Rocks and Soils | Chapter 1 | Geography | 8th Social Science - Soil and its Formation | 8th Social Science : Geography : Chapter 1 : Rocks and Soils
Chapter: 8th Social Science : Geography : Chapter 1 : Rocks and Soils
Soil and its Formation
Soil and its Formation
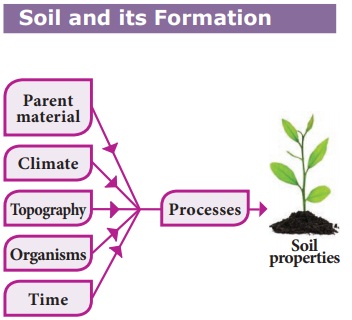
Soil is a mixture of organic matter,
minerals, gases, liquids and organisms that together support life. Soil minerals form the basis of soil.
It forms on the surface of the earth. It is known as the ‘skin of the earth’. Soils are formed from rocks (parent material)
through the processes of weathering
and natural erosion. Water, wind, temperature change, gravity, chemical
interaction, living organisms and pressure differences all help break down
parent material. It leads to the formation of loose material. In course of
time, they further break down into fine particles. This process release the
minerals locked in the rock fragments. Later on, the vegetative cover which
develop in that region forms humus content in the soil. This way the soil gets
matured gradually.
World Soil Day is
observed on 5th December, every year
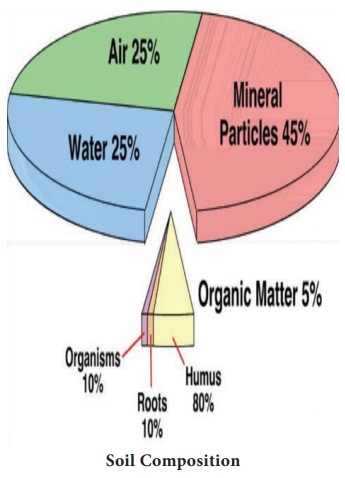
Soil Composition
The basic components of soil are
mineral, organic matter, water and air. It consists of about 45% mineral, 5%
organic matter, 25% of water and 25% air. It is only a generalized fact. The
composition of soil varies from place to place and time to time.
Soil profile
The soil profile is defined as the
vertical section of the soil from the ground surface and extends downwards.
ACTIVITY :
Collect sample of
soils from your place and exhibit in the class room.
Classification of soils
Soils are classified on the basis of
their formation, colour, physical and chemical properties. Based on these, soil
is classified into six major types. They are: Alluvial soil, Black soil, Red soil,
Laterite soil, Mountain soil, Desert soil
Alluvial soils
These soils are found in the regions
of river valleys, flood plains and coastal regions. These are formed by the
deposition of silt by the running water. It is the most productive of all
soils. It is suitable for the culitivation of sugarcane, jute, rice, wheat and
other food crops.
Black soils
These soils are formed by weathering
of igneous rocks. Black soil is clayey in nature. It is retensive of moisture.
It is ideal for growing cotton.
Red Soils
These soils are formed by weathering
of metamorphic rocks and crystalline rocks. The presence of iron oxide makes
this soil brown to red in colour. It is usually found in semi-arid regions. It
is not a fertile soil. It is suitable for millet cultivation.
Laterite soils
These are the typical soils of
tropical regions. These soils are found in the regions which experienced
alternate wet and dry condition. As these soils are formed by the process of
leaching, it is in fertile. It is suitable for plantation crops like tea and
coffee.
Mountain soils
These soils are found over the
slopes of mountain. Soils in these regions are thin and acidic. However
characteristic of soil differs from region to region based on the altitude.
Desert soils
These are sandy soil found in the
hot desert regions. These soils are porous and saline. Since it is infertile
agriculture in these soils are not so successful.
Soil Erosion
Soil erosion is the removal or
destruction of the top layer of soil by natural forces and human activities.
Soil erosion reduces the fertility of soil which in turn reduces the
agricultural productivity. Running water and wind are the major agents of soil erosion.
Sheet erosion, Rill erosion and Gully erosion are the major types of soil
erosion.
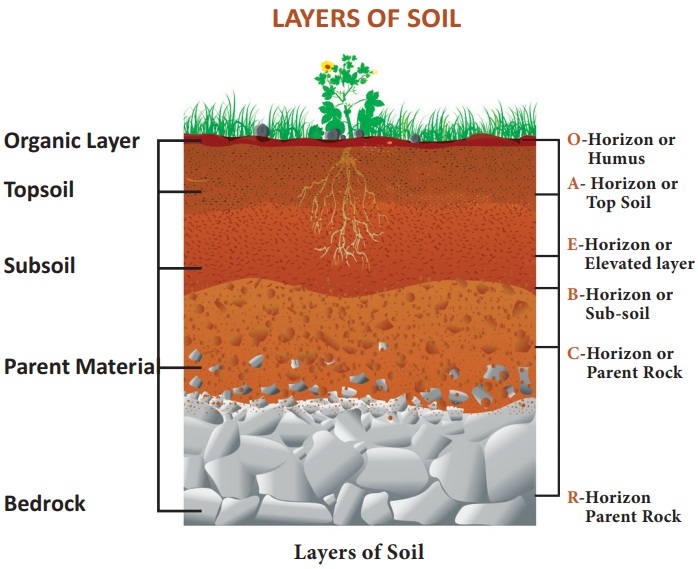
Layers of soil
O-Horizon or Humus: This layer is
dominated by organic material (leaves, needles, twigs, moss and lichens).
A-Horizon or Top Soil: It is a part of top
soil, composed of organic matter mixed wit mineral matter.
E- Horizon or Elevated layer: E-Stands for elevated
layer. This layer is significantly leached of clay, iron, and aluminum oxides,
which leaves a concentration of ore
B-Horizon or Sub-soil: This layer reflects
the chemical or physical alteration of parent material. Thus iron, clay,
aluminum and organic compounds are found accumulated in this horizon.
C-Horizon or Parent Rock: Partially weathered
parent material accumulates in this layer.
R- Horizon Parent Rock: This layer consists
of unweathered part of bed rock.
Soil conservation
Soil conservation is the process of
protecting the soil from erosion to maintain its fertility. The methods that
are widely practiced for conserving soil are afforestation, controlled grazing,
construction of dams, Crop rotation, Strip farming, contour ploughing, terrace
farming, checking shifting cultivation, wind break etc.,
How long does it take to form soil?
The time needed to
form a soil depends on the Climate. The environments which is characterized by
mild climate, takes 200-400 years to form one cm of soil and in wet tropical
area, soil formation is faster and takes upto 200 years. To become a well
matured soil, it takes about 3000 years.
Uses of soils
* Soil is one of the important
natural resource. It is a basic requirement for plant growth and supports
various life forms on the earth.
* The minerals present in the soil
enhance and nourishes the crops and plants.
* It is used in making of ceramics
or pottery.
* It is a source of material for
construction and handicraft works.
* It acts as natural filter of water
and purifies it.
* Soil supports ecosystem and play an
important role in land management.
Rocks and soils are the important renewable natural resources. Both of them play an important role in everyday life of human beings as well as economic development. Nowadays rock-based companies are in increase which provide employment to a sizeable population. Soils attract human settlement and other economic activities. As India is an agricultural country, the proper management of soil resource will lead to sustainable food production besides its use for various other purposes. So, the soil resources must be conserved.
Related Topics