Chapter: Mechanical : Gas Dynamics and Jet Propulsion : Jet Propulsion
Pulse Jet Engine
Pulse Jet Engine
The pulse jet engine is an intermittent, compressor
less aerodynamic power plant, with few or none of the mechanical features of
conventional aviation power plants. In its simplest form, the operation of the
pulse jet depends only on the properties of atmospheric air, a fuel, a shaped
tube and some type of flow-check valve, and not on the interposition of
pistons, impellers, blades or other mechanical part whose geometry and motion
are controllable. The pulse jet differs from other types of air breathing
engines, in that the air flow through it is intermittent. It can produce static
thrust.
Operations:
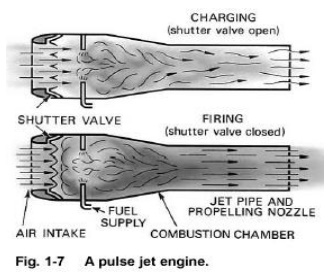
During starting compressed air is forced into the
inlet which opens the spring loaded flapper valves. In practice this may done
by blowing compressed air though the valve box or by the motion of the engine
through the air. The air that enters the engine passes by the fuel injector and
is mixed with the fuel(Fig. A)
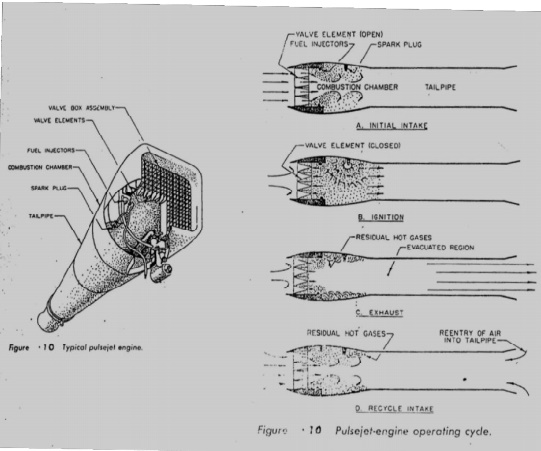
When the fuel-air mixture reaches the proper
proportion to burn, it is ignited by a spark plug. The burning takes place with
explosive force, thus causing a very rapid rise in pressure, the increase in
pressure forces the flapper valves shut and propels the charge of burned gases
out of the tail pipe, as in B of the figure.
The momentum of the gases leaving the
tailpipe causes the air to continue t flow out even after the pressure within
the engine has reached atmospheric pressure. The pressure within the engine is
therefore evacuated to below atmosphere, part C in figure.
After the pressure has
reached its lowest point, atmospheric pressure (and the ram pressure if the
engine is in flight) forces air into the engine through the flapper valves. At
the same time, air will also be drawn in through tailpipe, since the pressure
within the tailpipe is low and has nothing to prevent the entry of air, At this
point, part D in figure, the engine is ready to begin another cycle. The
fequency of cycles depends upon the duct shape and working temperature in V-1
rocket it was about 40 c/s which corresponds to about 2400 rpm of a two stroke
reciprocating engine.
Once the engine
operation has become established, the spark plug is no longer necessary. The
reignition between each cycle is accomplished when the fresh charge of fuel and
air is ignited by some residual flame which is left over from the preceding
cycle. The air flow which reenters the tailpipe is important from both the
engine operation and thrust stadpoints. Experiments have shown that the amount
of air which flows into the tailpipe can be several times as much as that which
flows into the inlet. This mass flow of air increases the thrust of the engine
by providing additional mass for the explosion pressure to work on. It also
increases the pressure within the engine at the beginning of each explosion
cycle, resulting in a more efficient burning process. Reentry of air into the
tailpipe is made more difficult as the airspeed surrounding the engine
increases. The thrust of the engine, therefore, tends to decrease with speed.
As the speed increases, the amount of reentering air flow decreases to the
point where the internal pressure is eventually too low to support combustion
and the engine will no longer operate.
Characteristics :
The chief advantages of the pulse jet are its
simplicity, light weight, low cost and good zero speed thrust characteristic.
Its particular disadvantages are its 650-800 km/h. operating speed limit,
rather limited altitude range and somewhat unpredictable valve life.
One interesting and sometimes objectionable, feature
of the pulse jet engine is the sound it makes when in operation. The sound is a
series of loud reports caused by the firing of the individual charges of fuel
and air in the combustion chamber. The frequency of the reports depends upon
the length of the engine form the inlet valves to the end of the tailpipe and
upon the temperature of the gases within the engine. The resulting sound is a
continuous, loud, and vibratory note that can usually be heard for several
kilometers.
The pulse jet has low
thermal efficiency. In early designs the efficiency obtained was about 2 to 3%
with a total flight life of 30 to 60 minutes. The maximum operating speed is
seriously limited by tow factors: (i) It is possible to design a good diffuser
at high speeds. (ii) The fiepper valves, the only mechanical part in the pulse
jet, also have certain natural frequency and if resonance with the cycle
frequency occurs then the valve may remain open and no compression will take
place. Also, as the speed increases it is difficult for air to flow back. This
reduces total compression pressure as well as the mass flow of air which
results in inefficient combustion and lower thrust. The reduction in thrust and
efficiency is quite sharp as the speed increases.
Advantages :
Ø This
is very simple device only next to ramjet and is light in weight. It requires
very small and occasional maintenance.
Unlike ramjet, it has
static thrust because of the compressed air starting, thusit does not need a
device for initial propulsion. The static thrust is even more than the cruise
thrust.
Ø It
can run on an almost any type of liquid fuel without much effect on the
performance. It can also operate on gaseous fuel with little modifications.
Ø Pulse
jet is relatively cheap.
Disadvantages :
Ø 1.The
biggest disadvantage is very short life of flapper valve and high rates of fuel
consumption. The SFC is as high as that of ramjet.
Ø The
speed of the pulse jet is limited within a very narrow range of about 650-800
km/h because of the limitations in the aerodynamic design of an efficient
diffuser suitable for a wide range.
Ø The
high degree of vibrations due to intermittent nature of the cycle and the
buzzing noise has made it suitable for pilotless crafts only.
Ø It
has lower propulsive efficiency that turbojet engine.
Ø The
operational range of the pulse jet is limited in altitude range.
Applications:
Ø German
V-1 buzz bomb,
Ø
American Helicopter company’s Jet Jeep
Helicopter,
Ø
Auxiliary power plant for sail planes.
Related Topics