Chapter: Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology: The Skeletal System
Rib Cage - Skeleton
RIB CAGE
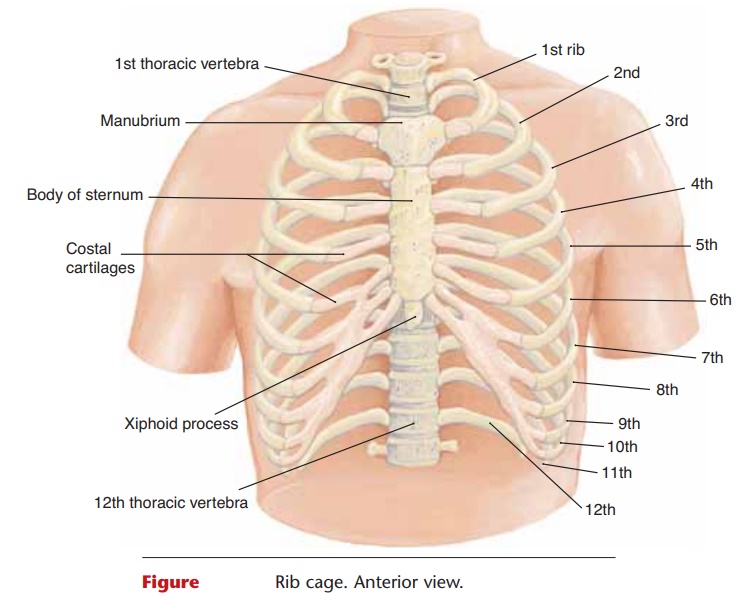
The rib cage consists of the 12 pairs of ribs and the sternum, or breastbone. The three parts of the ster-num are the uppermanubrium, the central body, and the lower xiphoid process (Fig. 6–11).
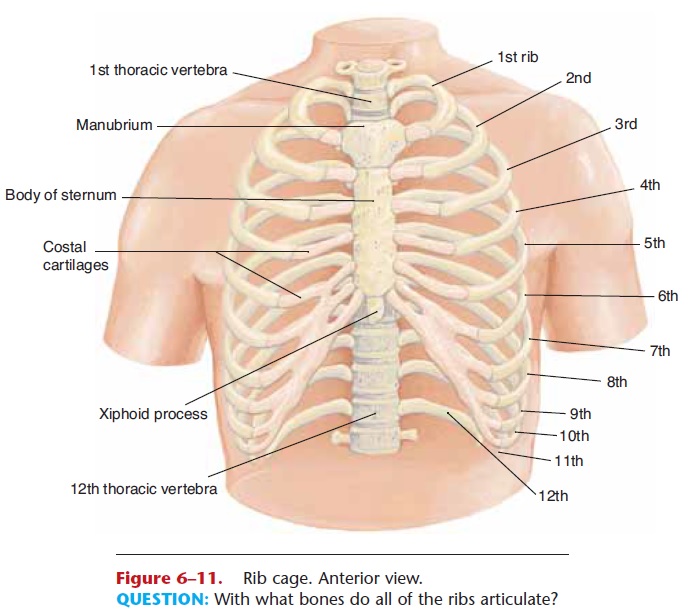
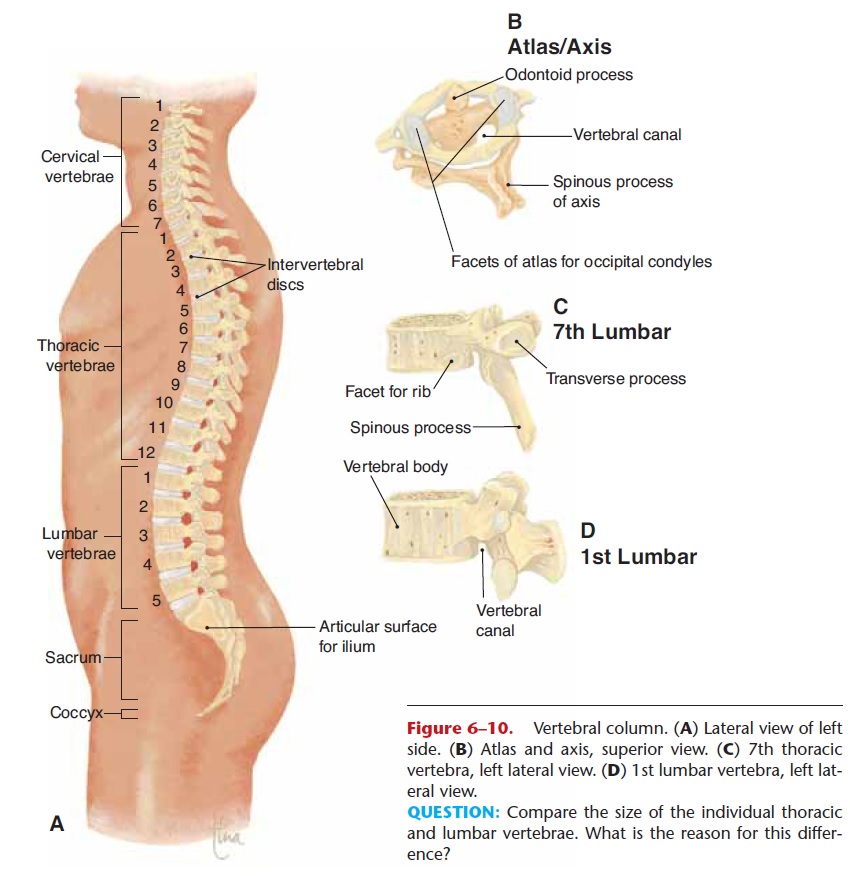
All of the ribs articulate posteriorly with the tho-racic vertebrae. The first seven pairs of ribs are called true ribs; they articulate directly with the manubrium and body of the sternum by means of costal cartilages. The next three pairs are called false ribs; their carti- lages join the 7th rib cartilage. The last two pairs are called floating ribs because they do not articulate with the sternum at all (see Fig. 6–10).
An obvious function of the rib cage is that it en-closes and protects the heart and lungs. Keep in mind, though, that the rib cage also protects organs in the upper abdominal cavity, such as the liver and spleen. The other important function of the rib cage depends upon its flexibility: The ribs are pulled upward and outward by the external intercostal muscles. This enlarges the chest cavity, which expands the lungs and contributes to inhalation.
Related Topics