The Living World of Plants | Term 1 Unit 4 | 6th Science - Plant forms and functions | 6th Science : Term 1 Unit 4 : The Living World of Plants
Chapter: 6th Science : Term 1 Unit 4 : The Living World of Plants
Plant forms and functions
Plant forms and functions:
Our body is made up
of many organs. Similarly the plant body is also made up of several organs such
as root, stem leaves and flowers. Plants are of many forms
and many colours, yet they are alike in some manner. That is, they all have
stems and leaves above the ground which we can see easily and roots below the
ground.
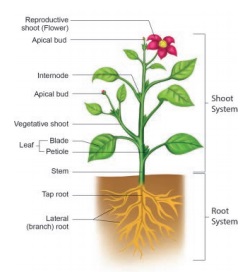
As shown in the
picture, a flowering plant consists of two main parts. They are,
1. Root system.
2. Shoot system
Let us learn about
these in detail.
1. Root system
Root
The underground
part of the main axis of a plant is known as root. It lies below the
surface of the soil. Root has no nodes and internodes. It has a root cap at the
tip. A tuft of root hairs is found just above the root tip. Roots are
positively geotropic in nature. Plants root system is classified into two
types.
1. Tap root system
2. Fibrous root system
1. Tap root system
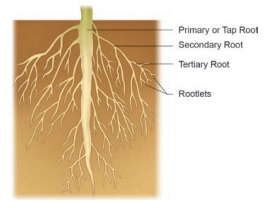
It consists of a
single root, called taproot, which grows straight down into the ground.
Smaller roots, called lateral roots arise from the taproot. They are seen in
dicotyledonous plants.
Example: Bean, Mango, Neem.
2. Fibrous root system
It consists of a
cluster of roots arising from the base of the stem. They are thin and uniform
in size.
It is generally
seen in monocotyledonous plants. Example: Grass, Paddy, Maize.

Functions of the Root
* Fixes the plant
to the soil.
* Absorbs water and minerals from the soil.
* Stores food in some plants like
Carrot and beet root.
Think it

Is it a Root or stem?
Answer: It is stem.
Activity
1
Water
absorption by Root
Aim:-
To observe absorption of water
by root
What
you need? A carrot, a glass
of water and blue ink.
What
to do? Place a carrot in
a glass of water with a few drops of blue ink. Leave the carrot in water
for two to three days. Then cut the carrot into half length wise and observe.
What
do you learn? Blue
colour appears in carrot which indicates water moves up wards in the
carrot showing that root conducts water.
2. Shoot system
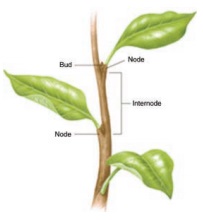
Stem
The aerial part of
the plant body above the ground is known as the shoot system. Main axis
of the shoot system is called the stem. The shoot system consists of
stem, leaves, flowers and fruits. Stem grows above the soil, and it grows towards
the sunlight. It has nodes and internodes. Nodes are the parts of stem,
where leaf arises. The part of the stem between two successive nodes is called
internode. The bud at the tip of the stem is known as apical or terminal bud,
and the buds at the axils of the leaves are called auxiliary buds.
Activity
2
Conduction
of water
Aim:-To observe conduction of water
by stem.
What
you need? A small twig of
balsam plant, a glass of water and a few drops of red ink
What
to do? Place the small
twig in the water with red ink.
What
do you see? The
stem be-comes reddish.
What
do you learn? This
is because red coloured water is being taken by the stem upwards.
Functions of the stem
The stem,
* supports the branches, leaves, flowers and fruits.
* transports water and minerals from roots to upper aerial plant parts.
* transports the prepared food from leaves to other parts through stem.
* stores food as in the case of
sugarcane.
Structure of a leaf
The leaf is a
green, flat expanded structure borne on the stem at the node.
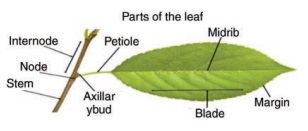
A leaf has a stalk
called petiole. The flat portion of the leaf is called leaf lamina or
leaf blade. On the lamina, there is a main vein called midrib. Other
veins are branchout from mid rib. The portion of the leaf connected in the
nodal region of the stem is known as the leaf base. Leaves of some
plants possess a pair of lateral outgrowth on the base, on either side of
auxiliary bud. These are called stipules.
The green colour of
the leaf is due to the presence of green coloured pigment called chlorophyll.
On the lower side of the leaf there are tiny pores or openings known as stomata.
Functions of the leaf
The green leaves
* Prepare food by the process of
photosynthesis.
* Helps in respiration.
* Carry out transpiration.
Victoria amazonica, the leaves of
this plant grow up to 3 metres across. A mature Victoria leaf can support an
evenly distributed Load of 45 Kilograms or apparently young person.

Related Topics