to the structure of carboxylate ions
• The hydrophilic carboxylate group
is soluble in water.
• The dirt in the cloth is due to
the presence of dust particles intact or grease which stick.
• When the soap is added to an oily
or greasy part of the cloth, the hydrocarbon part of the soap dissolve in the
grease, leaving the negatively charged carboxylate end exposed on the grease
surface.
• At the same time the negatively
charged carboxylate groups are strongly attracted by water, thus leading to the
formation of small droplets called micelles and grease is floated away from the
solid object.
• When the water is rinsed away,
the grease goes with it and the cloth gets free from dirt.
• The cleansing ability of a soap
depends upon its tendency to act as a emulsifying agent between water and water
insoluble greases.
12. Which sweetening agent are used to prepare sweets for a diabetic patient?
Artificial
sweetening agents used to prepare sweets for a diabetic patient because
synthetic compounds which imprint a sweet sensation and possess no or
negligible nutritional value.
Eg.
Saccharin, sucralose
13. What are narcotic and non – narcotic drugs. Give examples
Give examples
Non - narcotic drugs
They
relive pain by reducing local inflammatory responses.
Eg:
Ibuprofen, Aspirin
Narcotic drugs
They
relive pain and produce sleep.
Eg:
Morphine, codeine
14. What are anti fertility drugs? Give examples.
Anti
fertility drugs are synthetic hormones that suppresses ovulation / fertilisation.
Example
Synthetic
oestrogen - Ethynylestradiol, Menstranol
Synthetic
Progesterone - Norethindrone, Norethynodrel
15. Write a note on co –polymer
A
polymer containing two or more different kinds of monomer units is called a
copolymer.
Example:
Buna rubbers, Nylon
16. What are bio degradable polymers? Give examples.
The
polymer materials that are readily decomposed by microorganisms in the
environment are called biodegradable polymers.
Examples:
Polyglycolic
acid (PGA), Polylactic acid (PLA)
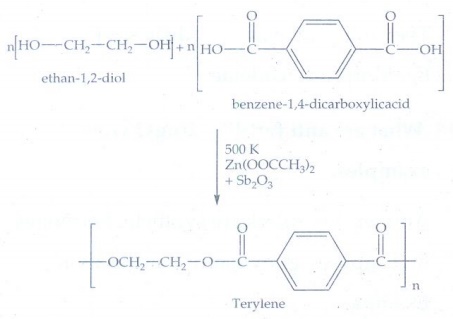
17. How is terylene prepared?
The
monomers are ethylene glycol and terephthalic acid (or) dimethylterephthalate
are mixed and heated at 500 K in the presence of zinc acetate and antimony
trioxide catalyst, terylene formed.
18. Write a note on vulcanization of rubber
• Natural rubber is mixed with 3-5%
sulphur and heated at 100−150°C causes cross linking of the cis-l,4-polyisoprene
chains through disulphide (-S-S-) bonds and made the polymer strong and
elastic.
• The physical properties of rubber
can be altered by controlling the amount of sulphur.
• Rubber made with about 1 to 3%
sulphur is soft and stretchy.
• Rubber with 3 to 10% sulphur is
harder but flexible.
19. Classify the following as linear, branched or cross linked polymers
a) Bakelite b) Nylon-6,6 c) LDPE d) HDPE
a)
Bakelite b) Nylon c) polythene
a)
Bakelite - Cross linked polymer
b)
Nylon - Linear polymer
c)
polythene - Linear polymer
20. Differentiate thermoplastic
and thermosetting.

Thermoplastic
•
They become soft on heating and hard on cooling
•
They can be remolded
Thermo setting
•
Do not become soft on heating but set to an infusible mass upon heating
•
They can not be remolded
Related Topics