Family Resource Management - Savings and Investments | 11th Home Science : Chapter 7 : Family Resource Management
Chapter: 11th Home Science : Chapter 7 : Family Resource Management
Savings and Investments
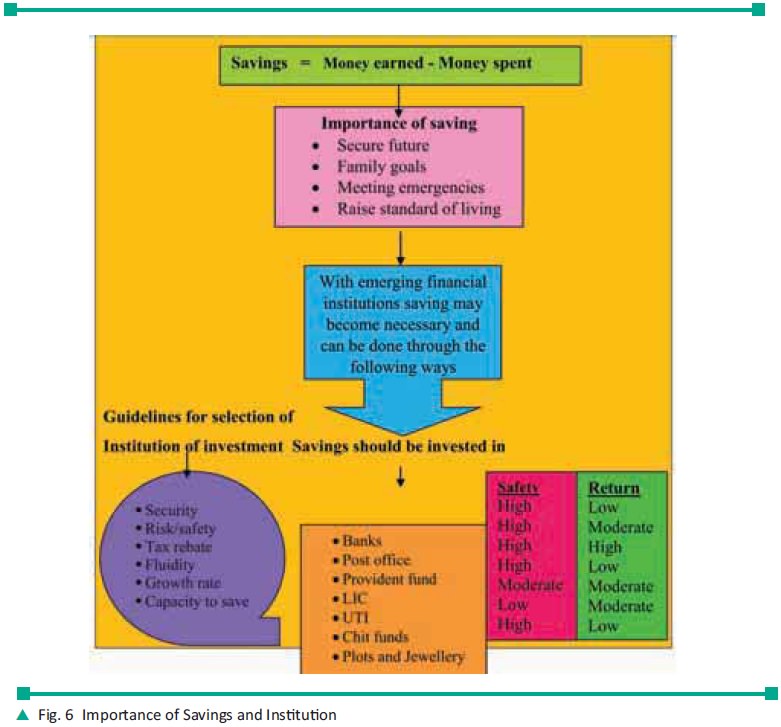
SAVINGS AND INVESTMENTS
Money from the present income that is
collected and put aside for future consumption is known as savings. Savings of a month is the difference between the income and
expenditure of that month. Families should make sure that they save by cutting
down their wasteful expendi-tures. The following figure shows the importance of
savings and various institu-tions for savings and guidelines for selec-tion of
those institutions.
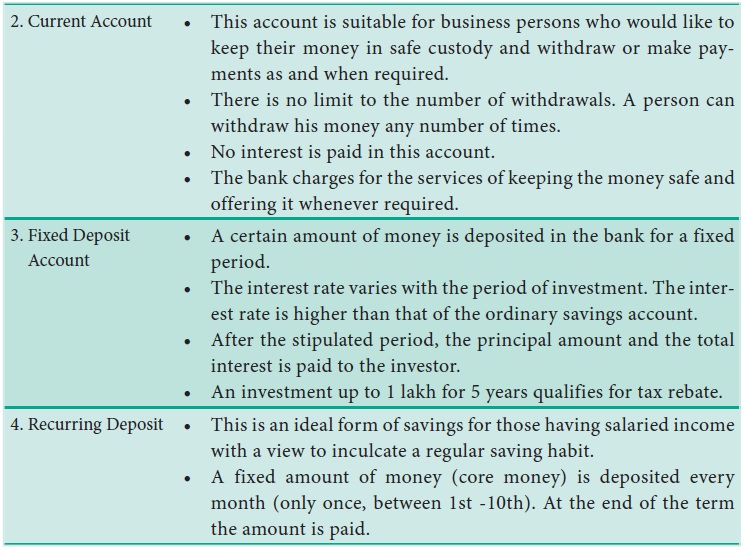
1. Bank Accounts
Savings Account
Current Account
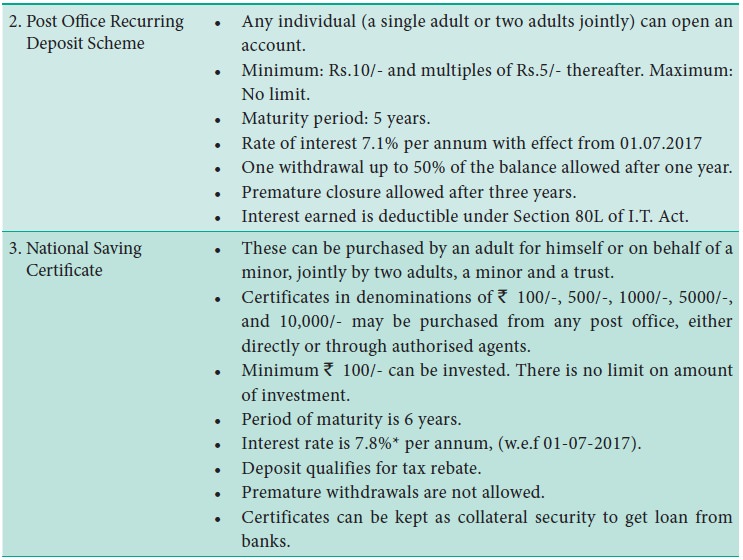
2. Post office
Savings Account
Recurring Deposit Scheme
Post Office Time Deposit Scheme
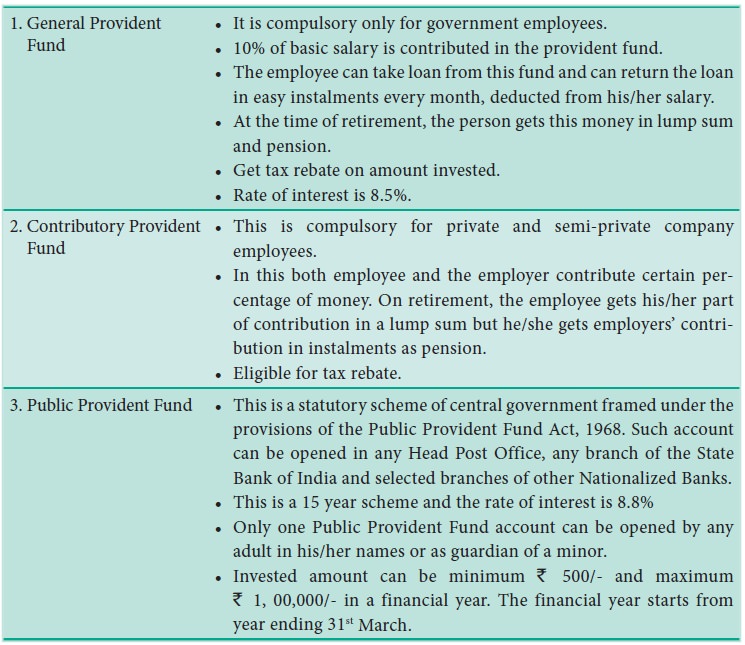
3. Provident Fund
General Provident Fund
Contributory Provident Fund
4. Life Insurance Scheme
LIC (Whole Life Policy)
Medical Insurance Scheme
Endowment Policy
5. Units of Unit Trust of India
6. Shares and debentures
7. Bonds
8. Chit Funds
9. Real Estate
10. Gold, Silver Jewellerys
Important Avenues of Investment
When the savings are made to grow, it is called investment. There are various ave-nues of investment. They are:
Banks
An investor deposits his savings in a bank
account which earns him a nominal rate of interest. Besides banking, the banks
offer a series of diverse financial ser-vices such as loans, credit cards, ATMs
(Automatic Teller Machines). With the computerization and networking of some of
the banks, their services have become faster and customers can operate their
account from any of its branches. This is called core banking. These are the
main accounts used for depositing money in a bank.

Post Office
Post offices are situated in every locality and are found even in remote areas. There are various post office schemes, each hav-ing its distinct advantages.

Provident fund
Insurance
Insurance is provided by private as well as
government institutions. Life Insurance Corporation is provided by government
of India. It is a means of providing against loss caused by natural or man-made
fac-tors. It is the most popular method of securing the future.
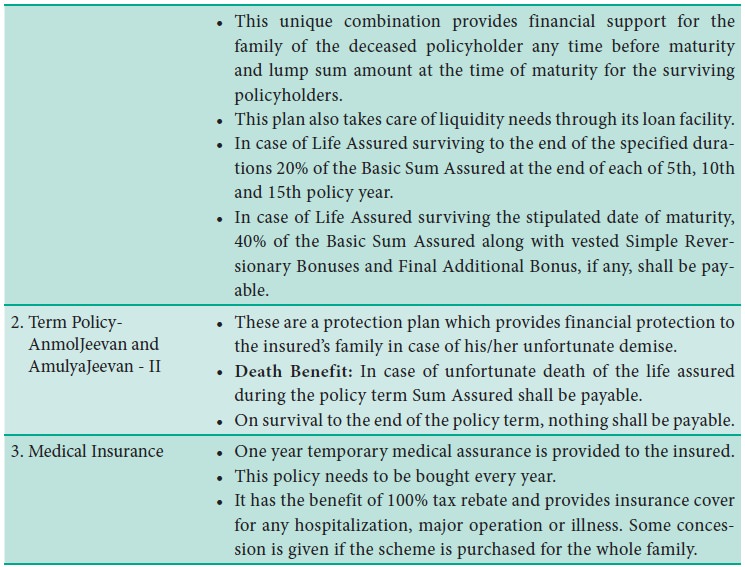
LIC has a variety of schemes to choose from.
These schemes cater to all categories of people and to their diverse needs.
Some of the popular schemes are given below:

Shares
Shares are a fractional part of the capital of
a company. When a company wants to
When
a person buys shares she becomes part owner of the company. She will then share
both profit and loss of the company. The profits are called dividends.
·
A person can get high rate of interest, if the company is making
profits.
·
Dividends are tax-free.
·
There is a risk of losing money, in case the company goes in a
loss.
·
Investor may not be able to find a suit-able buyer for his/her
shares or may not get a good price.
Debentures
A debenture is an instrument of debt.
Debenture holder is a creditor to the com-pany who loans funds to the company
for a period of time against a fixed rate of interest.
Units
Mutual fund is a public and private sector
financial institution which offers various schemes for attracting investments
from public. It issues units to the investors (unit holders) and invests the
collected amount in securities. Each unit is of Rs
10/-.
Profit and losses are shared by the investors
in proportion to their invest-ment. Mutual fund is required to be reg-istered
under SEBI (Securities Board of India), before it can collect funds from
public. SEBI protects the interest of inves-tors and regulates the securities
market.
·
Open end fund-scheme is available for subscription and
repurchase on a con-tinuous basis. These do not have a stip-ulated maturity
date.
·
Close end fund- these schemes have a stipulated maturity period.
Fund is open for subscription only for a speci-fied period of time.
·
Investors have an option to sell back the units to mutual fund
at the NAV (Net Asset Value) market value of assets.
·
Tax rebate is available under some schemes such as ULIP (Unit
Linked Insurance Plan and Pension Plans).
·
There is no limit on investment in some schemes.
·
Units can be pledged as security for loans.
·
Unit holders can switch from close end to open end schemes.
·
Some schemes may have high risk and high rate of interest. On
the other hand, some schemes have fixed rate of interest but no risk.
·
Dividends are tax free.
Bonds
Bonds are also debentures which are issued by
government or Government Company. On liquidation (closing) of the company, the
creditor is secured.
Chit Funds
This is an easy and simple device where a
group of people join as committee and agree to contribute a fixed sum every
month. Chits are taken out once every month. Chits are taken out once every
month. The promoter gets the first collection and after that, whosoever gets
his name on the chit drawn, gets the money.
Related Topics