Chapter: 12th Nursing : Chapter 7 : Midwifery Nursing
Reproductive Health Care and Family Planning
Reproductive Health Care and Family Planning
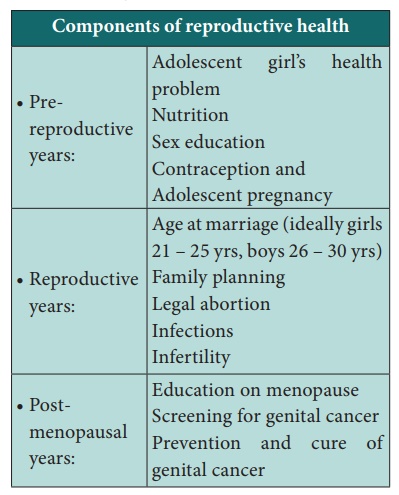
Definition Reproductive Health Care
·
Ability to reproduce and
regulate fertility
·
Safe motherhood – safe
pregnancy and child birth with resultant safe mother and infant
·
Safe sex with no fear of
pregnancy and of controlling diseases.
Definition Family Planning
Practices that help individuals or couples achieve the following:
Avoid unwanted pregnancy
·
Achieve wanted pregnancy
and child birth
· Spacing the pregnancies
·
Determine the number of
children in the family
·
Choose the age for
becoming pregnant
Contraception
Measures designed to prevent pregnancy due to coital act either
temporary or permanenty
Temporary Methods Of Contraception
I. Natural Method
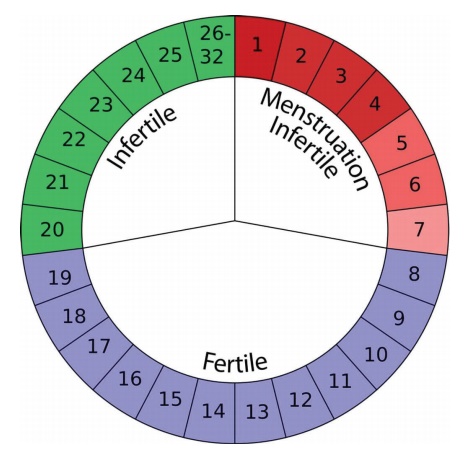
Rhythm Method:
The menstrual cycle is divided into three phases for purpose of
assessment of likelihood of conception.
Phase-1: relatively infertile phase last from onset of
menstruation until the time of preovulation.
Phase-2: fertile phase. last from seven days preovulation to 48hrs
post ovulation.
Phase-3: absolutely infertile phase lasts from 48hrs after
ovulation until the onset of menstrual, bleeding about 10 – 16 days.
Methods to determine the phase of the cycle:
Testing cervical mucus:
During phase 1 and 3, the mucus is scanty , thick and breaks
quickly when stretches. During phase 2, the mucus is more abundant thick and
clear and stretches easily.
Measuring basal body temperature:
Basal body temperature should be measured in the morning. A
sustained rise of temperature of 0.2 to 0.6 C indicates that ovulation has
occurred
Abstinence Complete abstinence
Coitus interruptus - During sex the man withdraws his penis
from the vagina before he ejaculates
Lactational Amenorrhoea Method
It suppresses ovulation and thickens cervical secretions. It is
effective in women less than 6 weeks of postpartum, who are breastfeeding.
Emergrncy Contraception
It reduces sperm transport and changes the endometrium thus unfavorable
for fertilization. It is effective for women who have had unprotected
intercourse within 72 hours and for victims of sexual assault.
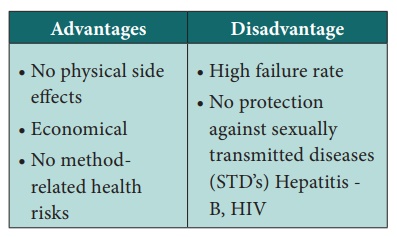
Advantages of natural methods
·
Natural method that does
not require devices or medicine in the body.
·
There are no side
effects.
·
No cost. Is morally and
culturally acceptable.
·
Better than not using
any birth control method
II. Barrier Methods
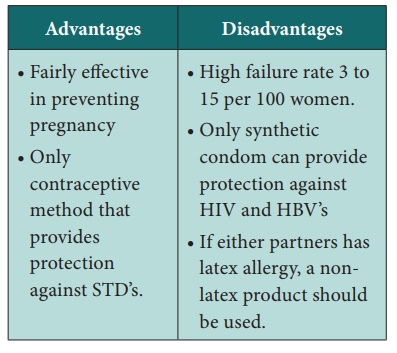
Condoms:
Types: -Latex (plain or treated with spermicide)
·
The spermicide will
immobilize or kills sperm providing added protection if breakage or leaks
occur.
Direction of use:
The condom should be applied before vaginal penetration and should
cover the entire length of the erected penis. Adequate lubrication should be
used and the condom should be removed immediately after ejaculation and
disposed properly.
Diaphragm:
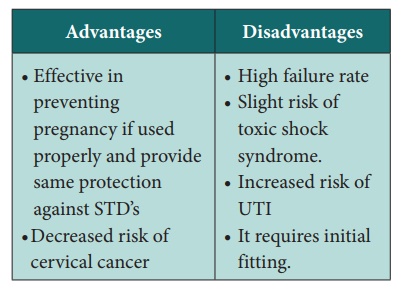
Types:
i) flat spring ii) Coil spring iii) Arching spring
The diaphragm should lie just posterior to symphysis pubis and
deep into the cul-de-sac, so that the cervix is completely covered and behind
the centre of the membrane. Spermicide should be applied before each coital
act. The diaphragm should left in place for a maximum of 8 hrs after the last
coital act.
Cervical Cap
·
It is a dome shaped cup
that fits over the cervix.
·
It cannot be left in the
cervix for more than 48 hours.
·
Only women with normal
pap smear can use.
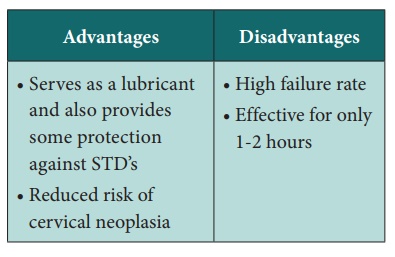
Spermicide
They are agents that cause destruction of the sperm cell membrane;
thereby affecting mobility.
·
Aerosol foams
·
Creams and Jellies
·
Vaginal suppositories
·
Films & sponges
All contain spermicidal agents usually nontoxic.
III Iucd- Intra Uterine CONTRACEPTIVE Devices
Modern Methods
They are flexible plastic device medicated with slowly released
hormones. Copper – released devices interferes with the ability of sperm to
pass through the uterine cavity.
Progestin releasing device thicken the cervical mucus and thin the
endometrial lining thus prevents conception.
Types:
Copper
·
Copper - T 380 A
·
Nova T
·
Multiload 375
Silastic
Hormone releasing
·
Progestasert
·
Levonova / Mirena
Insertion:
·
Bladder empty, lithotomy
position.
·
Posterior vaginal
speculum is introduced in vagina and cervix are cleansed by antiseptic lotion.
·
Anterior lip grasped by
Allis forceps. Uterine sound passed through the cervical canal to normal
position of uterus and length of cavity.
·
Insert the device
through the cervical Os up to the fundus and after positioning, inserter is
withdrawn keeping the plunger in position.
·
Excess of nylon thread
is to be cut.
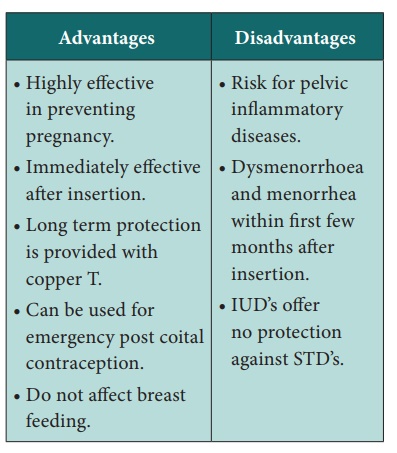
Side effects
·
Cramping
·
Abnormal menstrual
bleeding
Complications
·
Uterine and pelvic
infection
·
Expulsion
·
Uterine perforation
·
Ectopic pregnancy
IV. Hormonal Contraceptives
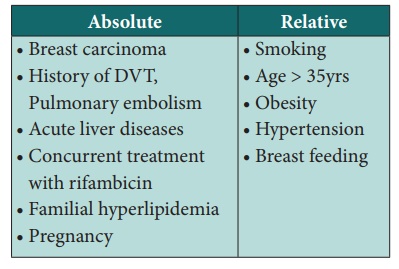
Combined oral contraceptives
They consist of synthetic oestrogen and progestin preparations,
act by suppressing lactation, thickening of cervical mucus and alteration of
endometrium.
Contraindication
Side effects
·
Amenorrhoea
·
Breast fullness or
tenderness
·
Depression, severe
vascular headache
·
Hypertension
·
Spoting or
intermenstrual bleeding
Missed pills
·
If one pill is missed,
instruct the patient to take two pills at the next scheduled time and complete
the pack as usual.
·
If two or more
consecutive pills are missed, instruct the patient to finish the package of
pills.
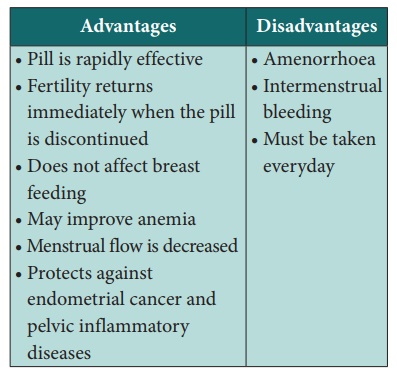
Progestron Only Pills
They cause suppression of ovulation, thickening of cervical mucus
and alteration of the endometrium.
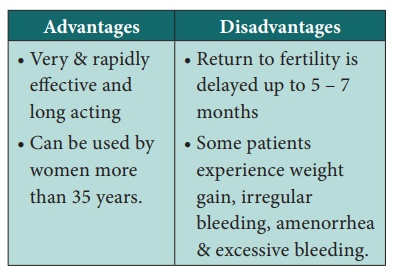
Progestron only Injectable Contraceptives
They cause suppression of ovulation, thickening of cervical mucus,
alteration of endometrium and change in tubal motility.
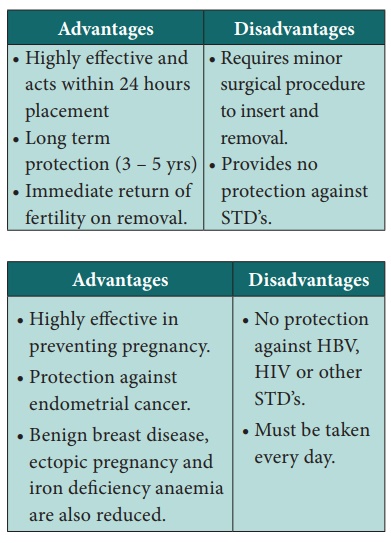
Implants (Norplant)
It consists of thin, flexible capsules filled with levonorgestrel
that are inserted under the skin of women’s arm. They cause suppression of
ovulation, thickening of cervical mucosa, alteration of the endometrium and
change in tubal motility.
Side effects
·
Mastalgia
·
Breast tenderness
·
Weight gain or loss
·
Irregular bleeding or
spotting
·
Amenorrhoea
·
tHirsutism
·
Hair loss
Permanent Method
Surgical Sterilization
It is appropriate to couples who desire permanent sterilization.
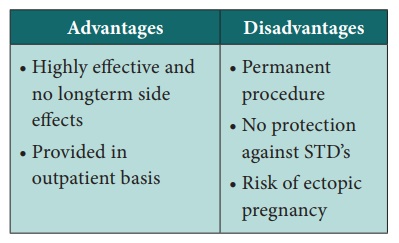
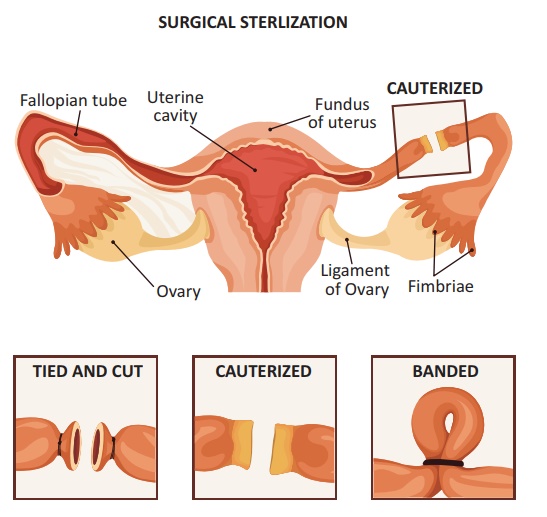
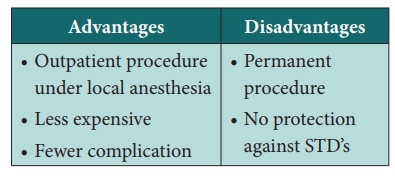
1. FEMALE: Tubal ligation OR Tubectomy
Types
·
Puerperal sterilization
·
2. Interval tubal
ligation:
·
Minilaprotomy: The
Pomeroy procedure performed using a 3 to 4 cm suprapubic incision under local
anaesthesia with sedation.
·
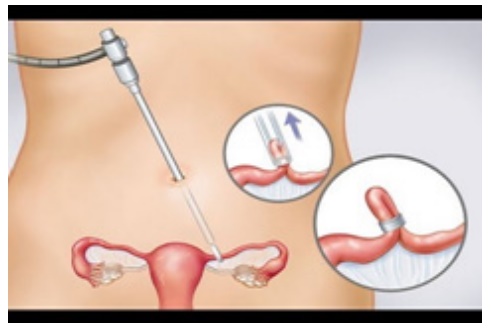
Laparoscopic: Silastic
rings are placed around loop of the tube, resulting in necrosis and occlusion.

Related Topics