Chapter: Medicine Study Notes : Evidence Based Medicine
Risks and Odds - Evidence Based Medicine
Risks and Odds
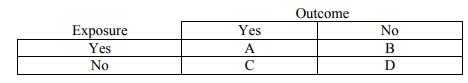
·
Event Rate: proportion of
patients in a group in whom an event is observed. Applied to Controls and
Experimental groups ® CER and EER
·
Relative Risk =
(A/(A+B))/(C/(C+D)) = EER/CER
·
Absolute Risk Reduction (ARR) =
C/(C+D) – A/(A+B) = CER - EER
·
Relative Risk Reduction: percent
reduction in events in the treat group event rate compared to the control group
= (CER – EER)/CER * 100 = (C/(C+D) – A/(A+B))/(C/(C+D))
·
Risk Ratio = EER/CER Odds: ratio
of events to non-events
·
Odds ratio: odds of an
experimental patient suffering an adverse event relative to a control patient =
(A/C)/(B/D)
·
Number needed to treat (NNT):
number of patients needing treatment to achieve one favourable outcome = 1 /ARR
– always rounded up to the nearest whole number and accompanied by the 95% CI
·
Number needed to harm (NNH):
number of patients who need to be treated to achieve one adverse outcome =
1/Absolute Risk Increase (ARI = EER - CER)
·
RRR and OR do not say anything
about absolute risk. An RR of 30% can mean a risk reduction from 60% to 20%, or
from 3% to 1%. The ARR and NNT varies dramatically
·
Time frame: all measures (RR,
RRR, ARR, OR) must be qualified by giving them a time frame (e.g. the length of
the period of the study)
Related Topics