Chapter: Transmission Lines and Waveguides : Transmission Line Theory
Reflection Coefficient
REFLECTION COEFFICIENT
Reflection
coefficient
The reflection coefficient is used in physics and electrical engineering when wave propagation in a medium containing discontinuities is considered. A reflection coefficient describes either the amplitude or the intensity of a reflected wave relative to an incident wave. The reflection coefficient is closely related to the transmission coefficient.
Reflection occurs because of the following
cases:
1)when the load end is open circuited
2)when the load end is short-circuited
3)when the line is not terminated in its
characteristic impedance.
When the line is either open or short
circuited, then there is not resistance at the receiving end to absorb all the
power transmitted from the source end. Hence all the power incident on the load
gets completely reflected back to the source causing reflections in the line.
When the line is terminated in its characteristic impedance, the load will
absorb some power and some will be reflected back thus producing reflections.
Reflection Coefficient can be defined as the
ratio of the reflected voltage to the incident voltage at the receiving end of
the line Reflection Coefficient K=Reflected Voltage at load /Incident voltage
at the load.
K=Vr/Vi
Telecommunications
In telecommunications, the reflection
coefficient is the ratio of the amplitude of the reflected wave to the
amplitude of the incident wave. In particular, at a discontinuity in a
transmission line, it is the complex ratio of the electric field strength of
the reflected wave (E − ) to that of the incident wave (E + ). This is
typically represented with a Γ (capital gamma) and can be written as
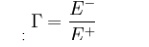
The reflection coefficient may also be
established using other field or circuit quantities.
The reflection coefficient can be given by the
equations below, where ZS is the impedance toward the source, ZL is the
impedance toward the load:
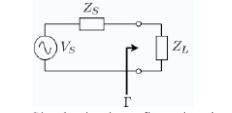
Simple circuit configuration showing
measurement location of reflection coefficient.
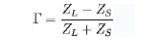
Notice that a negative reflection coefficient
means that the reflected wave receives a 180°, or π, phase shift.
The absolute magnitude
(designated by vertical bars) of the reflection coefficient can be calculated
from the standing wave ratio,
SWR:
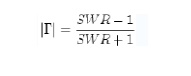
Related Topics