Chapter: Mechanical : Manufacturing Technology : Sheet Metal Process
Sheet Metal Process
SHEET METAL PROCESS
Now a day the automobile component, aircraft and ship building involves the usage of thin sheets of various metals. If the thickness of the metal is less than six ‘mm’ then it is called as sheet. Hence the knowledge about the sheet metal processing is necessary. This unit deals how the sheet metals are processed for meeting the requirement & Involves methods in which sheet metal is cut into required dimensions and shape; and/or forming by stamping, drawing, or pressing to the final shape. The surface finish of the sheet metals processed by this methods are good when compared to other process like welding, machining etc., A special class of metal forming where the thickness of the piece of material is small compared to the other dimensions. Cutting into shape involve shear forces Forming Processes involve tensile stresses.
The Major operations of sheet
Metal are;
(A)Shearing,
(B) Bending,
(C) Drawing and
(D)Squeezing
Shearing
The mechanical cutting of materials without the
information of chips or the use of Burning or melting for straight cutting
blades: shearing for curved blades: blanking, piercing, notching, trimming
Classifications
of Shearing Processes
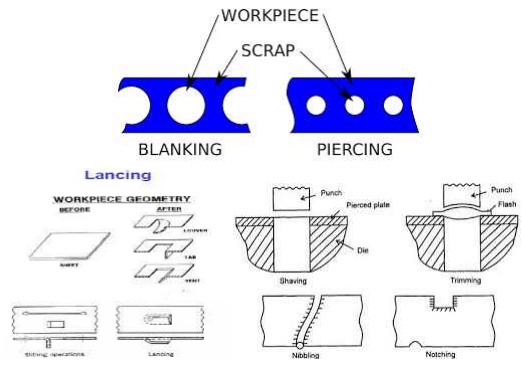
Blanking
Punching
Piercing
Trimming
Slitting
Notching
Nibbling
Shaving
Dinking
Perforating
Lancing
Cutoff
Spring
Back

Blanking.
Cutting a piece from the sheet
metal by leaving enough scrap around the opening to assure that the punch has
enough metal to cut along its entire edge, during which a metal work piece is
removed from the primary metal strip or sheet when it is punched.
Punching.
It is the operation to produce circular holes on a sheet metal
by a punch and a die. Here the pierced metal is the final product then the
operation is called as punching.
Piercing.
It is an operation to produce holes of any desired shape.
Piercing produces a raised hole rather than a cut hole. Piercing refers to
punching a hole.
Trimming.
It is the operation of cutting
and removing unwanted excess metal from the periphery of a previously formed
/forged/cast component.
Slitting
Shearing process used to cut rolls of sheet metal
into several rolls of narrower width used to cut a wide coil of metal into a
number of narrower coils as the main coil is moved through the slitter.
Shearing operations can be carried by means of a pair of circular blades.
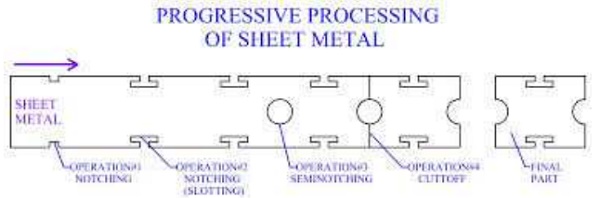
Notching
Same as piercing- edge of the
strip or black forms part of the punch-out perimeter. In this process the metal
is removed from the side (OR) EDGE of a sheet to get the desired shape.
Nibbling
Produces a series of overlapping
slits/notches. A machine called nibbler moves a small straight punch up and
down rapidly into a die.
Shaving
Finishing operation in which a
small amount of metal is sheared away from the edge of an already blanked part
.can be used to produce a smoother edge. The rough edges of a blanked part are
removed by cutting thin strip of metal along the edge on the periphery.
Dinking
Used to
blank shapes from low-strength materials such as rubber, fiber and cloth
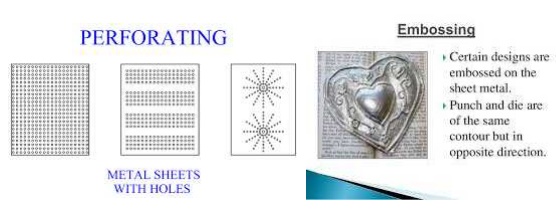
Perforating.
Process
of making multiple holes which are small in diameter and closed together.
Lancing.
Lancing refers to leaving a tab without removing any material.
It is an operationof cutting on one side and bending on the other side to form
a sort of tab (or) Louver. No metal is removed in this operation. Lancing
refers to leaving a tab without removing any material. It is an operationof
cutting on one side and bending on the other side to form a sort of tab (or)
Louver. No metal is removed in this operation.
Cutting Off.
In this operation a piece is removed from a strip by cutting
along a single line.Parting The sheet is sheared into two (Or) more pieces.
Spring back
The
elastic recovery of the material after unloading of the tools.
Bending
The
plastic deformation of metals about a linear axis with little or no change in
the surface area. The purpose of bending is to form sheet metal along a
straight line
STRETCH
FORMING OPERATIONS
In this
process, the sheet metal is clamped along the edges and then stretched over a
die (OR) FORM BLOCK, which moves upward, downward (or) side ways, depending on
the particular machine.
It is used to make aircraft wing-skin panels,
automobile door panels and window frames. The desirable qualities in the metal
for maximum strechability are as follows.
1.Fine grain structure. 2.toughness.
3.LARGE
SPREAD between the tensile yield and ultimate strength.
Working.
It consists of placing the sheet –metal
under a tensile load over a forming block and stretching it beyond its elastic
limit and to te plastic range, thus cause a permanent set to take place.
Two Basic Forms of Stretch forming are,
1.Stretch forming, 2.Stretch – Wrap
forming.
Advantages
1.
In a single operation, blanks can be stretched.
2.
Heat treatment before and after stretching process is not required.
3.
Spring back effect is minimized.
4.
Tooling cost is low.
5.
Direct bending is not introduced, and plastic
deformation is due to pure tension.
6.
It is suitable for low volume production.
Disadvantages.
1.uneven thickness of blank cannot be stretched.
2.The maintanence cost of the hydraulic cylinders is high.
SPECIAL FORMING PROCESS.
1.HYDRO
FORMING PROCESS
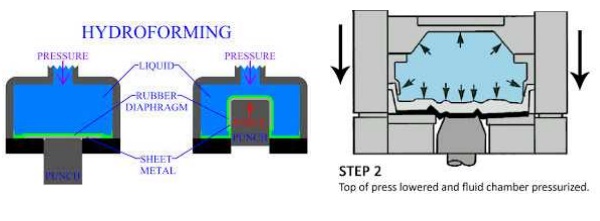
In this process te pressure over
the rubber membraneis controlled throughout the forming cycle, with maximum
pressure upto- 100 Mpa.This procedure allows close control of the part during
forming, to prevent wrinkling (or) tearing. This process is called hydroform or
fluif – Forming
Process.Hydro forming is a Drawing process.
Advantages of Hydro-formimg Process.
1.It is used for Mass production.
2.Tools can be quickly changed.
3.Complicted shapes , sharp
corners can be made by this method.
4.Spring back, Thining off metals
are removed.
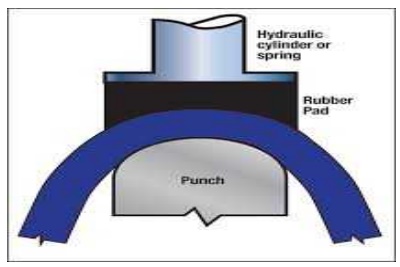
2.RUBBER
PAD FORMING
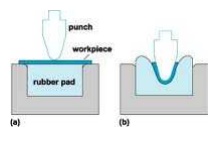
One of the die material is made
up of a flexible material (ex. Rubber) Or (poly-urethane material.In bending
and embossing of sheet metal , the female die is replaced with a rubber
pad.Pressure in the rubber pad forming is usually in the order of10Mpa.
The blank is placed under the
punch called male die.Then the ram (femal part) is moved so that punch touches
the top surface of the work. Then the force is appled and gradually. increased
on the blank through the rubber pad.
The blank holder ring
is used to distribute uniform pressure throughout the blank.
Thus the required shape is formed on the sheet metal between
male and female parts.
Advantages of rubber pad forming.
1.Number of shapes can be formed
on one rubber pad.
2.Thining in metal balank does
not take place.\
3.setting time of the tool is
less.
4.Wrinkle
– free ,
shrink flanges can be produced.
Disadvantages
1.Rapid wearing of rubber Pads is
a problem in this process. 2.Accurate sharp corners cannot be made by this
process.
3.Loss of pressure between hydraulic fluid and rubber pad
which is a major problem
Aplications.
Flanged Cylinders.
Rectangular cups,
Spherical Domes.
Unsymmetrical shaped components can be made.
3.PEEN FORMING PROCESS.
This process is used to produce
curvature on thin sheet metals by shot peening on surface of the sheet. A
stream of metal shots is blasted against the surface of the blank.
This
process is also called as peen forming technique.
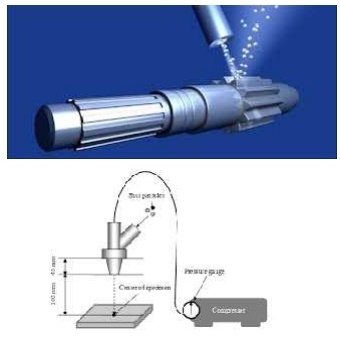
Peening is done with cast- iron
(or) Steel shot discharged either from a rotating wheel by an air blast made
from a nozzle.
Advantages of Peen forming
Complex shapes can be easily
produced . Die and Punch is not used.
Peening is used as a salvage operations for distorted parts
(OR) correcting part.
Disadvantages of peen forming.
This
process requires longer time for forming the required shape.
Requires additional devices for forcing out metal shots.
Applications of peen forming.
Specific portions on crankshafts , connecting rods, gears
Honey
comb panels like aircraft wings and large tubular shapes can be produced.
Related Topics