Computation of ratios | Accountancy - Profitability ratios | 12th Accountancy : Chapter 9 : Ratio Analysis
Chapter: 12th Accountancy : Chapter 9 : Ratio Analysis
Profitability ratios
Profitability ratios
Profitability ratios
help to assess the profitability of a business concern. These ratios also help
to analyse the earning capacity of the business in terms of utilisation of
resources employed in the business. Generally these ratios are expressed as a
percentage.
The profitability ratios
commonly used are
(i) Gross profit ratio
(ii) Operating cost
ratio
(iii) Operating profit
ratio
(iv) Net profit ratio
(v) Return on investment
(i) Gross profit ratio
Gross profit ratio is the
proportion of gross profit to net revenue from operations. Gross profit ratio
shows the margin of profit available out of revenue from operations. It is
computed as below:
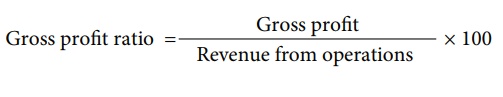
Gross profit ratio = [
Gross profit / Revenue from operations ] × 100
Gross profit = Revenue from operations – Cost of revenue from operations
A higher gross profit
ratio indicates high profitability. It should be sufficiently high to provide
for indirect expenses to be paid by a business.
Illustration 13
Calculate gross profit
ratio from the following:
Revenue from operations ₹ 1,00,000, Cost of revenue from operations ₹ 80,000 and purchases 62,500.
Solution

Gross profit = Revenue from operations – Cost of revenue from operations
= 1,00,000 – 80,000 = ₹ 20,000
(ii) Operating cost ratio
Operating cost ratio is
the proportion of operating cost to revenue from operations. This
ratio is a test of the operational efficiency of the business. It is calculated
as under.

Operating cost ratio =
[ Operating cost / Revenue from operations ] × 100
Operating cost is the
cost which is associated with the operating activities of the business.
Operating cost = Cost
of revenue from operations + Operating expenses
Operating expenses =
Employee benefit expenses + Depreciation + Other expenses related to office and
administration, selling and distribution
A lower operating ratio
indicates better profitability. Lesser the operating cost ratio, higher is the
margin available for payment of non operating expenses such as interest on
loans, loss on sale of fixed assets, etc.
Illustration 14
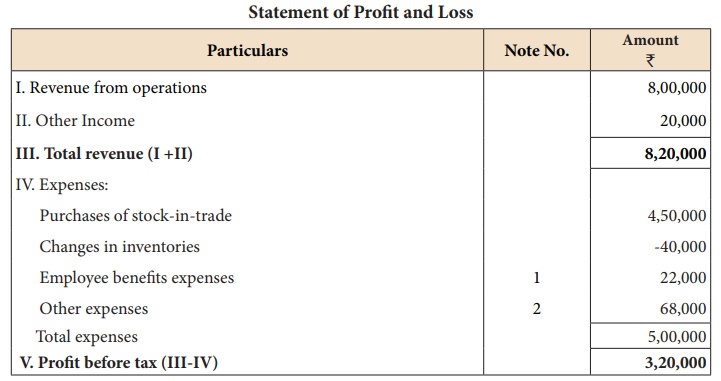
Following is the
statement of profit and loss of Maria Ltd. for the year ended 31st March, 2018.
Calculate the operating
cost ratio.
Solution

Operating cost ratio = [
Operating cost / Revenue from operations ] × 100
= 4,80,000 /8,00,000 ×
100 = 60%
Cost of revenue from
operations = Purchases of stock-in-trade + Change in inventories of stock in
trade + Direct expenses (wages) = 4,50,000 + (40,000) + 10,000 = ₹ 4,20,000
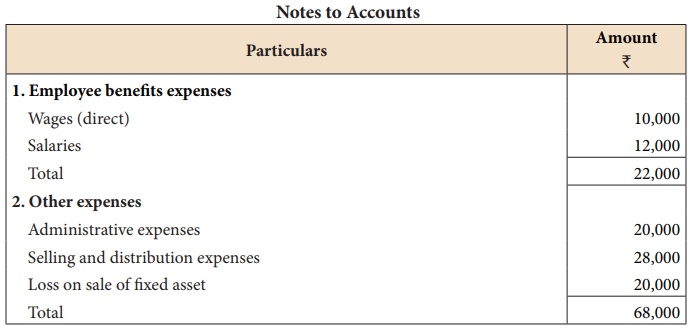
Operating expenses =
Administrative expenses+Selling and distributionexpenses+ Employee benefits expenses
(salaries) = 20,000 + 28,000 + 12,000 = ₹
60,000
Operating cost = Cost of
revenue from operations + Operating expenses
= 4,20,000 + 60,000= ₹ 4,80,000
Tutorial Note
Loss on sale of fixed
assets is a non-operating item, hence it is ignored.
(iii) Operating profit ratio
Operating profit ratio
gives the proportion of operating profit to revenue from operations. Operating
profit ratio is an indicator of operational efficiency of an organisation. It
may be computed as follows:

Operating profit ratio
= [ Operating profit x Revenue from operations ] × 100
Alternatively, it is
calculated as under.
Operating profit ratio
= 100 – Operating cost ratio
Operating profit = Revenue from operations – Operating cost
A higher ratio indicates
better profitability. Greater the operating ratio, higher is the margin
available for paying non-operating expenses.
Tutorial note
Operating cost ratio +
Operating profit ratio = 100%
Illustration 15
Calculate operating
profit ratio under the following cases.
Case 1: Revenue from
operations ₹ 10,00,000, Operating
profit ₹ 1,50,000.
Case 2: Revenue from
operations ₹ 15,00,000, Operating
cost ₹ 12,00,000.
Case 3: Revenue from
operations ₹ 20,00,000, Gross profit
30% on revenue from operations, Operating expenses ₹ 4,00,000
Solution
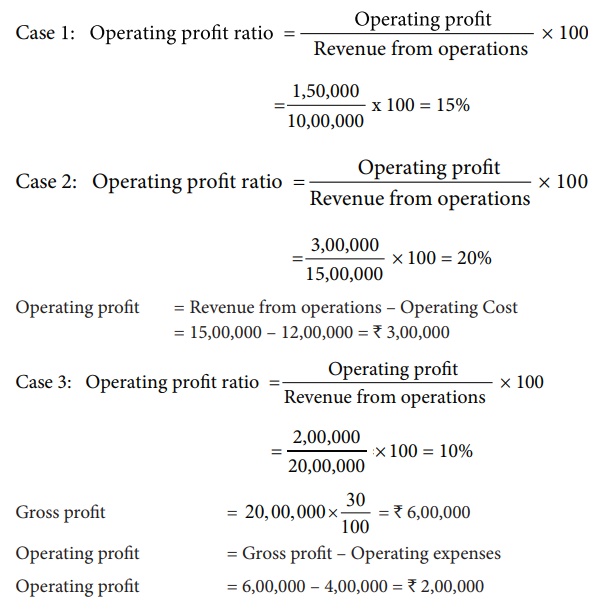
(iv) Net profit ratio
Net profit ratio is the
percentage of net profit on revenue from operations. It is calculated as under:

Net profit ratio = [
Net profit after tax / Revenue from operations ] × 100
Net profit after tax =
Gross profit + Indirect income – Indirect expenses – Tax (OR)
Net profit after tax =
Revenue from operations – Cost of revenue from operations – Operating expenses
–Non operating expenses + Non-operating income - Tax
Net profit ratio is an
indicator of the overall profitability of the business. A higher net profit
ratio indicates high profitability.
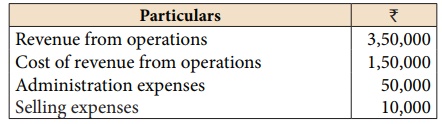
Illustration 16
From the following
details of a business concern calculate net profit ratio.
Solution

Net profit = Revenue
from operations – Cost of revenue from operations – Administration expenses –
Selling expenses = 3,50,000 – 1,50,000 – 50,000 – 10,000 = ₹ 1,40,000
Tutorial note
It is assumed that there
is no tax payable.
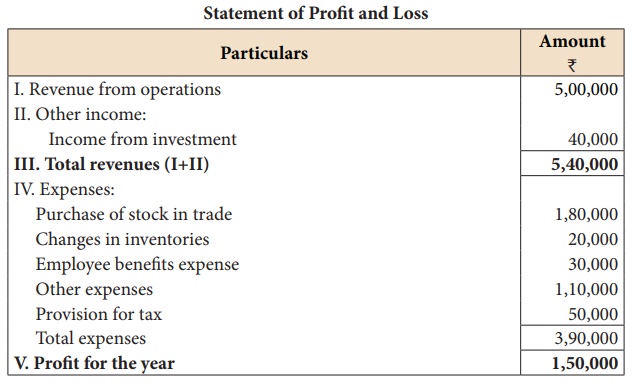
Illustration 17
From the following
statement of profit and loss of Mukesh Ltd. Calculate
(i) Gross profit ratio
(ii) Net profit ratio.
Solution
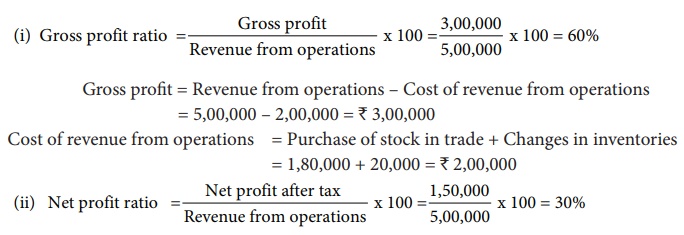
Illustration 18
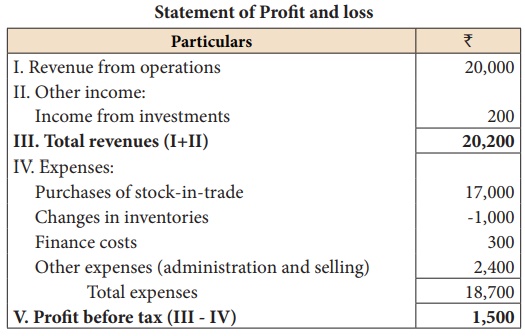
From the following
trading activities of Naveen Ltd. calculate
(i) Gross profit ratio
(ii) Net profit ratio (iii) Operating cost ratio (iv) Operating profit ratio
Solution

Cost of revenue from operations = Purchase of stock-in-trade + Changes in inventory + Direct expenses
= 17,000 – 1,000 + 0 = ₹ 16,000
Gross profit = Revenue from operations – Cost of revenue from operations
= 20,000 – 16,000 = ₹ 4,000

Tutorial note
It is assumed that there
is no tax payable.

Operating cost = Cost of revenue from operations + Operating expenses
Operating expenses = Other expenses = ₹ 2,400
Operating cost = 16,000 + 2,400 = ₹ 18,400

Operating profit = Revenue from operations – Operating cost
= 20,000 – 18,400 = ₹ 1,600
(v) Return on Investment (ROI)
Return on investment
shows the proportion of net profit before interest and tax to capital employed
(shareholders’ funds and long term debts). This ratio measures how efficiently
the capital employed is used in the business. It is an overall measure of
profitability of a business concern. It is computed as below:
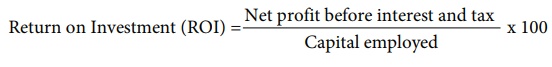
Return on Investment
(ROI) = [ Net profit before interest and tax / Capital employed ] x 100
Capital employed =
Shareholders’ funds + Non current liabilities
Greater the return on
investment better is the profitability of a business and vice versa.
Illustration 19
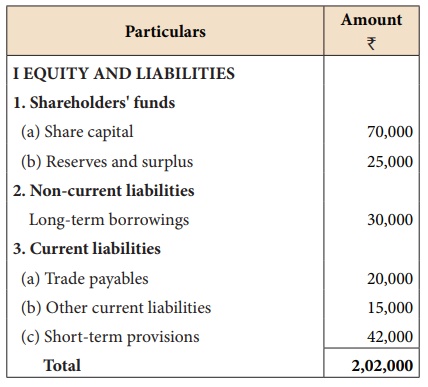
Following is the extract
of the balance sheet of Babu Ltd., as on 31st March, 2018:
Net profit before interest and tax
for the year was ₹ 25,000. Calculate the return on capital employed for the
year.
Solution
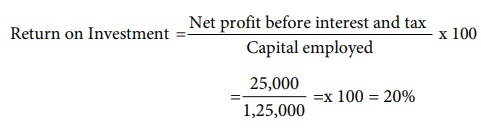
Capital employed = Share capital +
Reserves and surplus + Long term borrowings
= 70,000 + 25,000 +30,000 = ₹ 1,25,000
Related Topics