Chapter: Problem Solving and Python Programming : Control Flow, Functions
Fruitful Function - Python
Fruitful Function
· Fruitful function
· Void function
· Return values
· Parameters
· Local and global scope
· Function composition
· Recursion
Fruitful function:
A function that returns a value is called fruitful function.
Example:
Root=sqrt(25)
Example:
def add():
a=10
b=20
c=a+b
return c
c=add()
print(c)
Void Function
A function that perform action but don’t return any value.
Example:
print(“Hello”)
Example:
def add():
a=10
b=20
c=a+b
print(c)
add()
Return values:
return keywords are used to return the values from the function.
example:
return a – return 1 variable
return a,b– return 2 variables
return a,b,c– return 3 variables
return a+b– return expression
return 8– return value
PARAMETERS / ARGUMENTS:
v Parameters are the variables which used in the function definition. Parameters are inputs to functions. Parameter receives the input from the function call.
v It is possible to define more than one parameter in the function definition.
Types of parameters/Arguments:
1. Required/Positional parameters
2. Keyword parameters
3. Default parameters
4. Variable length parameters
Required/ Positional Parameter:
The number of parameter in the function definition should match exactly with number of arguments in the function call.
Example
def student( name, roll ):
print(name,roll)
student(“George”,98)
Output:
George 98
Keyword parameter:
When we call a function with some values, these values get assigned to the parameter according to their position. When we call functions in keyword parameter, the order of the arguments can be changed.
Example
def student(name,roll,mark):
print(name,roll,mark)
student(90,102,"bala")
Output:
90 102 bala
Default parameter:
Python allows function parameter to have default values; if the function is called without the argument, the argument gets its default value in function definition.
Example
def student( name, age=17):
print (name, age)
student( “kumar”):
student( “ajay”):
Output:
Kumar 17
Ajay 17
Variable length parameter
v Sometimes, we do not know in advance the number of arguments that will be passed into a function.
v Python allows us to handle this kind of situation through function calls with number of arguments.
v In the function definition we use an asterisk (*) before the parameter name to denote this is variable length of parameter.
Example
def student( name,*mark):
print(name,mark)
student (“bala”,102,90)
Output:
bala ( 102 ,90)
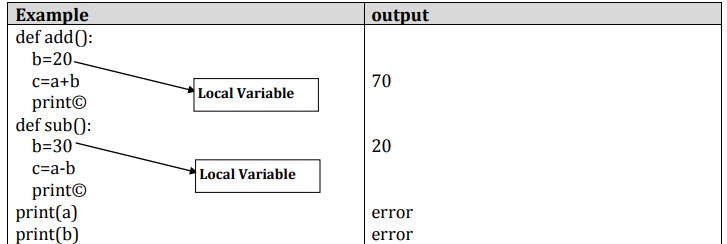
Local and Global Scope
Global Scope
v The scope of a variable refers to the places that you can see or access a variable.
v A variable with global scope can be used anywhere in the program.
v It can be created by defining a variable outside the function.
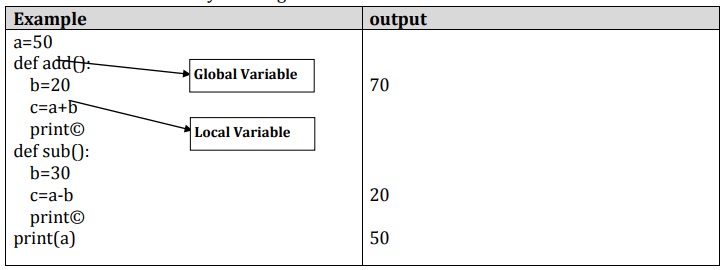
Local Scope A variable with local scope can be used only within the function .
Function Composition:
v Function Composition is the ability to call one function from within another function
v It is a way of combining functions such that the result of each function is passed as the argument of the next function.
v In other words the output of one function is given as the input of another function is known as function composition.
Example:
math.sqrt(math.log(10))
def add(a,b):
c=a+b
return c
def mul(c,d):
e=c*d
return e
c=add(10,20)
e=mul(c,30)
print(e)
Output:
900
find sum and average using function composition
def sum(a,b):
sum=a+b
return sum
def avg(sum):
avg=sum/2
return avg
a=eval(input("enter a:"))
b=eval(input("enter b:"))
sum=sum(a,b)
avg=avg(sum)
print("the avg is",avg)
output
enter a:4
enter b:8
the avg is 6.0
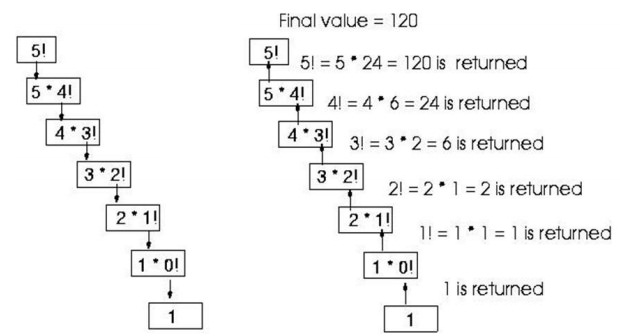
Recursion
A function calling itself till it reaches the base value - stop point of function call. Example: factorial of a given number using recursion
Factorial of n
def fact(n):
if(n==1):
return 1
else:
return n*fact(n-1)
n=eval(input("enter no. to find
fact:"))
fact=fact(n)
print("Fact is",fact)
Output
enter no. to find fact:5
Fact is 120
Explanation
Examples:
1. sum of n numbers using recursion
2. exponential of a number using recursion
Sum of n numbers
def sum(n):
if(n==1):
return 1
else:
return n*sum(n-1)
n=eval(input("enter no. to find
sum:"))
sum=sum(n)
print("Fact is",sum)
Output
enter no. to find sum:10
Fact is 55
Related Topics