Chapter: Basic & Clinical Pharmacology : Nitric Oxide
Septic Shock - Nitric Oxide in Disease
SEPTIC SHOCK
Sepsis
is a systemic inflammatory response caused by infection. Endotoxin components
from the bacterial wall along with endogenously generated tumor necrosis
factor-α
and other cytokines induce synthesis of iNOS in macrophages, neutro-phils, and
T cells, as well as hepatocytes, smooth muscle cells, endothelial cells, and
fibroblasts. This widespread generation of NO results in exaggerated
hypotension, shock, and, in some cases, death. This hypotension is reduced or
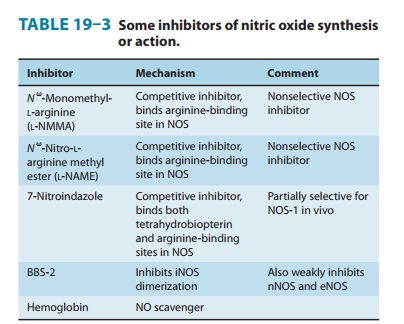
reversed by NOS inhibitors in humans as well as in animal models (Table 19–3).
A similar reversal of hypotension is produced by compounds that prevent the
action of NO, such as the sGC inhibitor meth-ylene blue. Furthermore, knockout
mice lacking a functional iNOS gene are more resistant to endotoxin than
wild-type mice. However, despite the ability of NOS inhibitors to ameliorate
hypotension in sepsis, there is no overall improvement in sur-vival in patients
with gram-negative sepsis treated with NOS inhibitors. The absence of benefit
may reflect the inability of the NOS inhibitors used in these trials to
differentiate between NOS isoforms, or may reflect concurrent inhibition of
beneficial aspects of iNOS signaling.
Related Topics