The Living World of Plants | Term 1 Unit 4 | 6th Science - Questions Answers | 6th Science : Term 1 Unit 4 : The Living World of Plants
Chapter: 6th Science : Term 1 Unit 4 : The Living World of Plants
Questions Answers
Evaluation
I. Multiple Choice Questions
1. Pond is an example of
a) Marine Habitat
b) Freshwater habitat
c) Deserts d) Mountain
Answer: (b) Freshwater Habitat
2. The important function of stomata is
a) Conduction
b) Transpiration
c) Photosynthesis
d) Absorption
Answer: (b) Transpiration
3. Organs of absorption
a) Root
b) Stem
c) Leaf
d) Flower
Answer: (a) Root
4. The habitat of water hyacinth
a) Aquatic
b) Terrestrial
c) Desert
d) Mountain
Answer: (a) Aquatic
II. True or False – If False give the
correct answer
1. Plants can live without water.
Plants cannot live without water.
2. All plants have chlorophyll.
Non green plants have not chlorophyll.
3. Plants have three parts: the root,
the stem and leaves.
4. Mountain is an example for
freshwater habitat.
5. Root is modified into spines.
Leaves is modified into spines.
6. Green plants need sunlight.
III. Fill in the Blanks
1. Earth's
surface is covered by 70 % of water.
2. The driest places on earth are desert .
3. Fixation and absorption are the main
functions of root.
4. Primary organs of photosynthesis are sunlight.
5. Tap root system present in dicot plants.
IV. Match the following
1. Mountain - Monocot
2. Desert - Branches
3. Stem - Dry place
4. Photosynthesis - Himalayas
5. Fibrous Root – Leaves
Answer:
1. Mountain - Himalayas
2. Desert - Dry place
3. Stem - Leaves
4. Photosynthesis - Branches
5. Fibrous Root - Monocot
V. Arrange in correct sequence
1. Leaf – Stem – Root – Flower
Root - Stem - Leaf - Flower
2. Transpiration – Conduction -
Absorption – Fixation
Fixation - Absorption
- Conduction - Transpiration.
VI. Very short answer
1. Classify the plants on the basis of their habitat.
Based on their habitat the plants
are classified into two namely Terrestial
plants
2. Identify the desert plants from the following - Cactus,
Hydrilla, Mango and Rose.
Cactus
3. Define the term habitat.
The surroundings where organisms live is called a habitat.
4. Relate the terms leaves and photosynthesis.
The green leaves Prepare food by the process of photosynthesis.
VII. Short Answer
1. Why do you call jasmine plants, a twiner ?
Some plants have weak stems. They cannot stand straight on their
own. They must climb on any support to survive. So jasmine plants are called as
twiner.
2. Compare the tap root and fibrous root systems.

Tap root systems
• It consists of a single longroot, called taproot or main root.
• Taproot grows straight down deep into the ground.
• They are seen in dicotyledonous plants.
• Example: Bean, Mango, Neem
Fibrous root systems
• Fibrous root not have a main root.
• All roots are similar.
• Not deep into ground.
• It is generally seen in monocotyledonous plants.
• Example: Grass, Paddy, Maize.
3. Distinguish between terrestrial and aquatic habitats.

Terrestrial habitats
• Terrestrial habitats are the ones that are found on land like forest,
grassland and desert.
• It includes man-made habitats like farms, towns and cities.
• Example : Rubber tree, teak tree and Neem tree.
Aquatic habitats
• Aquatic habitat are the ones that are found on water and surrounding
areas that are occasionally covered by water.
• It includes man-made habitats like aquarium
• Example: Lotus, Marine Algae, Sea grasses
4. List out the plants present in your school garden.
Zinnia, Rose, Marigold, Daisy, Blue bells,
VIII. Answer in detail
1. Make a list of the functions of
root and stem.
Functions of the root:
• Root fix the plants to the soil.
• Roots absorb water and minerals from the soil.
• Stores food as in the case of potato.
Functions of the stem
• The stem, supports the branches, leaves, flowers and fruits.
• Transports water and minerals from roots to upper aerial plant
parts.
• Transports the prepared food from leaves to other parts through
stem.
• Stores food as in the case of sugarcane.
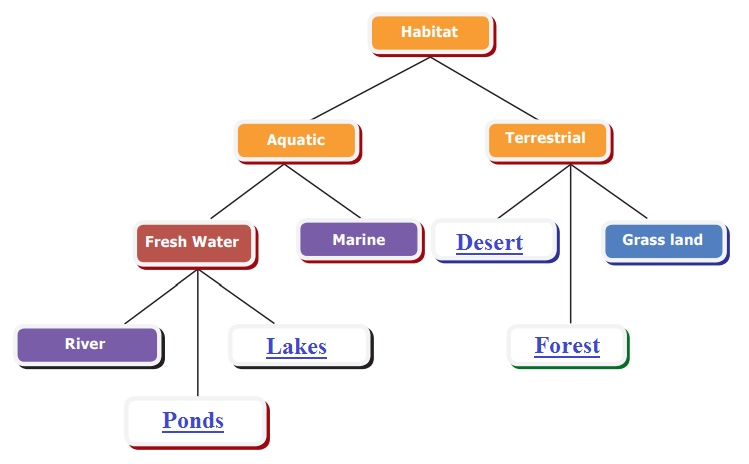
2. Study the given concept map. Connect them correcting by drawing
arrow marks. Complete the map by filling in the blanks.
Related Topics