Problem Solving and Python Programming - Python Control Flow, Functions: short important questions and answers | Problem Solving and Python Programming : Control Flow, Functions
Chapter: Problem Solving and Python Programming : Control Flow, Functions
Python Control Flow, Functions: short important questions and answers
CONTROL FLOW, FUNCTIONS
1. Define Boolean expression with example.
A boolean
expression is an expression that is either true or false. The values true and
false are called Boolean values.
Eg :
>>>5
== 6
False
True and
False are special values that belongs to the type bool; they are not strings:
2. What are the different types of operators?
·
Arithmetic Operator (+, -, *, /, %, **, // )
·
Relational operator
( == , !=, < >, < , >
, <=, >=)
·
Assignment Operator ( =, += , *= , - =, /=, %= ,**=
)
·
Logical Operator (AND, OR, NOT)
·
Membership Operator (in, not in)
·
Bitwise Operator (& (and), | (or) , ^ (binary
Xor), ~(binary 1’s complement , << (binary left shift), >> (binary
right shift))
·
Identity(is, is not)
3. Explain modulus operator with example.
The
modulus operator works on integers and yields the remainder when the first
operand is divided by the second. In Python, the modulus operator is a percent
sign (%). The syntax is the same as for other operators:
Eg:
>>>
remainder = 7 % 3
>>>
print remainder
1
So 7
divided by 3 is 2 with 1 left over.
4. Explain relational operators.
The ==
operator is one of the relational operators; the others are:
X! = y #
x is not equal to y
x > y
# x is greater than y
x < y
# x is less than y
x >= y
# x is greater than or equal to y
x <= y
# x is less than or equal to y
5. Explain Logical operators
There are
three logical operators: and, or, and not. For example, x > 0 and x < 10
is true only if x is greater than 0 and less than 10. n%2 == 0 or n%3 == 0 is
true if either of the conditions is true, that is, if the number is divisible
by 2 or 3. Finally, the not operator negates a Boolean expression, so not(x
> y) is true if x > y is false, that is, if x is less than or equal to y.
Non-zero number is said to be true in Boolean expressions.
6. What is conditional execution?
The
ability to check the condition and change the behavior of the program
accordingly is called conditional execution. Example:
If statement:
The
simplest form of if statement is:
Syntax:
if
statement:
Eg:
if x >
0:
print 'x
is positive'
The
boolean expression after ‘if’ is called the condition. If it is true, then the
indented statement gets executed. If not, nothing happens.
7. What is alternative execution?
A second
form of if statement is alternative execution, that is, if …else, where there
are two possibilities and the condition determines which one to execute.
Eg:
if x%2 ==
0:
print 'x
is even'
else:
print 'x
is odd'
8. What are chained conditionals?
Sometimes
there are more than two possibilities and we need more than two branches. One
way to express a computation like that is a chained conditional:
Eg:
if x <
y:
print 'x
is less than y'
elif x
> y:
print 'x
is greater than y'
else:
print 'x
and y are equal'
elif is
an abbreviation of “else if.” Again, exactly one branch will be executed. There
is no limit on the number of elif statements. If there is an else clause, it
has to be at the end, but there doesn’t have to be one.
9. Explain while loop with example. Eg:
def
countdown(n):
while n
> 0:
print n
n = n-1
print
'Blastoff!'
More
formally, here is the flow of execution for a while statement:
1. Evaluate
the condition, yielding True or False.
2. If the
condition is false, exit the while statement and continue execution at the next
statement.
3. If the
condition is true, execute the body and then go back to step 1
9. Explain ‘for loop’ with example.
The
general form of a for statement is
Syntax:
for
variable in sequence:
code
block
Eg:
x = 4
for i in
range(0, x):
print i
10. What is a break statement?
When a
break statement is encountered inside a loop, the loop is immediately
terminated and the program control resumes at the next statement following the
loop.
Eg:
while
True:
line =
raw_input('>')
if line
== 'done':
break
print
line
print'Done!'
11. What is a continue statement?
The
continue statement works somewhat like a break statement. Instead of forcing
termination, it forces the next iteration of the loop to take place, skipping
any code in between.
Eg:
for num
in range(2,10):
if
num%2==0;
print
“Found an even number”, num
continue
print
“Found a number”, num
12. Compare return value and composition. Return
Value:
Return
gives back or replies to the caller of the function. The return statement
causes our function to exit and hand over back a value to its caller.
Eg:
def area(radius):
temp =
math.pi * radius**2
return
temp
Composition:
Calling
one function from another is called composition.
Eg:
def
circle_area(xc, yc, xp, yp):
radius =
distance(xc, yc, xp, yp)
result =
area(radius)
return
result
13. What is recursion?
The
process in which a function calls itself directly or indirectly is called
recursion and the corresponding function is called as recursive function.
Eg:
def
factorial(n):
if n ==
1:
return 1
else:
return n
* factorial(n-1)
14. Explain global and local scope.
The scope
of a variable refers to the places that we can see or access a variable. If we
define a variable on the top of the script or module, the variable is called
global variable. The variables that are defined inside a class or function is
called local variable.
Eg:
def
my_local():
a=10
print(“This
is local variable”)
Eg:
a=10
def
my_global():
print(“This
is global variable”)
15. Compare string and string slices.
A string
is a sequence of character.
Eg: fruit
= ‘banana’
String Slices :
A segment
of a string is called string slice, selecting a slice is similar to selecting a
character. Eg: >>> s
='Monty Python'
>>> print
s[0:5]
Monty
>>> print
s[6:12]
Python
16. Define string immutability.
Python
strings are immutable. ‘a’ is not a string. It is a variable with string value.
We can’t mutate the string but can change what value of the variable to a new
string.
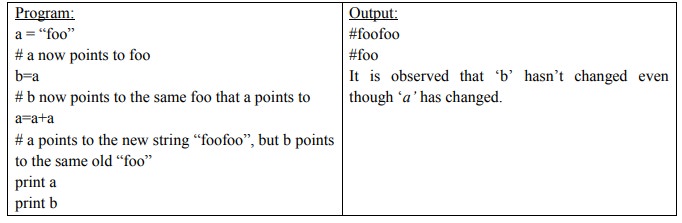
17. Mention a few string functions.
s.captilize()
– Capitalizes first character of string
s.count(sub)
– Count number of occurrences of sub in string
s.lower()
– converts a string to lower case
s.split()
– returns a list of words in string
18. What are string methods?
A method
is similar to a function—it takes arguments and returns a value—but the syntax
is different. For example, the method upper takes a string and returns a new
string with all uppercase letters:
Instead
of the function syntax upper(word), it uses the method syntax word.upper()
.>>> >>>word = 'banana'
>>> new_word
= word.upper()
>>> print
new_word
BANANA
19. Explain about string module.
The
string module contains number of useful constants and classes, as well as some
deprecated legacy functions that are also available as methods on strings.
Eg:
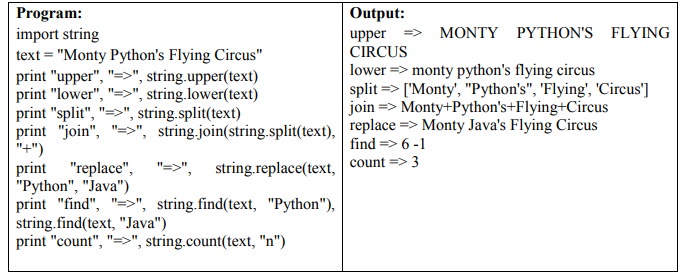
20. What is the purpose of pass statement?
Using a
pass statement is an explicit way of telling the interpreter to do nothing.
Eg:
def
bar():
ass
If the
function bar() is called, it does absolutely nothing.
Part A:
1.
What are Boolean
values?
2.
Define operator
and operand?
3.
Write the syntax
for if with example?
4.
Write the syntax
and flowchart for if else.
5.
Write the syntax
and flowchart for chained if.
6.
define state
7.
Write the syntax
for while loop with flowchart.
8.
Write the syntax
for for loopwith flowchart.
9.
Differentiate
break and continue.
10.
mention the use
of pass
11.
what is fruitful
function
12.
what is void
function
13.
mention the
different ways of writing return statement
14.
What is
parameter and list down its type?
15.
What is local
and global scope?
16.
Differentiate
local and global variable?
17.
What is function
composition, give an example?
18.
Define
recursion.
19.
Differentiate
iteration and recursion.
20.
Define string.
How to get a string at run time.
21.
What is slicing?
Give an example.
22.
What is
immutability of string?
23.
List out some
string built in function with example?
24.
Define string
module?
25.
How can list act
as array?
26.
write a program
to check the number is odd or even.
27.
write a program
to check the number positive or negative
28.
write a program
to check the year is leap year or not
29.
write a program
to find greatest of two numbers
30.
write a program
for checking eligibility for vote
31.
write a program
to find sum of n numbers
32.
write a program
to find factorial of given numbers
33.
write a program
to find sum of digits of a number
34.
Write a program
to reverse the given number.
35.
Write a program
to check the given number is palindrome or not.
36.
write a program
to check the given number is Armstrong or not
37.
how can you use
for loop in sequence.
38.
how can you use
else statement if loops.
39.
What is the
use of map() function?
Related Topics