Chapter: VLSI Design : Combinational and Sequential Circuit Design
Sequencing Static Circuits
SEQUENCING STATIC CIRCUITS
q Combinational
logic
– output depends on current inputs
q Sequential
logic
– output depends on current and previous inputs
– Requires separating previous, current, future
– Called state or tokens
– Ex: FSM, pipeline
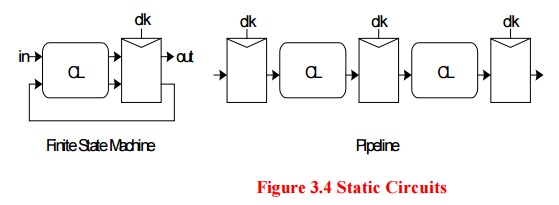
§ If tokens
moved through pipeline at constant speed, no sequencing elements would be
necessary
§ Ex:
fiber-optic cable
§ Light
pulses (tokens) are sent down cable
§ Next
pulse sent before first reaches end of cable
§ No need
for hardware to separate pulses
§ But
dispersion sets min time between pulses
§ This is
called wave pipelining in circuits
§ In most
circuits, dispersion is high
§ Delay
fast tokens so they don’t catch slow ones.
§ Use
flip-flops to delay fast tokens so they move through exactly one stage each
cycle.
§ Inevitably
adds some delay to the slow tokens
§ Makes
circuit slower than just the logic delay
§ Called
sequencing overhead
§ Some
people call this clocking overhead
§ But it
applies to asynchronous circuits too
§ Inevitable
side effect of maintaining sequence
Related Topics