Rocks and Soils | Chapter 1 | Geography | 8th Social Science - Questions with Answers | 8th Social Science : Geography : Chapter 1 : Rocks and Soils
Chapter: 8th Social Science : Geography : Chapter 1 : Rocks and Soils
Questions with Answers
Evaluation
I. Choose the correct
answer
1. Which of the following is known as sphere
of rocks
a. Atmosphere
b. Biosphere
c. Lithosphere
d. Hydrosphere
[Answer:
(c) Lithosphere]
2. World soil day is observed on
a. 15th August
b. 12th January
c. 15th October
d. 5th December
[Answer:
(d) 5th December]
3. Fossils are found in
a. Sedimentary rocks
b. Igneous rocks
c. Metamorphic rocks
d. Plutonic rocks
[Answer:
(a) Sedimentary rocks]
4. The top layer of soil is called as
a. organic layer or humas
b. topsoil
c. subsoil
d. bedrock
[Answer:
(b) topsoil]
5. Ideal soil for growing cotton is
a. Red soil
b. Black soil
c. Alluvial soil
d. Mountain soil
[Answer:
(b) Black soil]
6. The major components of soil is
a. Rocks
b. Minerals
c. Water
d. All the above
[Answer:
(b) Minerals]
7. Which one of the following is the most widespread most
and productive category of soil
a. Alluvial soil
b.Black soil
c. Red soil
d. Mountain soil
[Answer:
(a) Alluvial soil]
II Fill in the blanks
1. Scientific study of rocks is
called Petrology.
2. Red
soil is highly suitable for millets cultivation.
3. The “skin of earth” is Soil.
4. White Marble is the kind of metamorphic rock using which Taj Mahal was
built.
5. Igneous rock is known as the primary rocks.
III State whether the
following statements are true or false
1.
Igneous rocks are called primary
rocks.
[Answer: True]
2. Slate is formed from shale. [Answer: True]
3. Red soil is formed by the process
of leaching. [Answer: False]
Correct
statement: Laterites
soils is formed by the process of leaching.
4. M-sand is used as alternative for
natural sand in construction. [Answer: True]
5. Volcanic mountains are covered
with sedimentary rocks. [Answer: False]
Correct
statement: Sedimentary rocks are formed from
broken pieces of rocks.
IV Match the following
1)
a. Granite 1. Bed rock
b. Soil layer 2. Plutonic rock
c. Barren island 3. Strip farming
d. Soil conservation 4. Active
Volcano
A B C D
2 1 4 3
2 1 3 4
4 3 2 1
3 4 2 1
[Answer:
a) A - 2, B - 1, C - 4, D - 3.]
2)
a. Basalt 1. Anthracite
b. Limestone 2. Extrusive igneous
c. Coal 3. Metamorphic rock
d. Gneiss 4. Sedimentary rock
A B C D
2 4 3 1
2 4 1 3
3 1 2 4
3 1 4 2
[Answer:
b) A-2, B - 4, C - 1, D -3.]
V Choose the incorrect
statement from the following
1. a. Igneous rocks are called the
primary rocks.
b .Soil is the product of weathering
of rocks.
c. Sedimentary rocks are the hardest
ones.
d. Deccan plateau is the region of
Igneous rocks.
[Answer:
(c) Sedimentary rocks are the hardest ones.]
2. a. Soil erosion decreases its
fertility.
b. Dynamic metamorphism is caused by
high temperature.
c. Soil is a renewable source.
d. Humus is a part of the top layer
of soil.
[Answer:
(b) Dynamic metamorphism is caused by high temperature.]
VI Consider the
following statements and choose the right option from the given ones
1) Statement (1): Sedimentary rocks consist of many layers.
Statement (2): Sedimentary rocks are formed by the sediments deposited
at different points of time.
a. 1 and 2 are correct and 2
explains 1
b. 1 and 2 are correct but, 2 does
not explain 1
c. 1 is correct but, 2 is incorrect
d. 2 is correct but, 1 is incorrect.
[Answer:
(a) 1 and 2 are correct and 2 explains 1]
VII Give reasons
1. Chemical sedimentary rocks are found in the beds of
reservoirs.
Answer: Chemical Sedimentary rocks are formed by precipitating of
minerals from water. It is formed usually through evaporation of chemical rich
solutions.
2. Igneous rocks are found in the regions of volcanoes.
Answer: The igneous rocks are formed by the solidification of molten
magma.
VIII Distinguish
between
1. Metamorphic rock and sedimentary rock.
Answer:
Metamorphic Rocks / Sedimentary Rock
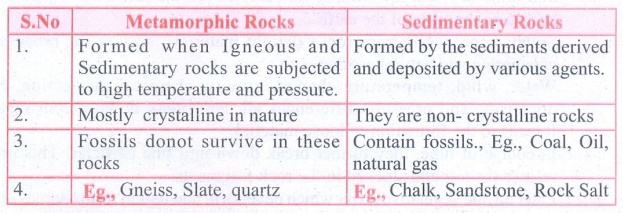
Metamorphic
Rocks
1. Formed when Igneous and Sedimentary rocks are subjected to
high temperature and pressure.
2. Mostly crystalline in nature
3. Fossils donot survive in these rocks
4. Eg., Gneiss, Slate, quartz
Sedimentary
Rock
1. Formed by the sediments derived and deposited by various
agents.
2. They are non- crystalline rocks
3. Contain fossils., Eg., Coal, Oil, natural gas
4. Eg Chalk, Sandstone, Rock Salt
2. Soil conservation and Soil erosion.
Answer:

Soil
conservation
1. The process of protecting the soil from erosion to maintain
its fertility.
2. Methods of soil conservation are afforestation, controlled
grazing, construction of dams, crop rotation etc.,
Soil
erosion
1. Removal or destruction of the top layer of soil by natural
forces and human activities.
2. Running water and wind are the major agents of Soil erosion.
Rill erosion and Gully erosion are the major types of soil erosion.
IX Answer briefly
1. How are igneous rocks formed?
Answer: The igneous rocks are formed by the solidification of molten
magma.
2. Describe about the composition of soil.
Answer: The basic components of soil are mineral, organic matter, water
and air. It consists of about 45% mineral, 5% organic matter, 25% of water and
25% air. It is only a generalized fact. The composition of soil varies from
place to place and time to time.
3. Define ‘rock’.
Answer:
(i) The rocks are the solid mineral, materials forming a part of
the surface of the earth and other similar planets.
(ii) A rock is an aggregate of one or more minerals. Rock is an
important natural resource and is found in solid state.
(iii) It may be hard or soft in nature.
4. State the types of soils.
Answer: Alluvial soil, Black soil, Red soil, Laterite soil, Mountain
soil, Desert soil.
5. What is soil conservation?
Answer: Soil conservation is the process of protecting the soil from
erosion to maintain its fertility.
X Answer in a
Paragraph
1. Explain the process of soil formation.
Answer:
(i) Soil is a mixture of organic matter, minerals, gases,
liquids and organisms that together support life.
(ii) Soil minerals form the basis of soil. It forms on the
surface of the earth. It is known as the ‘skin of the earth’.
(iii) Soils are produced from rocks (parent material) through
the processes of weathering and natural erosion.
(iv) Water, wind, temperature change, gravity, chemical
interaction, living organisms and pressure differences all help break down parent
material. It leads to the formation of loose material.
(v) In course of time, they further break down into fine
particles. This process release the minerals locked in the rock fragments.
(vi) Later on, the vegetative cover which develop in that region
forms humus content in the soil. This way the soil gets matured gradually.
2. Classify and explain the rocks.
Answer:
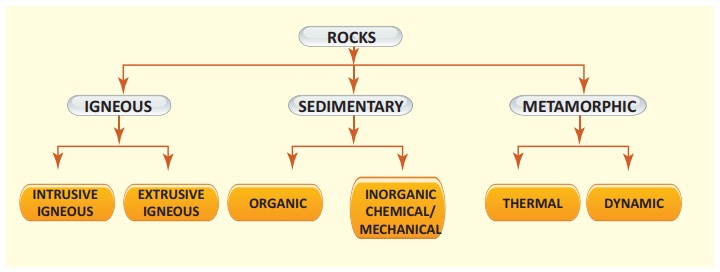
Igneous:
(i) The igneous rocks are formed by the solidification of molten
magma. Also called Primary or Parent Rocks.
(ii) Types: (1)
Extrusive Igneous Rocks, (2) Intrusive Igneous Rocks
(1)
Extrusive Igneous Rocks: Molten magma which
comes out from the interior of the earth’s surface, gets solidified and forms
such rocks. Fine grained and glassy in nature. Eg., Basalt, found in north
western peninsular India.
(2)
Intrusive Igneous rock: Molten magma cools
down deep inside the earth’s crust, becomes solid and forms such rocks. Form
large grains. Deep seated rocks are plutonic rock and ones at shallow depths -
Hypabysal rocks. Eg., Granite, Diorite.
Sedimentary:
(i) Formed by the sediments derived and deposited by various
agents. Also called stratified rocks. ?
(ii)
Types: (1) Organic sedimentary rocks, (2)
Mechanical sedimentary rocks, (3) Chemical sedimentary rocks
(1)
Organic sedimentary rocks: Formed due to
decomposition of dead Plants and Animals. Contains fossils. Eg., Chalk, Talc
(2)
Mechanical sedimentary rock: Formed
from the disintegration of Igneous and metamorphic rocks. Get deposited due to erosion
by natural agents. Get cemented after a long time to form rocks. Eg.,
Sandstone, Shale.
(3)
Chemical sedimentary rock: Formed by
precipitating of minerals from water. Formed due to evaporation of chemical
rich solution. Eg., Rock Salt.
Metamorphic:
(i) Formed when Igneous and sedimentary rocks are subjected to
high temperature and pressure.
(ii)
Types: (1) Thermal, (2) Dynamic
(1)
Thermal Metamorphic: If the change in rocks is
caused by high temperature.
(2)
Dynamic Metamorphic: If the change in rock is
caused by high pressure. Formed from Igneous rocks. Eg., Granite into gneiss
Formed from Sedimentary rocks. Eg., Shale into Slate
3. Give an account on different layers of soil.
Answer:
LAYERS OF SOIL
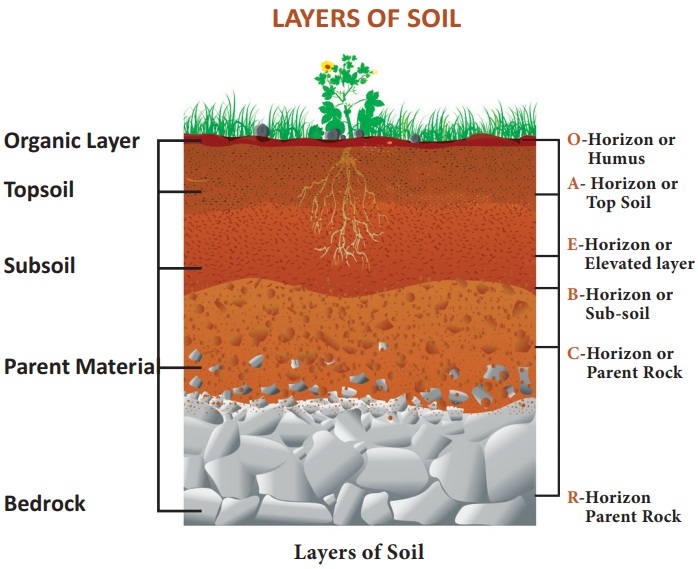
Layers of
soil
O-Horizon
or Humus - This layer is dominated by organic
material (leaves, needles, twigs, moss and lichens).
A-
Horizon or Top Soil - It is a part of top soil,
composed of organic matter mixed with mineral matter.
E-
Horizon or Elevated layer - E-Stands for
elevated layer. This layer is significantly leached of clay, iron, and aluminum
oxides, which leaves a concentration of ore
B-
Horizon or Sub-soil - This layer reflects
the chemical, or physical alteration of parent material. Thus iron, clay,
aluminum and organic compounds are found accumulated in this horizon.
C-
Horizon or Parent Rock - Partially weathered
parent material accumulates in this layer.
R-
Horizon Parent Rock- This layer consists of
unweathered part of bed rock.
4. Classify and explain the soil.
Answer:
Definition: Soil is a mixture of Organic matter, minerals, gases, liquids
and organisms that together support life.
Classification
of soils: Soils are classified on the basis of
their formation, colour, physical and chemical properties. Based on these, soil
is classified into six major types. They are: Alluvial soil, Black soil, Red
soil, Laterite soil, Mountain soil, Desert soil
Alluvial
soil:
(i) Found in the regions of river valleys, flood plains and
coastal regions.
(ii) Formed by the deposition of silt by the running water.
(iii) Most productive of all soils.
(iv) Suitable for the culitivation of sugarcane, jute, rice,
wheat.
Black
soils:
(i) Formed by weathering of igneous rocks.
(ii) Clayey in nature.
(iii) Retains moisture. .
(iv) Ideal for growing cotton.
Red
Soils:
(i) Formed by weathering of metamorphic rocks and crystalline
rocks.
(ii) Found in semi-arid regions.
(iii) Not a fertile.
(iv) Is soil brown red in colour due to the presence of iron
oxide
(v) Suitable for millet cultivation.
Laterite
soils:
(i) Formed by the process of leaching.
(ii) Found in trophical regions, which experienced alternate wet
and dry condition.
(iii) Infertile soil.
(iv) Suitable for plantation of tea and coffee.
Mountain
soils:
(i) Found in slopes of mountains.
(ii) Thin and acidic in nature.
(iii) Nature of soil differs based on the altitude.
Desert
soils:
(i) Found in hot desert region.
(ii) Porous and saline in nature.
(iii) Infertile in nature.
(iv) Agriculture not successful.
XI Activities
1. Complete the following table with
the help of internet source

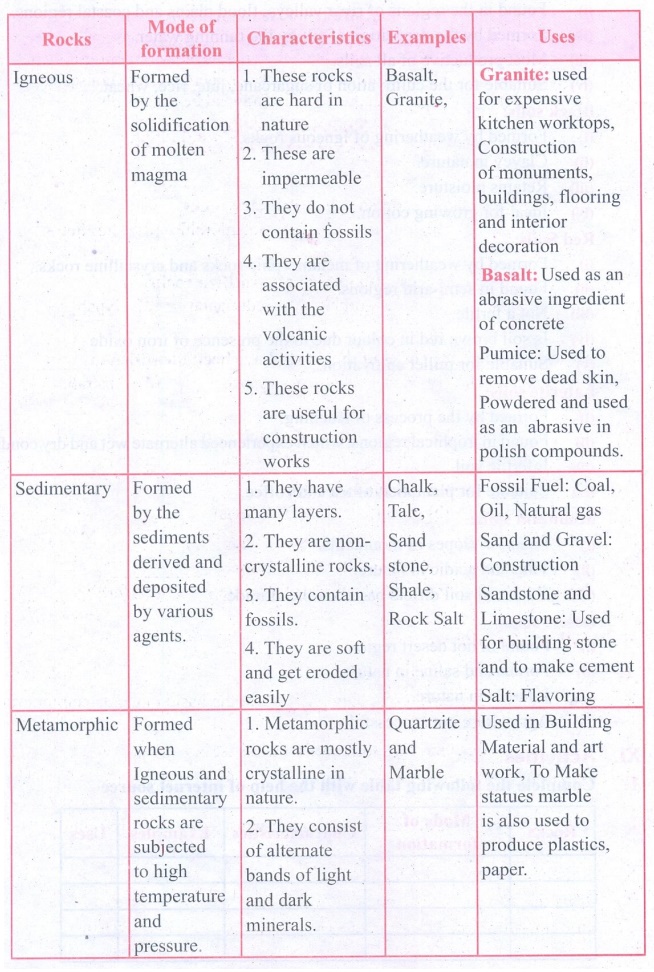
2. Exhibition: Collect the soil samples of different types and display
them with their names in the classroom .
3. Group Discussion: Natural sand is replaced by M-sand in
construction.
1. Status -
2. Advantages -
3. Disadvantages -
Related Topics