Rocks and Soils | Chapter 1 | Geography | 8th Social Science - Classification of Rocks | 8th Social Science : Geography : Chapter 1 : Rocks and Soils
Chapter: 8th Social Science : Geography : Chapter 1 : Rocks and Soils
Classification of Rocks
Rocks
The rocks are the solid mineral
materials forming a part of the surface of the earth and other similar planets.
The earth’s crust (Lithosphere) is composed of rocks. A rock is an aggregate of
one or more minerals. Rock is an important natural resource and is found in
solid state. It may be hard or soft in nature. An estimation reveals that there
are 2,000 different types of minerals found on the earth surface out of which
only 8 basic minerals commonly found all over the earth. Minerals are chemical
substances which exist in nature. They may occur either in the form of elements
or compounds.
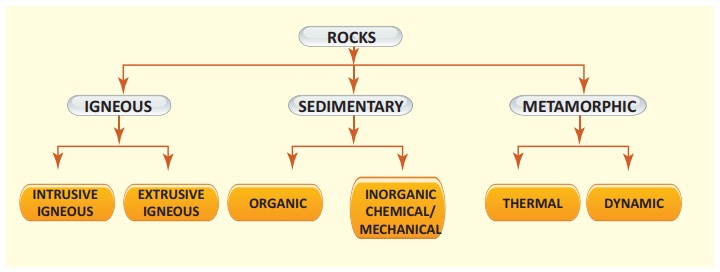
Classification of Rocks
According to the mode of formation
the rocks are classified into three types as follows.
1. Igneous Rocks
2. Sedimentary Rocks and
3. Metamorphic Rocks
1. Igneous Rocks
The igneous rocks are formed by the
solidification of molten magma. These rocks are also called as the ‘Primary
Rocks’ or ‘Parent Rocks’ as all other rocks are formed from these rocks.

The word Igneous is derived from the Latin word
‘Ignis’ means ‘fire’
Characteristics of Igneous Rocks
1. These rocks are hard in nature
2. These are impermeable
3. They do not contain fossils
4. They are associated with the
volcanic activities
5. These rocks are useful for
construction works
Types of Igneous Rocks
Igneous Rocks are of two types. They
are:
1.
Extrusive Igneous Rocks
2. Intrusive Igneous Rocks
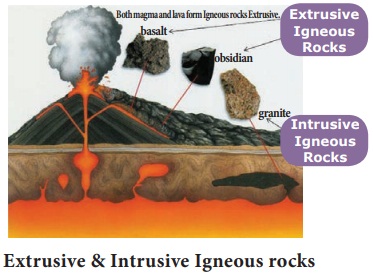
1. Extrusive Igneous Rocks
Can you visualize the lava comes out
from a volcano? Lava is actually a fiery red molten magma comes out from the
interior of the earth on its surface. After reaching the earth surface the
molten materials get solidified and form rocks. Rocks formed in such a way on
the crust are called Extrusive igneous rocks. These rocks are fine grained and
glassy in nature due to rapid solidification. Basalt found in the north western
part of peninsular India is the example for this type of rock.
2. Intrusive Igneous Rocks
The molten magma sometimes cools down
deep inside the earth’s crust and becomes solid. The rocks formed this way is
called ‘Intrusive Igneous Rocks’. Since the cool down
slowly and form crystals. Hence they
are called 'crystalline rocks'. Intrusive Igneous rocks are two types. They
are, 1. Plutonic rocks 2. Hypabysal rocks. The deep seated rocks are called
'Plutonic rocks' and the ones formed at shallow depths are called 'Hypabysal
rocks'. Granite, Diorite and Gabbro are the example of plutonic rocks and
dolerite is an example of hypabysal rocks.
Some major Active Volcanoes: Mount Vesuvius, Mt.
Stromboli and Mt. Etna in Italy and Mauna Loa and Mauna Kea in Hawaii Islands.
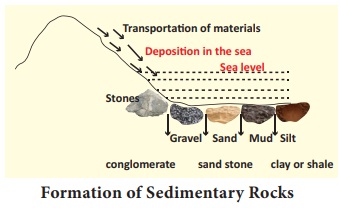
2. Sedimentary Rocks
The word ‘S e dimentar y ’ has been derived from Latin word ‘Sedimentum’ means settling down . The
sedimentary rocks are formed by the sediments derived and deposited by various
agents. Due to high temperature and pressure, the undisturbed sediments of long
period cemented to form sedimentary rocks. Sedimentary rocks consist of many
layers which were formed by the sediments deposited at different periods. As it
consists of many strata, it is also known as ‘Stratified rocks’.

Sedimentary rocks are
the important source of natural resources like coal, oil and natural gas.
Characteristics of Sedimentary rocks
1.
They have many layers.
2.
They are non-crystalline rocks.
3.
They contain fossils.
4. They are soft and get eroded
easily
Oldest sedimentary
rocks of the world has been identified in Greenland and estimated as 3.9
billion years old.
Types of Sedimentary Rocks
1. Organic Sedimentary Rocks
These rocks are formed as a result
of the decomposition of dead plants and animals. It contains fossils. Chalk,
Talc, Dolomite and Limestone rocks are of this category.
2. Mechanical Sedimentary Rocks
These rocks are formed due to the
disintegration of igneous and metamorphic rocks. The natural agents erode and
transport these rocks and deposit them at some places. After a long period of
time, they cemented to form rocks. Sandstone, Shale and Clay are the examples
of rocks of this type.
3. Chemical Sedimentary rocks
These are formed by precipitating of
minerals from water. It is formed usually through evaporation of chemical rich
solutions. These rocks are also called as evaporates. Gypsum is an example of
this kind.
3. Metamorphic Rocks
The word Metamorphic is derived from
two Greek words “Meta” and “Morpha”, Meta means change and Morpha means shape.
When Igneous and sedimentary rocks subject to high temperature and pressure,
the original rocks get altered to form a new kind of rock called metamorphic
rocks. Metamorphism is of two types. They are
1.
Thermal Metamorphism
2.
Dynamic Metamorphism
If the change in the rocks is mainly
caused by high temperature, the process is called as 'Thermal Metamorphism'.
If the change in the rock is mainly
caused by high pressure, the process is called as 'Dynamic Metamorphism'.
One of the world
wonders Taj Mahal in India was built with White Marbles a metamorphic rock.

Formation of Metamorphic Rocks from Igneous
rocks
1.
Granite into gneiss caused by dynamic metamorphism.
2. Basalt into slate caused by
thermal metamorphism.
Formation of Metamorphic Rocks from
Sedimentary rocks
1.
Sandstone into quartz caused by thermal metamorphism.
2.
Shale into slate caused by thermal metamorphism.
Characteristics of
Metamorphic Rocks
1.
Metamorphic rocks are mostly crystalline in nature.
2. They consist of alternate bands
of light and dark minerals.
Related Topics